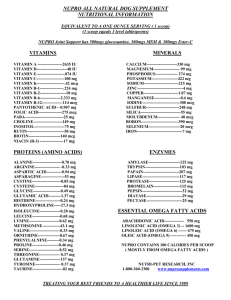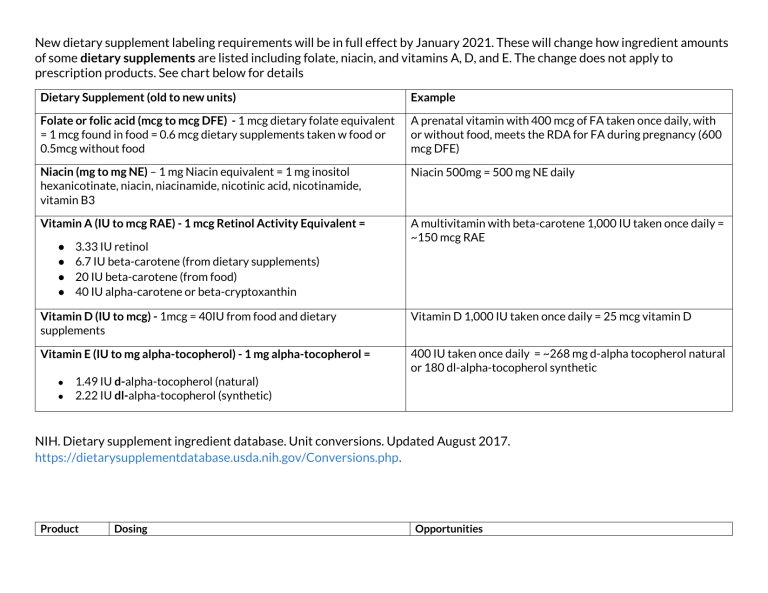
New dietary supplement labeling requirements will be in full effect by January 2021. These will change how ingredient amounts of some dietary supplements are listed including folate, niacin, and vitamins A, D, and E. The change does not apply to prescription products. See chart below for details Dietary Supplement (old to new units) Example Folate or folic acid (mcg to mcg DFE) - 1 mcg dietary folate equivalent = 1 mcg found in food = 0.6 mcg dietary supplements taken w food or 0.5mcg without food A prenatal vitamin with 400 mcg of FA taken once daily, with or without food, meets the RDA for FA during pregnancy (600 mcg DFE) Niacin (mg to mg NE) – 1 mg Niacin equivalent = 1 mg inositol hexanicotinate, niacin, niacinamide, nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, vitamin B3 Niacin 500mg = 500 mg NE daily Vitamin A (IU to mcg RAE) - 1 mcg Retinol Activity Equivalent = A multivitamin with beta-carotene 1,000 IU taken once daily = ~150 mcg RAE ● ● ● ● 3.33 IU retinol 6.7 IU beta-carotene (from dietary supplements) 20 IU beta-carotene (from food) 40 IU alpha-carotene or beta-cryptoxanthin Vitamin D (IU to mcg) - 1mcg = 40IU from food and dietary supplements Vitamin D 1,000 IU taken once daily = 25 mcg vitamin D Vitamin E (IU to mg alpha-tocopherol) - 1 mg alpha-tocopherol = 400 IU taken once daily = ~268 mg d-alpha tocopherol natural or 180 dl-alpha-tocopherol synthetic ● ● 1.49 IU d-alpha-tocopherol (natural) 2.22 IU dl-alpha-tocopherol (synthetic) NIH. Dietary supplement ingredient database. Unit conversions. Updated August 2017. https://dietarysupplementdatabase.usda.nih.gov/Conversions.php. Product Dosing Opportunities Vitamin D ● ● ● ● 10-20 mcg/day (400-800 IU) daily for adult under 50 20 -25 mcg (800 to 1,000 IU) daily for older adults North American Menopause Society recommends 8001000 IU daily for adults over 50 1.25mg (50,000) IU weekly for 8 weeks if level under 20ng/mL Vitamin D levels are inversely related to body mass index in obese patients, and anticonvulsants, glucocorticoids, antifungals, and HIV antivirals increase vitamin D catabolism. Therefore, obese patients or patients taking these medications may need two or three times more vitamin D than is generally recommended for their age group Vitamin B Niacinamide 500 mg once or twice daily Oral Nicotinamide to Reduce Actinic Cancer (ONTRAC) study Pre-natal Vitamins There are specific recommendations for certain ingredients in prenatal vitamins (e.g., calcium, folic acid, iron, and iodine). Calcium helps with healthy bones, folic acid with brain and spinal cord development, and iron prevents anemia. 15mg/kg (9 mg/kg elemental Mag)/day Magnesium 300-400mg daily Vitamin C 1-3 g/day are the most common doses (Cochrane Database Syst Rev) Bone health (D3 cholecalciferol) is more potent than D2 (ergocalciferol) Latest study did not prevent falls in elderly Advanced age with history of fall or nontraumatic fracture, malabsorption (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease, bariatric surgery), and use of anticonvulsants, glucocorticoids, antifungals, cholestyramine, or HIV antivirals. Pregnant or lactating women and people with dark skin tone. Dx of osteoporosis, osteomalacia, rickets, chronic kidney disease, liver failure, hyperparathyroidism, obesity, granulomatous disease, and lymphoma. Some evidence supporting fibromyalgia, asthma or even depression Niacinamide for Skin cancer Recommend Vit B12 for pt taking metformin Prevent leg cramp in pregnant women (fursultiamine 50 mg, hydroxocobalamin 250 mcg, pyridoxal phosphate 30 mg, and riboflavin 5 mg) Key ingredients – 400-800 mcg folic acid, 27mg elemental iron, 150mcg of iodine per day for most. Add additional Calcium 1000mg/day depending on the risks Pediatric migraine - Formulation may include riboflavin or melatonin Nighttime leg cramp (pregnant women) – Formulation may include Vit E, B complex and calcium Cold or flu Formulation may include echinacea, elderberry, honey, zinc