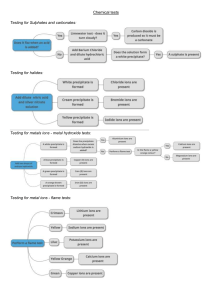
MASS SPECTROMETERY AND RELATIVE MASSES OF ATOMS, ISOTOPES AND MOLECULES A mass spectrometer measures the masses of atoms, molecules and fragments of molecules Ions are formed (positive ions). Ions are deflected by a magnetic field according to mass to charge ration (m/z) It calculates the relative abundance of each positive ions and displays it as a percentage Sample must be in the gaseous state The sample is injected in the mass spectrometer where it is vaporized The vapor is bombarded with high energy electrons. The electrons collide with the atoms or molecules One or more electrons are removed from the atoms to form positive ions The ions formed are accelerated with electric field The positive ions enter a magnetic field The ions are deflected based on their mass to charge ratio Ions with large mass to charge ratio are deflected less If ions have the same charge, then they are deflected based on their mass The deflection is inversely proportional to their mass The deflected ions pass through a narrow slit and are collected on a magnetic plate connected To an amplifier The strength of the magnetic field is then changed to detect positive ions with other m/z ratio Cl 35 Cl V