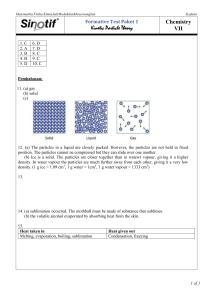
nd Chemistry Matters for GCE ‘O’ Level (2 Edition): Full Solutions to Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Kinetic Particle Theory Test Yourself 1.1 and 1.2 (page 6) 1. (a) Gaseous (b) Solid (c) Arrangement in (a): Arrangement in (b): solid gas 2. (a) The particles in a liquid are closely packed. However, the particles are not held in fixed positions. The particles cannot be compressed but they can move freely throughout the liquid. (b) Ice is a solid. The particles are closer together than in water vapour, giving it a higher density. In water vapour, the particles are much farther away from each other, giving it a very low density. 3 3 (1 g of ice has a volume of about 1.09 cm , 1 g of water has a volume of 1.0 cm and 1 g of water 3 vapour has a volume of about 1333 cm . Note: Ice has a larger volume than water as water expands on freezing.) Try It Out (page 13) plastic sheet small plant stones large container water collecting vessel sand To obtain more water, more plants can be placed inside the large container. © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1.1 nd Chemistry Matters for GCE ‘O’ Level (2 Edition): Full Solutions to Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Test Yourself 1.3 (page 15) 1. Temperature/°C 100 – liquid 80 – solid and liquid 70 – solid 40 – 0 Time/min 2. (a) Sublimation has occurred. The mothball must be made of a substance that sublimes. (b) Alcohol is volatile and evaporates upon absorbing heat from the skin. 3. Heat taken in by the particles sublimation, evaporation, boiling, melting Heat given out by the particles condensation, freezing Test Yourself 1.4 (page 19) 1. Chlorine, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen 2. Removal of unpleasant smells; removal of polluting gases; spreading of smell of flowers and perfumes 3. (a) Beaker III (b) Beaker I The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of diffusion. Get it Right (page 21) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) False. Gases have mass. False. A solid is made up of tiny particles that are able to vibrate in fixed positions. True False. When a solid is heated, its particles gain enough heat energy to overcome the attractive forces between them. They then begin to break away from their fixed positions. The solid melts to become a liquid. True True False. The lower the molecular mass, the higher the rate of diffusion. True © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1.2 nd Chemistry Matters for GCE ‘O’ Level (2 Edition): Full Solutions to Textbook Questions Chapter 1 Let’s Review (pages 21–22) Section A: Multiple-Choice Questions 1. C 2. C 3. A 4. D 5. A 6. B Section B: Structured Questions 1. (a) The smell given out by perfume is made up of tiny gas particles that move around freely. The particles diffuse from a region of higher concentration (the person) to a region of lower concentration (the other parts of the room). (b) An increase in temperature increases the speed of the particles. 2. (a) (i) E (ii) C and D (iii) A and B (b) As the temperature drops from 80°C, the gas particles lose kinetic energy and move more slowly. Eventually the movement of the particles is slow enough for the gas to change to a liquid at 58°C. On further cooling, the particles move slowly until the temperature reaches −7°C and the liquid becomes a solid. The particles can now only vibrate in fixed positions. As the temperature cools further to −10°C, the particles vibrate more slowly in their fixed positions. Section C: Free-Response Question 1. (a) 50°C (b) 26°C. The temperature shown in the graph does not drop below 26°C. (c) The particles gain kinetic energy and move more rapidly until they reach their boiling point of 128°C. They now have sufficient energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding them together. X is now a gas. (d) AB, BC and CD (e) Temperature/°C 140 gas liquid + gas 128 liquid 50 solid + liquid solid 30 0 Time/s © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1.3