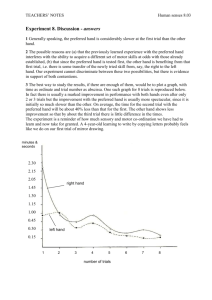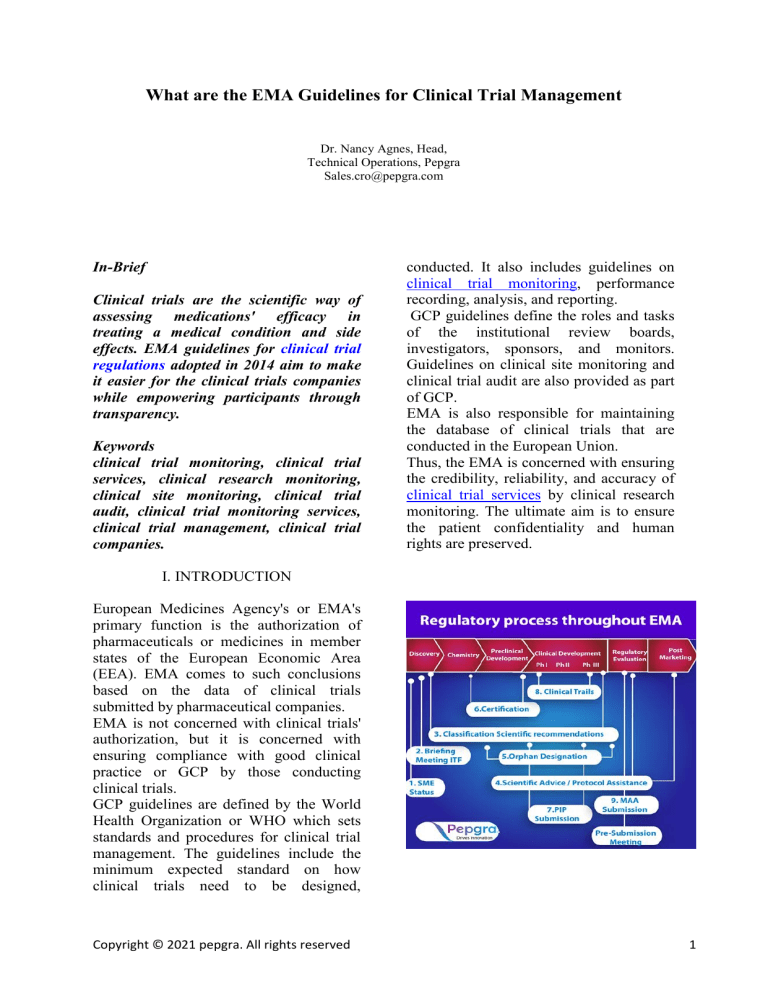
What are the EMA Guidelines for Clinical Trial Management Dr. Nancy Agnes, Head, Technical Operations, Pepgra Sales.cro@pepgra.com In-Brief Clinical trials are the scientific way of assessing medications' efficacy in treating a medical condition and side effects. EMA guidelines for clinical trial regulations adopted in 2014 aim to make it easier for the clinical trials companies while empowering participants through transparency. Keywords clinical trial monitoring, clinical trial services, clinical research monitoring, clinical site monitoring, clinical trial audit, clinical trial monitoring services, clinical trial management, clinical trial companies. conducted. It also includes guidelines on clinical trial monitoring, performance recording, analysis, and reporting. GCP guidelines define the roles and tasks of the institutional review boards, investigators, sponsors, and monitors. Guidelines on clinical site monitoring and clinical trial audit are also provided as part of GCP. EMA is also responsible for maintaining the database of clinical trials that are conducted in the European Union. Thus, the EMA is concerned with ensuring the credibility, reliability, and accuracy of clinical trial services by clinical research monitoring. The ultimate aim is to ensure the patient confidentiality and human rights are preserved. I. INTRODUCTION European Medicines Agency's or EMA's primary function is the authorization of pharmaceuticals or medicines in member states of the European Economic Area (EEA). EMA comes to such conclusions based on the data of clinical trials submitted by pharmaceutical companies. EMA is not concerned with clinical trials' authorization, but it is concerned with ensuring compliance with good clinical practice or GCP by those conducting clinical trials. GCP guidelines are defined by the World Health Organization or WHO which sets standards and procedures for clinical trial management. The guidelines include the minimum expected standard on how clinical trials need to be designed, Copyright © 2021 pepgra. All rights reserved 1 II. CLINICAL TRIAL REGULATORY PROCESS THROUGHOUT EMA Clinical Trial Regulation (EU no 536/2014) was adopted on 16th April 2014 replacing the older 2001/20/EC directive. However, the application was made six months after confirmation of the EU portal and EU database's full functionality. This document is the primary document that is referred to by clinical trial companies. Objectives-CTR The Clinical Trial Directive of 2001 was implemented through national laws. However, the Clinical Trial Regulation (CTR) was directly applicable. The overall objective of the CTR was to make the European Union attractive for Research & Development. The other objectives include: To protect the human rights, safety, wellbeing, and dignity of the clinical trial participants. To ensure the credibility, reliability, and accuracy of the data generated and reported in clinical trials. To simplify the process of application to clinical trials by the clinical trial monitoring services. To encourage innovation and research. To increase transparency and responsibility in clinical trials. To keep the balance between protecting public health, stimulating innovation and research, and safeguarding the clinical trial sponsors' economic interests. Scope-CTR The scope was confined to clinical trials of medicines intended for the use of human beings only. A new category of low-intervention clinical trials was introduced with an adaptation of some of the requirements. There can be an only minimal additional risk to patient safety compared to clinical medicine's routine practice. Copyright © 2021 pepgra. All rights reserved The investigational medicinal products (IMP) are authorized and used only following terms of Medicines Agencies. If not, then use of these medicines should be supported by scientific publications. Non-interventional trials are out of the scope of the CTR. Also, clinical research monitoring trials that do not include medicines like surgery, devices, etc., are not included in the CTR scope. New Processes-CTR The CTR introduced several processes to make it easier for clinical trial companies and participants. Minimum standard of competence for GCP requires to be done through an esubmission link at the European Union portal, which is easily accessible to Ethics Committees and all member states concerned at one go. E-submission includes submission of all structured data and documents. A harmonized dossier for one trial was made to ease out the process. Increased cooperation and coordination were to be ensured between the reporting member state and the concerned member state. It also provides workspace with collaboration tools for coordinated assessment between member state concerned. Member state concerned can have only one decision. Distribution of the burden, among others, is ensured through this process. A risk-adapted approach was introduced for those trials where the medications are already authorized for use in practice. The use of this drug in clinical trial posed only minimally increased risk compared to the risk in routine clinical practice. It was achieved by introducing less stringent rules to these trials. 2 New provisions were introduced in the process of consent taking. Union controls were reintroduced in member states to enforce supervision of clinical trials. It was done to ensure strict obedience to CTR, enforcement through supervision. Increasing transparency of clinical trials procedures and the data generated. They also introduced guidelines for those clinical trials that are conducted outside the EU with participants or are referred to a clinical trial application within the EU. In such cases, the clinical trial company will have to comply with regulatory requirements in sync with those defined for practice in the EU. Collaboration tools facilitate the joint assessment for Part 1. It also mentions that all clinical trialrelated data will be reviewed and not in parts. Provides information that is open to the public. EudraVigilance clinical trial mode module was upgraded for electronic reporting of patient safety-related adverse reactions. It also requires and delivers a repository of Annual safety reports. Transparency clauses-CTR Article 81(4) of Regulation (EU) No. 536/2014 EU database is accessible to the open public with the following exceptions: Personal data protection Confidential communication between a member state and the EU with relation to the assessment report Protection of confidential information relating to the medicines agencies status of medicines, unless disclosure is required to endure public interest To ensure effective clinical trial monitoring and supervision III. CONCLUSION Copyright © 2021 pepgra. All rights reserved EMA guidelines for clinical trials are aimed at making the process streamlined, the agencies accountable, increasing coordination among member states concerned, and improving the transparency to all stakeholders. Increasing transparency develops confidence, stimulates concerted research, and empowers participants. REFERENCES 1. 2. 3. 4. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/humanregulatory/research-development/clinical-trialshuman-medicines https://ec.europa.eu/health//sites/health/files/files/eu dralex/vol-1/reg_2014_536/reg_2014_536_en.pdf WHO handbook for good clinical research practice (GCP) – guidance for implementation. REGULATION (EU) No 536/2014 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL published in the official journal of the European Union. 2