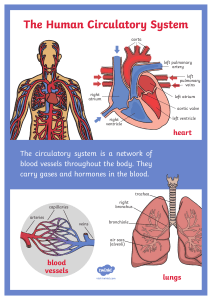
8.2 Blood Vessels: Specification Ref: 3.1.2 : The circulatory system was an essential step in the _________ of larger animals. A circulatory system can be found in almost all animals ________ than 1 cm in diameter, length and depth. This is due to the animals having a lower _______ __ _________ _____. This means animal can no longer survive on the movement of vital molecules such as _______ and ________ by ________ alone. As the _____ of diffusion over a greater distance to the cells at the centre point of the animal would be too _____, to keep up with the animals cellular ___________ and __________ demands. Even insects have an _____ circulatory system with a suspended heart in their __________ cavity. Pumping not blood but the liquid called _____________. And open circulatory system means that the system has a heart but no ______ ________, meaning that _____________ is simply circulated around the inside cavity of the organism. Larger animals need to direct blood flow more ___________ towards target organs which have a greater demand for essential chemicals such as ________ and _______. While delivering the same molecules across the entire organism at a faster enough rate to keep all the types of cell in the organism ______ and __________. A circulatory system means that a significant _____ of the organism is always moving creating a _____ _________ system a concept known as mass _____ . Purely evolved to overcome the limitations of relying on ________ alone as a __________ process. In the circulatory system where the blood flow directed in vessels it is known as a ________ circulatory system. There is essentially only five types of vessel in a ________ circulatory system, and one organ, the _______. The five types of vessel are the _______, _____, _________, __________ and _____________. ____________ and ______ have evolved a _________ circulatory system, this means that the blood passes through the heart ______ as it travels around the body. It also means that there are two circuits of blood vessels travelling from a heart and back to the heart again. The first circuit is known as the _________ circuit, which takes blood from the ____ side of the heart through the largest artery known as the ______, delivering the it to all the capillaries across the body supplying all ________ with oxygen and glucose. The blood then returns to the heart, collected from the capillaries in ________, and travel through ______ into the largest veins in the body the _________ and _________ ____ _____. The _________ bringing blood from the upper half of the body, and the _________ bringing blood back from the lower half of the body to the heart. The blood then travels through the second circuit, known as __________ circuit. Which takes land from the _____ side of the heart through the __________ ______ breaking into smaller ______ and then __________ delivering to the lungs into the ____________ where diffusion takes place allowing ___ __________. Then back to the heart through the pulmonary _____. Missing Words and Terms: (they made used more than once or not at all, harsh?) metabolic flow double mass alive tissues arterioles diffusion inferior open left pulmonary artery five aorta pulmonary Vena Cavas blood vessels didgeridoo specifically oxygen heart closed slow venules superior systemic respiring capillaries Mammals rate larger respiratory twice haemolymph arteries mass transport right glucose transport birds abdomen evolution veins surface area to volume ratio gas exchange toucan Correction Sheet The circulatory system was an essential step in the evolution of larger animals. A circulatory system can be found in almost all animals larger than 1 cm in diameter, length and depth. This is due to the animals having a lower surface area to volume ratio. This means animal can no longer survive on the movement of vital molecules such as oxygen and glucose by diffusion alone. As the rate of diffusion over a greater distance to the cells at the centre point of the animal would be too slow, to keep up with the animals cellular respiratory and metabolic demands. Even insects have an open circulatory system with a suspended heart in their abdomen cavity. Pumping not blood but the liquid called haemolymph. And open circulatory system means that the system has a heart but no blood vessels, meaning that hemolymph is simply circulated around the inside cavity of the organism. Larger animals need to direct blood flow more specifically towards target organs which have a greater demand for essential chemicals such as oxygen and glucose. While delivering the same molecules across the entire organism at a faster enough rate to keep all the types of cell in the organism alive and respiring. A circulatory system means that a significant mass of the organism is always moving creating a mass transport system a concept known as mass flow. Purely evolved to overcome the limitations of relying on diffusion alone as a transport process. In the circulatory system where the blood flow directed in vessels it is known as a closed circulatory system. There is essentially only five types of vessel in a closed circulatory system, and one organ, the heart. The five types of vessel are the arteries, veins, venules, arterioles and capillaries. Mammals and birds have evolved a double circulatory system, this means that the blood passes through the heart twice as it travels around the body. It also means that there are two circuits of blood vessels travelling from a heart and back to the heart again. The first circuit is known as the systemic circuit, which takes blood from the left side of the heart through the largest artery known as the aorta, delivering the it to all the capillaries across the body supplying all tissues with oxygen and glucose. The blood then returns to the heart, collected from the capillaries in venules, and travel through veins into the largest veins in the body the superior and inferior Vena Cavas. The Superior bringing blood from the upper half of the body, and the inferior bringing blood back from the lower half of the body to the heart. The blood then travels through the second circuit, known as pulmonary circuit. Which takes land from the right side of the heart through the pulmonary artery breaking into smaller arteries and then arterioles delivering to the lungs into the capillaries where diffusion takes place allowing gas exchange. Then back to the heart through the pulmonary veins.