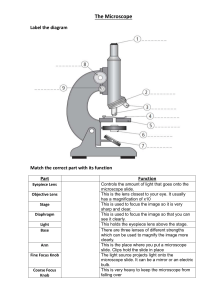
1. The microscope is a very important tool in studying living things which magnifies the image of an object. What is the etymology of the word microscope? A. micro- very small and skopos- magnify B. mikros- tiny and scopy- study of C. microscopic- small and scopes- watcher D. mikros- very small and skopos- watcher 2. Which of the following parts of the microscope functions as a connecting hollow tube, attached to the arm that connects the eyepiece to the objectives? A. Stage B. Base C. Body Tube D. Ocular Lens 3. What part of the microscope raises or lowers the body tube in large movements to bring the objectives in approximate focus and is usually used together with the LPO? A. Coarse Adjustment Knob B. Low Power Objective C. Fine Adjustment Knob D. Revolving Nosepiece 4. Which part of the microscope is comprised of lenses used to focus and concentrate maximum light from the illuminator into the specimen and allows the control of the intensity of the light? A. Iris Diaphragm B. Ocular Lens C. Mirror/ Light Source D. Condenser 5. Which of the following objectives is the shortest, is marked by either 3X, 4X or 5X and is used to give a general overview of the specimen? A. Oil Immersion Objective B. High Power Objective C. Low Power Objective D. Scanner 6. A part of the microscope which is used to collect, reflect and direct the light up through the condenser, the opening of the stage, and specimen being viewed. A. Light Bulb B. Light Source C. Mirror D. Iris Diaphragm 7. What do you call the object or material that is being viewed or examined under the microscope? A. Cell B. Specimen C. Virus D. Sample 8. In viewing a specimen under the microscope, what part is used to hold the specimen in place in order to avoid unnecessary movement of the slides. A. Stage B. Aperture C. Nosepiece D. Stage Clips 9. What is the best way to look through the microscope with one ocular? A. Look through the eyepiece using your right eye while covering the left eye or vice versa B. Cover both eyes for 10 seconds before looking through the eyepiece and repeat if necessary C. Look through the eyepiece with one eye while keeping both eyes open D. Center the eyepiece in between your two eyes, approximately on the bridge of your nose, and keep both eyes open 10. What do you use to focus and vary the distance between the specimen and the objective? A. Coarse Adjustment Knob B. Both A and B C. Fine Adjustment Knob D. Only B 11. If you look through the microscope and it looks dark which one of these will NOT help? A. Adjusting the mirror or light B. Checking the diaphragm C. Turning the coarse adjustment knob D. Making sure that nosepiece is clicked into place Page 1 of 5 12. In focusing the microscope, if you want to move the image up, which way should you move the slide? A. Upward B. Downward C. Sideward D. Any of the choices 13. What do you call the smallest living entity that can function on its own and is considered as the basic building block of life? A. Atom B. Molecule C. Organelle D. Cell 14. When many organ systems work together, they can form a(n) ___________. A. Organ B. Cells C. Organ System D. Organism 15. A group of toads falls under which level of organization? A. Population B. Community C. Biome D. Ecosystem 16. The tundra, savanna, desert, tropical rain-forest, and grassland is an example of what level of organization? A. Population B. Community C. Biome D. Ecosystem 17. The root and shoot system of the plants is considered as what level of organization? A. Organ B. Cells C. Organ System D. Organism 18. Which level of organization contains the interaction or interplay between the biotic and abiotic factors? A. Population B. Community C. Biome D. Ecosystem 19. In which of the following items would you expect to find cells? A. Onion Skin B. Golden Ring C. Pebbles D. Plastic Bottle 20. Which of the following is NOT an example of animal cells? A. Cheek Cells B. Red Blood Cells C. Skin Cells D. Leaf Cells 21. Plant and animal cells are alike in possessing what organelle? A. Cell Membrane B. Centrioles C. Cell Wall D. Chloroplast 22. What is the outermost boundary of an animal cell? A. The Cell Wall B. The Cytoplasm C. The Plasma Membrane D. The Nuclear Envelope 23. Which organelle functions as storage areas in cells and are found in both plant and animal cells but occupies over 50% of the plant cell’s volume? A. Mitochondria B. Ribosome C. Vacuoles D. Lysosomes 24. Which of the following organelles are present in plant cells but not in animal cells? A. Cell Wall B. Both A and D C. Centrioles D. Chloroplast 25. Which of the following parts of the microscope is correctly matched? A. Illuminating Part: Diaphragm B. Mechanical Part: Revolving Nosepiece C. Magnifying Part: Condenser D. Mechanical Part: Ocular Lens Page 2 of 5 26. The picture at the right shows a microscope. What are the functions of parts labelled A and B? A. X: To magnify the object. X Y: To hold the slide on the stage. B. X: To adjust the fine focus. Y: To hold the slide on the stage. C. X: To adjust the coarse focus. Y: To illuminate the object being viewed. Y D. X: To magnify the object. Y: To illuminate the object being viewed. 27. Which two parts of a microscope combine to give a magnified view of a cell? A. Eyepiece and objective lens B. Eyepiece and focus knob C. Stage and eyepiece D. Light source and objective lens 28. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Microscope slides should always be prepared with a tissue over the specimen. B. When using a monocular microscope, the correct technique is to look through the eyepiece with one eye and keep the other eye open. C. When you view a specimen through a microscope the image is upside down so when you move the slide to the right, the image moves to the right and when you move it to the left, the image moves to the left as well. D. All the statements are true. 29. From the following list, choose the correct order in which light passes through a light microscope. A. Mirror ➞ slide ➞ objective lens ➞ eyepiece B. Slide ➞ eyepiece ➞ objective lens ➞ mirror C. Mirror ➞ eyepiece ➞ objective lens ➞ slide D. Mirror ➞ objective lens ➞ eyepiece ➞ slide 30. Why is a cover slip or cover glass placed over the specimen before viewing it under the microscope? A. To protect the stage from any spillage of the dye. B. To protect the objectives and to prevent the slide from drying out. C. To make a clearer image and to magnify the specimen being viewed. D. To protect the eyepiece from any dust coming from the specimen that could damage the lenses. 31. Nerraw is walking to school with her best friend Areon. They begin talking about everything they see including the mahogany trees, carabao grass, hagunoy plant, ants, chickens and their classmates walking to school as well. They also notice how cold it is, how there are several large puffy clouds out with small gushes of wind from time to time, and how the sun is just starting to come up. What level of organization are they discussing? A. Population B. Community C. Biome D. Ecosystem Page 3 of 5 32. Overlapping circles can be used to show relationships. In this diagram, levels of organization within living things are shown. If each circle is made from the smaller circles inside it, what does circle “W” stand for if “Z” represents the cells? A. Organs B. Cells C. Tissues D. Organ Systems 33. Which answer correctly identifies the 5 levels of cell organization in a dog’s body from simple to most complex? A. bone cell, bone tissue, femur (thigh bone), skeleton, dog B. dog, skeleton, femur, bone tissue, bone cell C. skeleton, bone tissue, bone cell, dog, femur D. bone tissue, bone cell, femur, skeleton, dog 34. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE? I. All cells have a cell membrane. II. All cells contain a chloroplast. III. Animal cells have large central vacuoles. IV. Plant cells have cell walls. A. Statement I and II are true B. Statements II, III, and IV are true C. Statements I, II and IV are true D. Statements I and IV are true 35. Rengel is viewing a cell under the microscope. She noticed that the cell lacks centrioles but has an extra layer of protection surrounding the cell aside from the plasma membrane, contains dark greenish bodies floating around and a nucleus. What type of cell is being viewed by Rengel? A. Animal Cell B. Plant Cell C. Bacterial Cell D. All of the choices are correct 36. Which of the following is a correct list of structures found in both plant and animal cells? A. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall B. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm C. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts D. Mitochondria, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell wall, chloroplasts 37. A plant cell is viewed using a 10x eyepiece magnification and 43x HPO. How many times will it be magnified? A. 10 times B. 143 times C. 43 times D. 430 times 38. The following are the steps in focusing a microscope. Which of the following enumerates the CORRECT SEQUENCE of doing these steps? I. Look through the eyepiece and adjust the mirror to look for a light source. II. Turn the revolving nosepiece to LPO. III. Rotate the Course Adjustment Knob until the specimen can be clearly seen. IV. Place the slide so that it directly aligns with the center hole of the stage. A. I, IV, II, III B. II, III, IV, I C. III, II, I, IV D. III, I, IV, II Page 4 of 5 39. Cancer starts from cells that start to grow uncontrollably fast. They destroy tissues and organs. What does this say about the effects of diseased cells on the higher levels of organization in an organism? a. Diseased cells do not affect the other parts of an organism. b. Cancer involves only certain kinds of cells and does not affect any other kind of cell. c. Diseased cells affect only the next higher levels of organization that they make up-the tissues. d. Diseased cells damage the higher levels of organization that they make up: tissues, organs, organ systems and eventually, the whole organism. 40. Analyze the table below and identify which two cells could possibly have come from the same organism and which cell is a plant cell. A. Cell A and B could be from the same organism and Cell B is a plant cell. B. Cell B and C could be from the same organism and Cell A is a plant cell. C. Cell A and C could be from the same organism and Cell B is a plant cell. D. Cell A and C could be from the same organism and no cell is a plant cell. Prepared by: NOERA ANGEL M. MONTEMAYOR Science Teacher Angilan NHS Checked by: DESIREE T. ROBERTS Principal I Angilan NHS Page 5 of 5