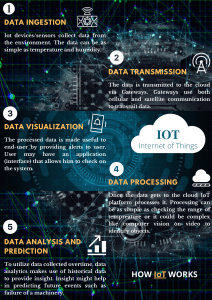
https://www.perle.com/articles/quality-control-in-the-era-of-iot-and-automation-40189762.shtml https://www.industryweek.com/operations/quality/article/21965233/six-ways-the-internet-ofthings-can-boost-quality https://www.cisin.com/coffee-break/Enterprise/how-iot-can-help-control-quality-in-pharmaproduction.html Software Quality Assurance Role Redefined: • Quality Assurance focuses on preventing defect. Quality Assurance ensures that the approaches, techniques, methods and processes are designed for the projects are implemented correctly. • Quality assurance activities monitor and verify that the processes used to manage and make the deliverables are followed and are operative, influencing both development and operational processes using IOT. Strategy for effective IOT software testing: Automation rules-Develop automation systems, through code, that can ensure quality standards at each level and which assures – Response Time, Data Validation, Real Time Data Accuracy, Secure Access control, Early detection of issues at design time, Needs more detailed Acceptance Criteria, Minimal manual end to end testing etc. Impact of IOT on Quality Assurance : For manufacturers, IOT technologies represent the next step in real- time monitoring, process automation and data analytics. By outfitting production lines with dozens of IOT sensors, plant managers can keep track of environmental conditions, equipment performance and more. In today's tech-centric landscape, the ability to monitor and control production equipment is paramount to the quality of manufactured goods. Technicians are constantly recalibrating equipment and optimizing production lines to ensure consistent process parameters and eliminate time-wasting inefficiencies. The same retooling is also taking place in the later stages of production, with automated systems and robotics playing a key role. Historically, manufacturing plants employed workforces of trained quality assurance specialists to verify the integrity of finished goods. How IoT is impacting quality control For manufacturers, IoT technologies represent the next step in realtime monitoring, process automation and data analytics. By outfitting production lines with dozens of IoT sensors, plant managers can keep track of environmental conditions, equipment performance and more. This added insight can allow manufacturers to better understand where quality control take action with renewed confidence. In terms of specific applications, IoT is helping manufacturing companies. Perform predictive maintenance: Instead of waiting for a piece of machinery to fail, manufacturers are using IoT sensors to help forecast when certain internal components will break down. By remaining proactive about maintenance and repair, manufacturers can simultaneously lower their overhead costs and reduce rejection rates. Monitor production remotely: Another benefit of IoT systems is that they can be monitored and controlled by off-site employees. This capability is especially important in the current business climate, where the COVID-19 pandemic has forced companies to curtail their physical operations. Using vision inspection systems, manufacturers can continue to perform key quality control tasks without the need for manual intervention. For example, thanks to recent innovations from Sightline Process Control Inc., bakeries around the world are able to integrate high-speed visual measurement tools into their workflows, AZO Materials reported. These systems are able to analyze up to 100 objects per second, helping identify defective baked goods before they're sent out to customers. Emerging IoT Applications On Quality Assurance • Once a manufacturing plant is outfitted with IoT sensors, worksite managers can begin integrating robotic process automation and other technologies to help make their operations more reliable. • • • • • • Information & Analysis Tracking Behavior : SCM, Trucks with sensors for predictive maintenance Enhanced Situational Awareness : Examples- Weather Warning Systems Sensor-driven Decision Analytics : Examples- Oil and gas company optimizing oilfield production Automation & and Control Process Optimization : Examples-Manufacturing Assembly Line Optimized Resource Consumption : Examples-Energy Distribution Networks Complex Autonomous Systems : Examples- Collision Avoidance Systems The massive amount of data these sensors collect can be fed into a machine-learning algorithm or an AI-powered platform to help drive real-time insights. In a fully networked manufacturing environment — one that is equipped with machine-to-machine communications — automated systems can detect output variations and send that data to downstream equipment. This can allow the equipment itself to make minor adjustments on the fly, including those that impact product quality. .