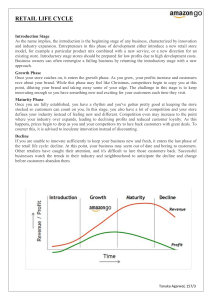
MARKET SEGMENTATION, TARGETING AND POSITIONING Introduction Today, companies are using target marketing instead of mass marketing. Target marketing is the marketing approach which focuses on serving a specific type of customers. It is based on the concept that the market for a particular product is not homogeneous. Target marketing involves market segmentation. Mass marketing Mass marketing is the marketing approach which involves serving all customers using the same marketing mix. Mass marketing does not involve market segmentation. Mass marketing (No market segmentation) Stages of target marketing Market segmentation=dividing the market into smaller submarkets with common needs or characteristics Market targeting=selection of one or more market segments to enter Market positioning=communicating the unique benefits of the product to the selected market Market segmentation Market segmentation is the process of dividing a market into different groups of customers with similar needs and characteristics. . Each submarket is known as a market segment. Reasons for market segmentation It is too difficult to satisfy the needs and wants of all consumers Customers are too numerous, too widely spread, and have different needs and buying practices. Benefits of market segmentation It helps to identify individuals with common characteristics, needs, and patterns of behavior. It provides information that helps to design the suitable marketing mix that specifically meets the customer needs It helps to set the appropriate timing of the promotion efforts Benefits of market segmentation It helps the firm to make proper allocation of resources It helps to gain competitive advantage It helps to overcome cannibalization (domination of a market by one large firm) Segmentation criteria Measurability---the segment should be identifiable and measurable. There should be information telling the size, purchasing power and profiles of the segment. Homogeneity--- the segment should be homogeneous. People within a segment should have common needs and characteristics that distinguish them from other segments. Differentiability/ heterogeneity---a market segment must be unique (different from others) in its response to a marketing mix. Segmentation criteria Accessibility---the segment should be reachable and accessible by communication and distribution channels. Substantiality---a segment must be large enough to be profitable. Actionability---a segment should be of appropriate size for the company’s resources to handle Stability---the segment should be stable (not likely to change). Bases for market segmentation There are four main ways of segmenting consumer markets: Geographic segmentation Demographic segmentation Psychographic segmentation Behavioral segmentation Geographic segmentation Involves dividing the market into different geographic units such as nations, regions, states,neighbourhood, cities or climate. Demand for some goods and services can vary according to the geographic region This approach can be appropriate for the following products Clothing items Drinks Air conditioning equipment Farm equipment Pampers This ad is an example of geographic segmentation. When visiting the web site look for the different countries Pampers markets to. Demographic segmentation Involves dividing the market based on demographic variables. Demographic factors used in segmenting the market are: Age Gender Family size Family lifecycle Demographic variables Income Occupation Education Ethnicity Nationality Religion Segmentation by sex Segmentation by age Income segmentation Watch for elite class Watch for middle class , Examples Markets for the following products can be segmented using demographic variables: Cosmetics Clothing Games Toys Video show Books Hotels Recreational places Luxury cars Calculators Cigarette Type of food Music Psychographic segmentation Involves dividing the market on the basis of lifestyle, personality and social class. Lifestyles: values, attitudes, opinions, interest For example, two young married women, each with two children and equal family income, may live two different lifestyles, which affect their particular buying patterns Examples Segmentation of the market for Clothing Luxury cars Restaurant Pizza Cruise Behavioural segmentation Involves dividing the market into groups based on their knowledge, attitudes, uses and responses to the product. The following are commonly applied behavioral segments Occasions : Groups individuals according to the occasions when they purchase, use or think of buying a product. Benefits Sought : Groups individuals according to the benefits they seek from the product. Usage Rate : Groups individuals according to the level of usage they make of the product, be it Heavy, Medium or Light usage. User Status : Groups individuals according to whether they are non-users, potential users, first-time users, regular users, or ex-users of a product Market targeting Market targeting is the process of evaluating the attractiveness of each market segment and selecting one or more of the segments to enter Determinants of attractiveness of the market segment Size of the market segment (number of customers) Growth rate of the segment Competition in the market Brand loyalty of existing customers in the segment Sales potential Target market selection strategies Undifferentiated marketing (mass marketing) Differentiated marketing Concentrated marketing Micro marketing Undifferentiated marketing (mass marketing) : Occurs when a firm produces only one product or product line and uses the same marketing mix to serve the entire market. There is no market segmentation.The firm decides to ignore market segment differences This strategy may be useful where a monopolistic situation exists. E.g. the strategy employed by DAWASCO Differentiated marketing When a firm produces numerous products and uses different marketing mix to serve different segments Differentiated marketing of laundry detergents Differentiated marketing . Marketing of coca cola Concentrated marketing (niche marketing) when a firm commits all of its marketing resources to serve a single market segment Cosmetics for ethnic women who have thirst for the exotic Micro marketing is when a the marketing mix is tailored on an individual consumer basis. Micromarketing includes local marketing and individual marketing. Market positioning Positioning is the process of creating a distinct image for the product in the mind of customers. Positioning indicates how a company wants customers to perceive its product relative to competing products. That is- how the company wants customers to see its product. Positioning involves finding a place in the mind of the customer to put its product. Positioning is used in conjunction with branding (e.g. business logo) and advertising slogans. “How can I make my business stand out in the crowd?” Product position Product position is the place the product occupies in the customer’s mind. Examples of positioning Volvo is positioned as the most durable, safest and spacious car by the slogan “the safest, most durable wagon in which your family can ride” Stella Artois lager was once positioned as a lager of high quality denoted by high price by the slogan “reassuringly expensive” Sunflower oil is positioned as cholesterol free cooking oil Blue band margarine by Unilever is positioned and advertised as stronger brand to promote faster growth. Examples of positioning BMW electric vehicles are positioned as ultra-premium brand NIVEA is positioned as a day cream, a night cream, a cream for different weather conditions, a moisturizer, and a protective cream. de beers diamond is positioned beers that promote loving and long-lasting relationship by the slogan “A diamond is forever” Benefits of positioning To ensure that the product is differentiated in the mind of customers To strengthen the power of messages directed at customers To decide on the grounds on which to compete Positioning process The process of positioning involves three activities or steps: Identification of possible competitive advantages. ( position of differentiation) Choosing the right competitive advantage (selecting the unique selling proposition) Selecting an overall positioning strategy. Positioning strategies Positioning by attributes. This approach is based on specific features of the product. E.g. durability, safety, designs etc. Positioning by quality or price Positioning with respect to benefits e.g. white dent is positioned as the tooth paste for cavity protection, homo detergent is positioned as dirt and odor remover. Positioning with respect to uses/application/occasion or time. Eg iodex for sprain and muscle pain, Vicks Vacorub for child’s cold at night INDIVIDUAL ASSIGMENT Submission date : 4th Jan 2021 1. Give reasons why marketing mix is referred to as controllable variables. 2. List and briefly explain functions of marketing 3. Give reasons why income and gender segmentation are considered popular Positioning strategies Positioning with respect to users e.g. blue band for promoting quick growth in kids Positioning against competitors (without mentioning their name) e.g. “vodacom, the leading cellular network”, “when you are number two, you try harder” by Avis against Hertz car company in rental car services. Positioning by product category/class.