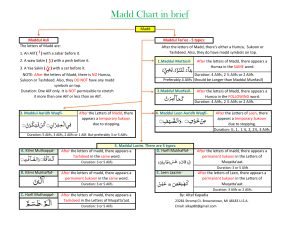
Al-Madd املد Al-Madd means: It is to stretch or to prolong. • Madd letters are: 1. Alif preceded by any letter with a Fat-hah on it. Written as ( ( اor ( ) ا. 2. Waaoo Saakinah, preceded by any letter with a Dhammah on it. Written as ( ( وor ()و 3. Yaa Saakinah preceded by any letter with a Kasrah under it. Written as ( )يor The way of pronunciation : • A Madd letter is pronounced by prolonging or stretching the Harakah on the letter before it. • Al-Madd can be prolonged from two to six counts depending upon its kind. • There are 2 types of Madd: 1- Original Madd. 2- Secondry Madd. • There are 2 reasons for Secondry Madd: 1- If there is Hamzah after the Madd. 2- If there is Sukoon after the Madd. Madd Tabee’ee • Madd Tabee’ee means the natural Madd. • The natural Madd is simply one of the Madd letters اor وor ىHuroof maddeya not followed by a Hamzah ءor a Saakin letter. • - The natural Madd is prolonged two counts. Examples: Madd Al-Badal • Every Hamza followed by Madd ُء و ِء يـَء ا • - Madd Badal is prolonged two counts. Examples: Made E’wadh • Madd ‘Ewadh is the replacement of a Tanween Fathah present at the end of a word while stopping at it, with an Alif Madd. • - Madd E’wadh is prolonged two counts. • Except for Taa Marbuta “ ”ة.. The Reader should stop on Taa Marbuta and pronounce it like Haa” “ هـwith Sukoon. جَرة َش َجَره َ َش Examples: Madd Wajib Muttasil • Is a Madd letter ( اor وor ) ىfollowed by a Hamzah ء,which is present in the same word. • - Madd Wajib Muttasil is prolonged 4-5 counts. Examples: Madd Jaa’ez Munfasil • Is a Madd letter ( اor وor ) ىfollowed by a Hamzah ء,which is present in 2 different word. • Madd present at the end of a word is followed by a Hamzah ( ( ءwhich is present in the beginning of the next word. • Madd Jaa’ez Munfasil is prolonged 4-5 counts. Examples: Madd As-Silah • A هـon the end of a word (last letter), must not be part of the original word, It is voweled either with a dhammah or a kasrah, positioned between two voweled letters, the reader is not stopping on it, • It has two cases: • 1= IF it is not followed by a hamzah : It’s called Madd Silah Sughra . • - Madd Silah Sughra (dammah or kasra) is prolonged two counts. *Two exemptions for silah sughra are as follow: • Here there is no madd although all the madd silah sughra conditions are met: • Here there is a madd although not all the madd silah sughra conditions are met (there is a harf saakin before the haa): 2= IF it is followed by a hamzah : It’s called Madd Silah Kubra . • - Madd Silah Kubra (dammah or kasra) is prolonged 4-5 counts. • When stopping on this هـwe stop with a regular sukoon, and the two count medd is dropped. Madd Al-‘Aarid Lil Sukoon • Madd Aridh Li-Ssukoon means “temporary Madd for stopping ”. • If a Madd Tabee’ee is followed by a letter at the end of a word, which has been made Saakin temporarily because the reader has to stop at the word, the reader should prolong the Madd Tabee’ee to be Madd Aridh Li-Ssukoon. • Madd Al-‘Aarid Lil Sukoon is prolonged 2-4-6 counts. Note: • This Madd only exists if the reader stops on that word. If the reader does not stop on it, it should be considered as a Madd Tabee’ee (2 counts). Examples: Madd Al-Leen • Madd Al-Leen “temporary Madd for stopping ”. • If Al-Leen letter (letter Yaa’ or Waaw Saakinah preceded by Letter has Fathah) is followed by a letter at the end of a word, which has been made Saakin temporarily because the reader has to stop at the word, the reader should prolong the Leen Letter to be Madd Leen. • Madd Al-Leen is prolonged 2-4-6 counts. Examples: Al-Madd Al-Laazim • If The Madd letter is followed by a letter with original Sukoon on it, the reader should prolong the Madd Letter to be Madd Laazim. • This Madd has two kinds = 1- kalimee (word based) 2-Harfee (letter based) • Al-Madd Al-Laazim is prolonged 6 counts. My best wishes for success Teacher Moshira