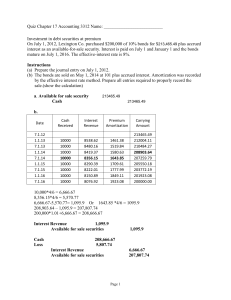
Midterm: Saturday Oct 12, 1:00PM Part 1: Introduction ch.1-3 Chapter 1: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets Chapter 2: An overview of the financial system: The Growth of Finance: - Much growth is related to asset management and household credit Function of Financial Markets: - - - - - Channel funds from economic players that have surplus funds to those that have a shortage of funds Plays important role in the economy o Promote efficiency: efficient allocation of capital o Improve consumer’s wellbeing allows consumers to time their purchases Direct and indirect finance o Direct: borrow funds directly from lenders by selling securities o Indirect: borrow funds through financial intermediaries Classification of financial markets o Debt and equity o Primary and secondary (OTC, organized exchange) o Money markets and capital markets Debt and equity markets o Debt: A contract between a borrower and lender o Maturity: the number of years until the debt instruments expiration Short term < 1 year Long term>10 years Intermediate 1<10 Equity o Dividends: [periodic payments o Capital gain: increase in price o Disadvantage Shareholder is a residual claimant o Advantage Confers ownership rights on the equity holders Primary and secondary markets: - Primary markets: new issues of a security are sold to initial buyers by the corporation or government agency borrowing the funds. o Not well known to the public o Investment bank assists in the initial sale of securities by underwriting securities - - - - - Secondary market: o Stock Exchange o Bond market o Other examples of secondary markets: FX markets Future markets Options markets o Brokers and dealers are crucial for well functioning secondary markets Brokers: agents who match buyers with sellers of securities Dealers: buying and selling securities at stated prices o Functions of the secondary markets Increase the liquidity of instruments Determine the price of the security that the issuing firm sells in the primary market o Secondary market: Echanges and OTC markets Organize exchanges: buyers and sellers of securities meet in one central location to conduct trades OTC market: Networks of dealers at different locations who have an inventory of securities stand ready to buy and sell securities Small stocks, bonds, etc. o Money and Capital Markets Money Market – trade short-term debt instruments Capital Market – trade longer term debt and equity o Money Market is more liquid: Less price fluctuation Corps and banks actively use money markets Money Market Instruments o Government of Canada Treasury Bills o Commercial Paper o Repurchase Agreement o Overnight Funds Government of Canada Treasury Bills o The most liquid of all the money market instruments o The safest of all money market instruments Commercial Paper o Unsecured short-term debt instrument is issued by large banks and well-known corps o Only the largest and most credit worthy corps issue commercial paper o The interest rates the corp is charged reflects the firm’s level of risk o Interest rate is low Repurchase Agreements o Short term loans for which treasury bills serve as collateral Collateral: an asset that lender receives if the borrower does not pay back the loan Important source of bank funds - - - - - - - The most important lenders are large corporations Overnight Funds: o Loans by banks to other banks o The overnight market responds to the credit needs of the deposit-taking institutions Overnight interest rate is closely watched barometer of the tightness of credit market conditions in the banks system Capital Market Instruments: Debt and equity instruments with maturities > 1 year o Stocks o Mortgages and mortgage-backed securities o Corporate bonds o Government of Canada bonds o Consumer and bank commercial loans Mortgages o Loans to households or firms to purchase housing, land, or other real structures, where the structure or land serves as collateral for the loans. o The mortgage market is the largest debt market in Canada o Mortgage-backed securities is a bond-like debt instrument which is backed by a bundle of individual mortgages Corporate bonds o Issued by corporations with strong credit rating o The corporate bond market is far more important to a firm’s financing decisions than the behaviour of the stock market: Although the size of the corporate bond market is substantially smaller than that of the stock market, the volume of new corporate bonds issued each year is substantially greater than the volume of new stock issues Not as liquid as Government of Canada bonds Government of Canada Bonds o Intermediate-term and long-term bonds o The most liquid security traded in the capital market o They are held by the Bank of Canada, banks, households, and foreign investors Consumer and Bank Commercial Loans o Loans to consumers and businesses made principally by banks o Consumer loans by finance companies o Canadian household debt to income ratio is 170.4 % in 2017 Canadians now spend an average of 14% of after-tax income on their debts, up from 11% in 1990 Consumer debt: Mortgage, bank loan, credit card, auto loan Function of Financial Intermediaries: indirect Finance o Reduce transaction costs (time and money spent in carrying out financial transactions) o Economics of scale: Loan contract can be used for many loans Specialized software / expertise for risk management o Risk Sharing - - - - - Asset transformation: Financial intermediaries create and sell assets with risk characteristics that people are comfortable with Diversification: investing in a collection (portfolio) of assets whose returns do not always move together Deal with asymmetric information problems Asymmetric information: one party does not know enough about other party Types of Financial Intermediaries o Depository Institutions Chartered Banks Trusts and Mortgage Loan Companies Credit Unions o Contractual Savings Institutions Life Insurance companies Property and Casual Insurance Companies Pension Funds and Government Retirement Funds o Investment Intermediaries: Finance Companies, Mutual Funds Depository Institutions o Raise funds by issuing deposits Liability: Source of fund o Use these funds to mark commercial, consumer, and mortgage loans and to buy Canadian government securities and municipal bonds Assets: use of fund Contractual Saving Institutions o Acquire funds at periodic intervals Primum from policies (liability) o Can predict with reasonable accuracy how much they will have to pay out in benefits in the coming years o Liquidity of assets is not as important a consideration for them as it is for depository institutions o Tend to invest their funds primarily in long-term securities such as corporate bonds, stocks, and mortgages (assets) Investment Intermediaries o Financing companies: Raise funds by issuing CP, stocks and bonds (liabilities) Lend the money to consumers and small businesses (assets) o Mutual Funds (MF) and Money market mutual funds (MMF): Raise funds by selling shares (liabilities) Use the fund to purchase stocks and bonds (assets) o Investment banks: Advise the corporation on which type of security to issue Then underwrites the securities by purchasing them from the corporation at a predetermined price and reselling them in the market Regulation of Financial Markets: Primary Reasons for Regulation: o Increase information to investors o Ex. Provincial securities and exchange commissions require corporations to disclose information and restrict insider trading Ensuring the soundness of intermediaries Disclosure, periodic inspection, report information to the public Deposit insurance, Canada Deposit Insurance Corp ensures each depositor to a loss of $100, 000 per account