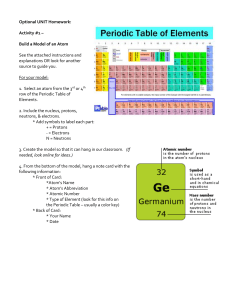
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 1 Structure of the Atom element Matter made from one type of atom atom Smallest part of an element – nucleus contains most of its mass nucleus Has a positive charge and made of protons and neutrons proton S ubatomic partials with positive charge neutron S ubatomic partials with no charge electron S ubatomic partials with negative charge quark S mallest property of atom, used to make protons & neutrons, total of G roup of electrons rotating around nucleus electron cloud 6 electron cloud quarks nucleus atom proton or neutron Timeline of the changes that have occurred in modeling the atomic structure since the 1800’s Current Model Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 2 Masses of Atoms mass atomic number mass number isotope average atomic mass amount of matter in an object a number equal to the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons the average mass of the mixture of isotopes of an element A. Nucleus of atom contains most of the mass of an atom masses of protons and neutrons in a nucleus are nearly identical electron’s mass is so small it is not included in atomic mass B. Atomic mass unit amu appropriate unit for measuring the size of a particle equals one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom each proton and each neutron has a mass of about 1 amu C. Protons number of protons is used to identify elements each element has different number of protons number of protons equals the atomic number of the element number of electrons equals the number of protons in an element D. Mass number equals the sum of the number of protons plus neutrons of an atom atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons and a different mass number Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3 The Periodic Table chemical property periodic table period group electron dot diagram Organizing the Elements any characteristic of a substance that indicates whether it can undergo a certain chemical change an arrangement of the elements by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties a horizontal row of elements on the periodic table a vertical column of elements on the periodic table the symbol of an element with dots representing the number of electrons in the outer energy level Compare Mendeleev’s early periodic table to that of today by completing the Venn diagram. Mendeleev Today (Moseley) Both increasing atomic mass vertically The Atom and the Periodic Table predict properties of unknown elements; allow for future additions repeating patterns increasing atomic number horizontally Sequence the energy levels in the electron cloud diagram and write the maximum number of electrons that can be contained in each level. Level 4; 32 Level 3; 18 Level 2; 8 Level 1; 2 Nucleus; 0 Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table Section 3 The Periodic Table (contd) Analyze how electron dot diagrams show similarities between elements within a group. Elements within a group all have the same electron dot diagrams, because they have the same number of electrons in their outer energy levels. They are similar in how they combine with other elements to fill the outermost level. Classify the regions of the periodic table as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids. Regions of the Periodic Table • Shade the regions on the blank periodic table. • Label each region and write its characteristics. Write a paragraph showing the relationship between chemistry and physics based on what you’ve learned from the periodic table. The chemical behavior of matter can be described in terms of energy and forces, both electrical and magnetic. The structure of the atom is described in terms of energy levels. Reactivity between atoms is described in terms of energy as well. Wrap-Up Now that you have read the chapter, think about what you have learned and complete the table below. 1. Write an A if you agree with the statement. 2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement. Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table After You Read • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that still has all the properties of the element. D • An atom is made up of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. A • Quarks are so tiny that they orbit the nucleus with the electrons. D • Isotopes of an element only differ in their number of neutrons. A • An element’s chemical/physical properties may be predicted by its location on the periodic table. A