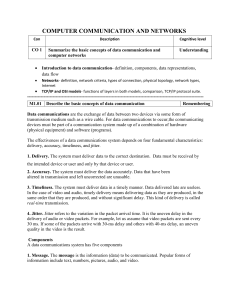
Things you need to know … Data Communication & Networking Instructor: Office: Introduction Data Communications and Networking Communications - Behrouz A. Forouzan Data and Computer Communications - Computer Networks - Andrew S. Tanenbaum RQ 3 Data Communication Communication at a distance, includes telephony, telegraphy, television etc. RQ 4 Message, Sender, Receiver, Medium, Protocol Transfer of data from one or more sources to one or more destinations. A set of rules that governs data communication A network of data processing nodes that are interconnected for the purpose of data communication. The data (information) to be communicated Node RQ Telecommunication Computer Network Information transfer, according to agreed conventions using hand signals, language, Morse code, smoke signals etc. Components of data communication system What is … ? refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the parties creating and using the data. Communication Reference Book: 2 Data William Stallings Take appointment before meeting, preferably via email What is … ? Text Books: mnaseem105@gmail.com Student Consultation: RQ Things you need to know … 2nd Floor, Block-B Email: Dr. Rehan Qureshi / Muhammad Naseem A node can be a computer or printer etc. or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data. The physical path by which a message travels 5 RQ 6 1 Effectiveness of Data Communication System Data representation Depends on few characteristics, such as … To deliver data to correct destination To deliver data accurately (unaltered) Timeliness To deliver data in a timely manner RQ 7 Direction of data flow Simplex Half-duplex RQ 8 Networks A network is a set of devices (nodes) connected by communication links. Because of networks we can … Full-duplex RQ 9 Types of Connection RQ Share resources ( Peripherals, files, internet connection etc.) Communicate and collaborate Save data RQ 10 Point-to-point connection A link is a communications pathway that transfers data from one device to another Point-to-point American Standard Code for Information Interchange Extended ASCII Unicode Numbers Images Audio Video ASCII Accuracy Delivery Text Multipoint 11 RQ Provides a dedicated link between devices. Entire capacity of the link is reserved for the two devices. 12 2 Multipoint connection Network Topology More than two specific devices share a single link. The capacity of the channel is shared. RQ 13 Mesh topology RQ 15 Bus topology RQ RQ 14 Star topology Every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device. A fully connected mesh network has n(n-1)/2 physical (duplex) channels to connect n devices with each device having n-1 I/O ports. It refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically. It is a geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and linking devices to one another. Each device has a dedicated point-to-point link to a central controller (usually a hub). Less expensive than mesh. RQ 16 Ring topology One long cable acts as a backbone to link all devices. Multipoint connection (shared link) 17 RQ Each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection only with two other devices. A signal is passed along the ring in one direction. 18 3 Hybrid topology Categories of networks A network can have hybrid or a combination of different topologies Example: a star backbone with three bus networks RQ 19 Local Area Network (LAN) RQ 20 LAN Usually owned by same organization as attached devices Data rates much higher Usually broadcast systems 21 Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) RQ Building or small campus RQ A Network is categorized with respect to its size, its ownership, the distance it covers and its physical architecture. Smaller scope RQ 22 Wide Area Network (WAN) Middle ground between LAN and WAN May be owned by Private company or a service provided by a public company It normally covers the area inside a town or a city 23 RQ Provides long-distance communication over large geographic areas that may comprise a large region, a country, a continent, or even the whole world. 24 4 Interconnection of Networks: Internetwork Wide Area Network (WAN) When two or more networks are connected, they become an internetwork, or internet. Can be as complex as the backbones that connect the Internet (switched WAN) Can be as simple as a dial-up line that connects a home computer to the Internet (point-to-point WAN) RQ 25 RQ The Internet Protocol The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks. It is a network of networks that consists of millions networks, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. RQ A protocol is a set of rules that govern data communications. A protocol defines … 27 28 Standards Organizations Standards provide guidelines to manufacturers, vendors, government agencies, and other service providers to ensure the kind of interconnectivity necessary in today's marketplace and in international communications. Standards are developed through the cooperation of standards creation committees, forums, and government regulatory agencies, such as … RQ what is communicated how it is communicated when it is communicated RQ Standards 26 29 RQ International Organization for Standardization (ISO) International Telecommunication UnionTelecommunication Standards Sector (ITU-T) American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) European Telecommunications Standards Institute 30 (ETSI) 5 Internet Standards An Internet Standard is a specification of a technology or methodology applicable to the Internet. specified as one or more Request for Comments (RFC) document(s) published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Contributions to the IETF start as an Internet Draft. This is a working document (a work in progress) with no official status and limited lifetime Upon recommendation from the Internet authorities, a draft may be promoted to RFC. RFCs may be labeled as Proposed Standards, Draft Standards or Internet Standards depending on their RQ maturity level. 31 Summary RQ Data communication and networking basic terminology Types of connections Network topology Categories of networks Protocols and Standards 32 6