Bloom's Taxonomy Explained: Cognitive, Affective, Psychomotor Domains
advertisement

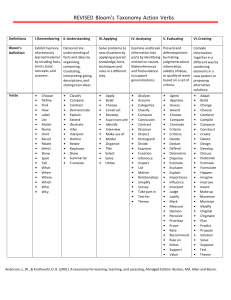
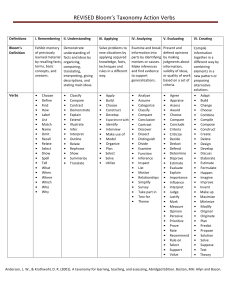
Bloom’s Ta x o n o m y HUMERA SAJID BLOOM’S TAXONOMY Taxonomi is a Greek word. Taxis=arrangement, nomos=science, the science of arrangement. It is fancy word for classification. This taxonomy refers to the classifications of skills that a learner should acquire. Skills are divided into three domains. Bloom's Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist Dr Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking in education, such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles, rather than just remembering facts (rote learning). It is most often used when designing educational, training, and learning processes. WHY BLOOM’S TAXONOMY Learner as a whole person with experiences and previous knowledge. How can one write learning outcomes? Bloom taxonomy 3 DOMAINS OF LEARNING 1. Cognitive domain or stimulation of the mind 2. Affective domain or influencing the emotions 3. Psychomotor domain or physical action 3 Hs : Head, Hand and Heart Learning outcomes refer to obser vable and measurable • knowledge • skills • attitudes KSA/SKA/ASK= Knowledge, Skills and Attitude Cognitive Domain Bloom (1956) proposed that knowing is composed of six successive levels arranged in a hierarchy. (OLD VERSION) 6. Evaluation 5. Synthesis 4.Analysis 3. Application 2. Comprehension 1. Knowledge Revised version 5 years later by Krathwohl and Anderson Affective Domain 5. Internalizing 4. Organizing 3.Valuing 2. Responding 1. Receiving Integration of beliefs, ideas and attitudes Comparing, relating, synthesising values Commitment to a value Active participation in own learning Willingness to receive information Psychomotor Domain NaturalizationAutomated, unconscious mastery of activity and related skills at strategic level. Articulation: Adapt and integrate expertise to satisfy a non-standard objective. Precision: Execute skill reliably, independent of help. Manipulation: Reproduce activity from instructions or memory Imitation: Copy the action of another. Observe and replicate. COGNITIVE DOMAIN 1. Remember - ability to recall or remember facts without necessarily understanding them • Use action verbs such as: 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember Arrange, collect, define, describe, duplicate, enumerate, examine, find, identify, label, list, locate, memorise, name, order, outline, present, quote, recall, recognise, recollect, record, recount, relate, repeat, reproduce, show, state, tabulate, tell. 2. Understand - ability to understand and interpret learned information • Use action verbs such as: 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember Associate, change, clarify, classify, construct, contrast, convert, decode, defend, describe, differentiate, discriminate, discuss, distinguish, estimate, explain, express, extend, generalise, identify, illustrate, indicate, infer, interpret, locate, predict, recognise, report, restate, review, select, solve, translate. 3. Application: Using information to solve problems; transferring abstract or theoretical situations, e.g. Put ideas and concepts to work in solving problems 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember • Use action verbs such as: Apply, assess, calculate, change, choose, complete, compute, construct, demonstrate, develop, design, discover, dramatise, employ, examine, experiment, find, illustrate, interpret, manipulate, modify, operate, organise, practice, predict, prepare, produce, relate, schedule, select, show, sketch, solve, transfer, use. 4. Analysis: ability to break down information into its components, e .g. Look for inter-relationships and ideas (understanding of organisational structure) 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember • Use action verbs such as: Analyse, appraise, arrange, break down, calculate, categorise, classify, compare, connect, contrast, criticise, debate, deduce, determine, differentiate, discriminate, distinguish, divide, examine, experiment, identify, illustrate, infer, inspect, investigate, order, outline, point out, question, recognise, relate, separate, solve, sub-divide, test. 6 . Evaluation: Ability to make Judgements about information,valididty of ideas or validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember • Use action verbs such as: Appraise, ascertain, argue, assess, attach, choose, compare, conclude, contrast, convince, criticise, decide, defend, discriminate, explain, evaluate, interpret, judge, justify, measure, predict, rate, recommend, relate, resolve, revise, score, summarise, support, validate, value. 5. Synthesis/create - ability to put parts together and create new ideas from old concepts • Use action verbs such as: 6. Create 5. Evaluate 4.Analyze 3. Apply 2. Understand 1. Remember Argue, arrange, assemble, categorise, collect, combine, compile, compose, construct, create, design, develop, devise, establish, explain, formulate, generalise, generate, infer, integrate, invent, make, manage, modify, organise, originate, plan, prepare, propose, rearrange, reconstruct, relate, reorganise, revise, rewrite, set up, summarise. EXAMPLES TO CLARIFY LEVELS IN BLOOMS TAXONOMY • Remember: who is the main character? • Understanding: what is the main idea of the story? • Applying: what questions would you like to ask in an interview with the main characters? • Analysis: How is the story related to your life? • Evaluation: what choices would you have made if you were in the story? • Create: How would you adapt the plot to create a different story? Work sheet: Fill the empty pyramid with appropriate action verbs (Not possible in an online class) HOTs LOTs in Cognitive domain Why we are learning about Bloom’s Taxonomy? How this taxonomy helps teachers? • It provides a common language for teachers to discuss and exchange learning and assessment methods. • It is commonly used to assess learning on a variety of cognitive levels • Blooms taxonomy provide a checklist to verify that learners are not just passively acquiring knowledge, but they also learn how to apply knowledge, how to integrate it in their thinking and how to reflect upon it by using critical thinking. • Bloom’s puts a magnifying lens on all aspects of course design. With greater clarity in assessment, teachers are able to more clearly state a course’s learning outcomes. ALTERNATIVE TAXONOMY