Educational Psychology Quiz: Transfer, Motivation, Problem Solving
advertisement

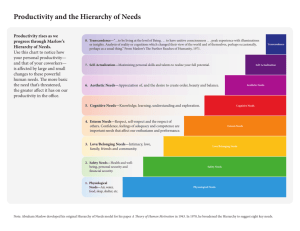
1. _____ is when understanding of the first topic is helpful but not essential to knowledge from the second one. a. Vertical transfer b. Positive transfer c. Lateral transfer d. Negative transfer 2. Near transfer does not involve situations or problems that are similar in both superficial features and underlying relationships. * True/ False 3. Which of the following is a Factor Affecting Transfer? a. The probability of transfer increases as the time interval between the original task and the transfer task decreases. b. Transfer reduces when the cultural environment reassures and expects the transfer c. Principles are difficult transferred than discrete facts. d. Significant knowledge upholds enhanced transfer than rote knowledge. 4. Arousal refers to an organism’s current level of internal energy. * True / False 5. In the Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs the need for development, creativity, and growth can be best described by: a. Psychological need b. Self-esteem need c. Self-actualization need d. Love/ belonging need KEY 1. C 2. False 3. D 4. True 5. C 1.All of the following are cognitive factors affecting problem solving except: a. Working memory capacity b. Effort and dedication c. Retrieval from long term d. Metacognition 2. True or false: Transfer can involve declarative knowledge, procedural knowledge, or an interplay between the two. 3.All of the following are components of a problem except: a.solution b. goal c.givens d.operations 4. ________ transfer involves instances in which the original learning task and the transfer task overlap in some way. While __________transfer is when the original task and the transfer task are different in both content and structure. A.Near, far B. vertical, latheral C.latheral, vertical D. Specific, general 5.The need for food, water, exercise, and rest belongs to what category of Maslow's hierarchy of need? A. Esteem B. Safety C. Love and Belonging D. Physiological 6. A basic need to believe obe can deal effectively with their environment is ________ A. Competence B. Motivation C. Self-Worth D.Self-Efficacy 7. Which of the following is an example of self handicapping? A. Procrastinating B. Low self esteem C. Goal setting D. Deficiency Answer Key: 1. Answer: B 2.Answer: True 3.Answer: A 4. Answer: D 5. Answer: D 6. Answer: A. 7. Answer:A. 1. Maslow proposed that people have five distinct kinds of needs: which of the following is not of the 5 needs. a. Psychological needs b. Safety needs c. Esteem needs d. Physiological needs Answer: A 1. Which of the following human needs according to Maslow states that “People seek affectionate relationships with others and like to feel that they belong to and are accepted in a social group”? a. Sexual and acceptance needs b. Psychological needs c. Love and belonging needs d. Esteem needs 1. Learning is more effective when students are extrinsically motivated rather than being intrinsically motivative. · True / False 2. Intrinsic motivation is obtained by usage of an outside incentive or rewards. · True/False Key: 1.C. Love and belonging needs 2. False 3.False 1. Tom frequently reads books that shed light on topics that inspire and fascinate him. This is an example of _______. a. extrinsic motivation b. situated motivation c. intrinsic motivation d. arousal 2. True or False: Arousal is an internal state that moves us to action, pushes us in a particular direction, and keeps us engaged in certain activities. 3. Toddlers' sense of independence and desire for control of the things they do especially during the "terrible twos" is an example of: a. self-efficacy b. autonomy c. competence d. self-worth 4. True or False: People who think or know their performance will be evaluated have a lower sense of autonomy. Answer Key: 1. c. 2. False 3. b 4. True 1. When something you learned in one situation affects how you learn or perform in another is called: a. critical thinking b. transfer c. problem solving d inert knowledge 2. When driving a car with an automatic transmission, people accustomed to driving a standard transmission may step on a clutch that isn’t there. This is a perfect example of ______________. a. negative transfer b. latheral transfer c. specific transfer. d. positive transfer 3. True or False: Problem solving can be defined as using previously learnt skills to address an unanswered question or troubling situation. 4. True or False: Heuristics and algorithms are two categories of problem solving strategies. Key: 1. b 2. a 3. True 4. True