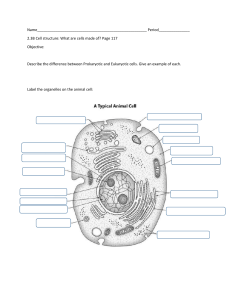
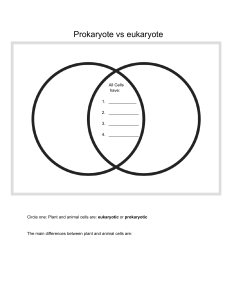
CELL STRUCTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE CELL Jefferyl Kae S. Pandac, RMT The Cell “Structural units of all living things.” 💡 The term cell was coined by Robert Hooke from the long rows of monk rooms at the monastery. Cell Theory ■ A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. ■ The activity of the organism depends on the collective activities of its cells. ■ According to the principle of complementarity, the activities of cells are dictated by their structure, which determines function. ■ Continuity of life has a cellular basis. Carbon Chemical Composition of Cells Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Basic Features of Cells ■ Plasma membrane ■ Semi-fluid substance (cytosol) ■ Chromosomes (carry genes) ■ Ribosomes (synthesize proteins) Cell Types Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea Eukaryotes: Protists, fungi, plants, animals Prokaryotic Cell ■ No nucleus ■ Genetic material is in an unbound region called nucleoid ■ No membrane-bound organelles ■ Cytoplasm is bound by the plasma membrane Eukaryotic Cell True cell Genetic material is bound by a membranous nuclear envelope Membrane-bound organelles Cytoplasm in the region between the plasma membrane and the nucleus 💡 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions. Please watch the supplementary video provided.