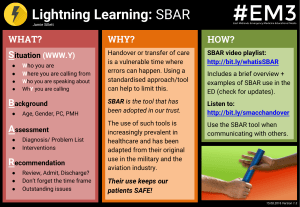
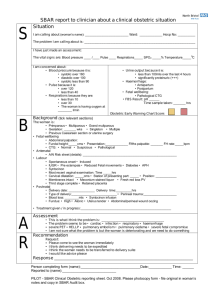
SBAR - Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation Home > Service Improvement Tools Download PDF What is it? SBAR is an easy-to-remember mechanism that you can use to frame conversations, especially critical ones, requiring a clinician ’s immediate attention and action. It enables you to clarify what information should be communicated between members of the team, and how. It can also help you to develop teamwork and foster a culture of patient safety. The tool consists of standardised prompt questions within four sections, to ensure that staff are sharing concise and focused information. It allows staff to communicate assertively and effectively, reducing the need for repetition. The tool helps staff anticipate the information needed by colleagues and encourages assessment skills. Using SBAR prompts staff to formulate information with the right level of detail. Back to top How will it help achieve 18 weeks? The NHS is often criticised for poor communication, however, there are few tools around that actively focus on how to improve communication, in particular verbal communication. The tool can be used to shape communication at any stage of the patient ’s journey, from the content of a GP’s referral letter, consultant to consultant referrals through to communicating discharge back to a GP. When staff use the tool in a clinical setting, they make a recommendation which ensures that the reason for the communication is clear. This is particularly important in situations where staff may be uncomfortable about making a recommendation ie those who are inexperienced or who need to communicate up the hierarchy. The use of recommendation prevents the hit and miss process of ‘hinting and hoping ’. Back to top How to use it A sample NHS SBAR template to show to use SBAR in your hospital can be viewed in the following document: SBAR Diagram A detailed description of the steps involved: S Situation: l l l Identify yourself the site/unit you are calling from Identify the patient by name and the reason for your report Describe your concern Firstly, describe the specific situation about which you are calling, including the patient ’s name, physician, patient location, code status, and vital signs. An example of a script would be: “This is Lou, a registered nurse on Nightingale Ward. The reason I ’m calling is that Mrs Taylor in room 225 has become suddenly short of breath, her oxygen saturation has dropped to 88 per cent on room air, her respiration rate is 24 per minute, her heart rate is 110 and her blood pressure is 85/50. We have placed her on 6 litres of oxygen and her saturation is 93 per cent, her work of breathing is increased, she is anxious, her breath sounds are clear throughout and her respiratory rate remains greater than 20. She has a full code status. ” B Background: l l l Give the patient’s reason for admission Explain significant medical history You then inform the physician of the patient ’s background: admitting diagnosis, date of admission, prior procedures, current medications, allergies, pertinent laboratory results and other relevant diagnostic results. For this, you need to have collected information from the patient ’s chart, flow sheets and progress notes. For example: "Mrs. Smith is a 69-year-old woman who was admitted ten days ago, following a MVC, with a T 5 burst fracture and a T 6 ASIA B SCI. She had T 3-T 7 instrumentation and fusion nine days ago, her only complication was a right haemothorax for which a chest tube was put in place. The tube was removed five days ago and her CXR has shown significant improvement. She has been mobilising with physio and has been progressing well. Her haemoglobin is 100 gm/L; otherwise her blood work is within normal limits. She has been on Enoxaparin for DVT prophylaxis and Oxycodone for pain management." A Assessment: l l l Vital signs Contraction pattern Clinical impressions, concerns You need to think critically when informing the doctor of your assessment of the situation. This means that you have considered what might be the underlying reason for your patient ’s condition. Not only have you reviewed your findings from your assessment, you have also consolidated these with other objective indicators, such as laboratory results. If you do not have an assessment, you may say: "I think she may have had a pulmonary embolus.'" "I’m not sure what the problem is, but I am worried." R Recommendation: l l l Explain what you need - be specific about request and time frame Make suggestions Clarify expectations Finally, what is your recommendation? That is, what would you like to happen by the end of the conversation with the physician? Any order that is given on the phone needs to be repeated back to ensure accuracy. “Would you like me get a stat CXR? and ABGs? Start an IV?" “Should I begin organising a spiral CT? ” “When are you going to be able to get here? ” Incorporating SBAR may seem simple, but it takes considerable training. It can be very difficult to change the way people communicate, particularly with senior staff. Recommended uses for SBAR: l l l Inpatient or outpatient Urgent or non -urgent communications Conversations with a physician, either in person or over the phone l l l l l Urgent or non -urgent communications Conversations with a physician, either in person or over the phone – particularly useful in nurse to doctor communications – also helpful in doctor to doctor consultation Discussions with allied health professionals – Respiratory Therapy – Physical Therapy Conversations with peers – Change of shift report Escalating a concern Tips for implementation: Anxiety about giving ‘recommendations ’ In the UK, less experienced clinical staff have sometimes found making recommendations a challenge. 'Recommendation' is important as it clearly describes the action the messenger needs. Where staff are anxious about giving recommendations, they will need extra support and encouragement. A good place to start is by trying the tool with supportive colleagues. Remembering to use the communication tool Hospitals using SBAR have found the following useful: l l l Notepads or paper with the tool printed on them Pocket cards Stickers on or next to telephones to act as a visual prompt Back to top Examples The Multidisciplinary Team meeting is an example of the process in action. Many clinicians are present. Most will be in a position to help formulate the most appropriate management for the patient. The doctor directly responsible presents the present situation and the relevant background. The assessment will include a cross examination of the clinician to clarify the clinical findings and a joint review of the results of all relevant investigations. Recommendations will be agreed by all present. These will be documented in the patient ’s records for implementation. Another example where this tool would add to clarity and better care is the emergency call to a sleeping senior colleague for advice about patient management. When woken in the night it takes some time to absorb the facts and respond. This is greatly aided by a clear presentation of the situation, the background, the assessment and the proposed treatment. In the surgical situation it is possible and even quite likely that the senior colleague is needed to help with the assessment and / or to carry out the recommended surgery. The request for direct help should be made clear as part of the recommendation so there is no misunderstanding. After all, it would not be surprising if the senior colleagues ’ preference was to go back to sleep! Back to top What next? Once you have started testing this as a communication tool, you will need to assess if it has made a difference. You should focus on making sure that the checklist (you could invent your own) and principles of good communication are being used by people in practice. If it is proving successful, the next step is to get this into people ’s everyday habits, so it becomes ' the way things are done around here'. Ways of doing this include: l l l l Using prompts and visual cues: EG stickers on the telephone, letter templates, patient notes Ensuring people feel it ’s alright to prompt each other using your agreed framework. For example ' Can I make sure I ’m understanding you? What is your recommendation here?' Make time for team discussion, reflection and refinement of the tool Disseminate your good practice to other teams by modelling the communication behaviour you ’re aiming for from them Links to other useful tools on this website: Another excellent communications tool that would aid the use of SBAR is the Art of Listening. Back to top Additional resources Websites: A very useful summary of SBAR by R Lertzman in 2005 titled ‘No More Hinting and Hoping: An Interview with Frances Griffin ’. This is accessed through the NHS National Patient Safety Agency website. The IHI website contains some SBAR tools that have been adapted for specific settings. Back to top Background Originally used in the military and aviation industries, SBAR was developed for healthcare by Dr M Leonard and colleagues from Kaiser Permanente in Colorado, USA. In one health care setting, the incidence of harm to patients fell by 50 per cent after implementing SBAR. Back to top Acknowledgements / sources Back to top © Copyright NHS Institute for Innovation and Improvement 2008