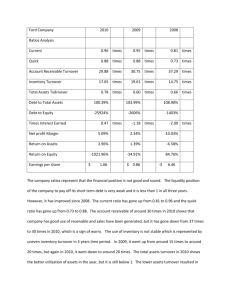
1.0 COMPANY BACKGROUND 1.1 FAJARBARU BUILDER GROUP BHD Fajarbaru Builder Group Bhd is an organization that is driven by the passion of becoming the one trusted partner for all construction and property demands. The Group started its operation in Malaysia on 6 May 1976, as a turnkey contractor with principal activities in civil and infrastructure works, as well as building construction. Since then, the Group has registered with the Pusat Khidmat Kontraktor (PKK) as a Class A contractor and is recognized by the Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB) as a Class G7 contractor, effectively enabling us to tender for government and private projects of any size. The Group is also registered as a turnkey contractor with Petroliam Nasional Berhad, and is a certified ISO 9001:2015 company. With these qualifications and many more, Fajarbaru Builder Group Bhd has progressed leaps and bounds to become a vertically integrated construction set-up, wellpositioned as a ‘One Stop Agency’ capable of undertaking a wide range of projects no matter the size. In addition, our extensive expertise in earthworks, infrastructure works, superstructure works and finishing works, with in-house design and build capabilities allow us to spearhead intricate projects with ease. Some of the Group’s notable projects include the Low-Cost Carrier Terminal (LCCT), Gleneagles Hospital Ampang, Kelana Jaya and Ampang LRT Station. 1 On the property front, the Group is making a prominent mark in both Malaysia and Australia. The Rica Residence Sentul, as part of the extensive series of Rica Residences, was launched in 2017 to rousing reception from the public for its modern design and convenient location. Our two other projects, Rica Residence Kinrara and Rica Residence Malacca are in the pipeline for launch. In Melbourne, Australia, the Group completed its maiden project Gardenhill, an award-winning development in early 2017. Gardenhill was honored with the “Game Changer of the Year” title at the Annual REA Excellence Awards for its off-lead dog park, Australia’s first exclusive and private dog park in a high-rise apartment project. A subsequent project, luxury skyscraper Paragon was launched the same year and won the award for Best High-rise Residential category at the Asia Pacific Property Awards. Fajarbaru Builder Group also has business interests in timber logging, trading and logistics. VISION To be the most valued construction and property company in the markets we serve. MISSION With stakeholder satisfaction as our core, we further focus on individual goals to achieve the bigger collective aspiration. ADDRESS No.61 & 63, Jalan SS 6/12, Kelana Jaya, 47301 Petaling Jaya, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia. PHONE 03-7804 9698 WEBSITE http://fajarbaru.com.my/index.html 2 1.2 HO HUP CONSTRUCTION COMPANY Ho Hup Construction Company was co-founded in 1960 by Mr. Low Chee. It has grown to become one of the largest companies in construction and related services in Malaysia. As a market leader in Malaysia, Ho Hup Construction Company brings together a comprehensive range of capabilities in building, civil engineering, specialized intelligent building, trading, and related services. Ho Hup Construction Company also known as the company with a very comprehensive fleet of light and heavy modern construction equipment. With strong roots in its local markets and through its network of subsidiaries, Ho Hup Construction Company Berhad also plays a significant role in the world market for major engineering structures, civil engineering, dredging, road building and infrastructure projects. To date, Ho Hup Construction Company has successfully incorporated its subsidiaries in India, Madagascar, Mauritius, China, South Africa, Thailand and Indonesia. Locally, Ho Hup Construction Company has completed numerous projects from both the private and government sectors for high-rise intelligent buildings, stadiums, airports, highway & bridges, railways & light rapid transit, off shore marine works, oil & gas works, commercial building development, deep foundation worksand many more. Ho Hup Construction Company is known as the company with vast involvement in national projects namely the Petronas Twin Towers, National Sports Complex, Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA), Light Rail Transit System (LRT), Malaysia –Singapore second crossing and major highways. “Our Projects” page highlights the details of work executed at the projects of which have contributed in shaping our history. 3 On 25th February 1991, Ho Hup became a Public Limited Company listed on the main board of Bursa Malaysia. This significant step has led to the birth of the name of Ho Hup Construction Bhd. The company underwent a major transformation in 2009 and to date, the Group's spectrum of activities now consists of three main divisions namely, property development, construction & civil engineering works and ready mix. VISION To Create and Enhance Shareholders Value MISSION Amalgamate all these with HoHup’s “quality driven” mission and wide knowledge in this field places the company above and gives it an edge over many other construction companies. ADDRESS No. 18 Jalan 17 / 155C, Bandar Bukit Jalil, 57000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. PHONE CONTACT 03-8993 9168 WEBSITE http://www.hohupgroup.com.my/cont.html E-MAIL corporate@hohupgroup.com.my 4 2.0 RATIO CALCULATION 2.1 FAJARBARU BUILDER GROUP BHD 2.2 HO HUP CONSTRUCTION COMPANY 5 3.0 RATIO ANALYSIS 3.1 FAJARBARU BUILDER GROUP BHD Liquidity Ratios a) Current Ratios Based on current ration of Fajarbaru Builder in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 2.53 in 2017 to 2.42 in 2018. For every RM 1 of current liabilities, the company only has RM 2.53 of current as a backup in 2017. Meanwhile, in 2018 Fajarbaru Builder only has RM 2.42 of current asset as backup. This show that the company is not able to meet short term obligation compare to 2017. b) Quick Ratios Based on quick ratio calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from 1.53 in 2017 to 1.81 in 2018. This show that the company able to meet short-term obligation without relying on inventories. c) Net Working Capital Based on net working capital of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the amount is increase from RM 241, 573,775 in 2017 to RM 313,823,977 in 2018. This is a positive net working capital because the amount of current asset financed by long term debt (LTD). Efficiency Ratios a) Inventory Turnover Based on the calculation for inventory turnover for Fajarbaru Builder, the ratio is increase from 1.20 in 2017 to 2.93 in 2018. Its good because the efficient in inventory management and no overstocking problem in the company. 6 b) Average Collection Period (ACP) Based on the average collection period for Fajarbaru Builder, the average of the collection period is increase from 67.82 days in 2017 to 89.99 days in 2018. It means the company is unable to collect their account receivable in short period. c) Fixed Asset Turnover Based on the fixed asset turnover for Fajarbaru, the ratio is increase from 3.83 in 2017 to 9.34 in 2018. So that Fajarbaru is efficient in utilizing their net fixed asset to generate higher sales. d) Total Asset Turnover Based on the total asset turnover for Fajarbaru, the ratio decreases from 0.88 in 2017 to 0.74 in 2018. This company is not efficient in utilizing their total asset to generate higher sales. Leverage Ratios a) Debt Ratio Based on debt ratio calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 38.39% in 2017 to 27% in 2018. Good performance. This show that the company lower financial risk. b) Debt Equity Ratio Based on debt equity ratio calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 62.32% in 2017 to 45% in 2018. Good performance. This show that the company use more equity compared to debt as their source of financing. c) Times Interest Earned Based on times interest earned calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from 3.89 times in 2017 to 5.58 times in 2018. Good performance. This show that the company able to cover interest charges and the company face no risk of bankruptcy. 7 Profitability Ratios a) Gross Profit Margin Based on gross profit margin calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from 57.80% in 2017 to 78% in 2018. Good performance. This show that the company are efficient in controlling cost of goods sold and have a good pricing policy. b) Operating Profit Margin Based on operating profit margin calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from 23.66% in 2017 to 25% in 2018. Good performance. This show that the company are efficient in controlling their operating costs. c) Net Profit Margin Based on net profit margin calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 17.57% in 2017 to 10% in 2018. Poor performance. This show that the company not able to generate higher net income. d) Return on Asset Based on return on asset calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 15.39% in 2017 to 8% in 2018. Poor performance. This show that the company not able to make profit from their investment in fixed assets. e) Return on Equity Based on return on equity calculation of Fajarbaru in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from 24.99% in 2017 to 13% in 2018. Poor performance. This show that the company not able to maximize their shareholder’s wealth. 8 3.2 HO HUP CONSTRUCTION COMPANY Liquidity Ratio a) Current Ratio Based on the current ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 1.70x in 2017 and 1.62x in 2018. For RM 1 of current liabilities, the company has RM 1.70 of current assets as backup in 2017. Meanwhile, in 2018, the company has RM 1.62 of current assets as backup. This company show that is not able to meet short-term obligation compare to 2017. b) Quick Ratio Based on the quick ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 1.71x and 1.61x in 2018. This show that the company unable to pay its short-term obligations and rely on the sale of its inventory to settle of all the debt that company faces. c) Net Working Capital Based on the net working capital of Ho hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is increase from RM 252, 008 in 2017 and RM 308, 645 in 2018. Its show that the company’s amount is financed by long-term debt. Efficiency Ratio a) Inventory Turnover Based on the inventory turnover of Ho Hup company in 2017, the ratio is decrease from 472.32x and 17.64x on 2018. It indicates the company is very efficient in inventory management. The company also not facing any overstocking problems. b) Average Collection Period Based on the average collection period of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the period of days decreases from 116.62 days in 2017 and 28.13 days in 2018. It shows that the company is good in management time and be able to collect their account receivable in short period. 9 c) Fixed Asset Turnover Based on the fixed asset turnover of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the asset is increase from 0.63x in 2017 and 2.81x in 2018. This show that the company is good and efficient in utilizing their net fixed asset to generate higher sales for the company. d) Total Asset turnover Based on the total asset turnover for Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the asset is increase from 0.20 in 2017 and 0.45 in 2018. This show the company’s is good and efficient in utilizing their total asset to generate higher sales for the company. Leverage Ratio a) Debt Ratio Based on the debt ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 61% in 2017 and 49% in 2018. This shows the company is efficiency in money management and lower financial risk. b) Debt Equity Ratio Based on debt equity ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 156% in 2017 and 75% in 2018. This shows that the company is good in manage company money and use more equity compared to debt as their source of financing. c) Times Interest Earned Based on times interest earned ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the ratio is decrease from 4.77 times in 2017 and 3.56 times in 2018. This shows that’s the company is poor and not be able to meet interest charges. Because of that, the company has a higher risk of bankruptcy. 10 Profitability Ratio a) Gross Profit Margin Based on the gross profit margin ratio of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the profit is decrease from 47% in 2017 and 32.95 in 2018. This show the company is not efficient in the selling price of goods, without any decrease in the cost of goods sold. Unfavorable purchasing or markup policies. b) Operating Profit Margin Based on the operating profit margin of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the profit is decrease from 47.2% in 2017 and 15.07% in 2018. This ratio shows that the company is not so efficient in controlling their operating costs. c) Net Profit Margin Based on the net profit margin of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the profit is decrease from 21.45% in 2017 and 10.83% in 2018. It shows that the company is poor and not be able to generate higher net income. d) Return on Asset Based on return on asset of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the profit shows that the asset is increase from 4.30% in 2017 and 4.86% in 2018. It shows that the company be able to make profit from the company’s investment in fixed assets. e) Return on Equity Based on the return on equity of Ho Hup company in 2017 and 2018, the profits earned is decrease from 11.03% in 2017 and 7.49% in 2018. It shows that the company poor and not be able to maximize their shareholder’s wealth. 11 4.0 POSSIBLE CAUSES 4.1 FAJARBARU BUILDER GROUP BHD Liquidity Ratios a) Current Ratios Low values for the current ratio (values less than 1) indicate that a firm may have difficulty meeting current obligations. However, an investor should also take note of a company's operating cash flow in order to get a better sense of its liquidity. A low current ratio can often be supported by a strong operating cash flow. b) Quick Ratios A low quick ratio is generally a riskier position since you do not have adequate current assets, without inventory, to cover near-term debt. This also means you rely heavily on efficient inventory turnover to keep you afloat in the short-term. A significant downturn in sales could leave you in a bind. A low ratio also causes concern with potential investors and creditors because of your short-term risks c) Net Working Capital Positive working capital is the excess of current assets over current liabilities. In other words, when the net working capital is a positive figure, it is said that the firm has a positive working capital. It is the situation when the short-term receivable of a company is more than its short-term payables. This is a desirable situation for the company it ensures no bankruptcy circumstances. Meanwhile, negative working capital is when a company's current liabilities exceed its current assets. This means that the liabilities that need to be paid within one year exceed the current assets that are monetizable over the same period 12 Efficiency Ratios a) Inventory Turnover Inventory turnover shows how many times a company has sold and replaced inventory during a given period. This helps businesses make better decisions on pricing, manufacturing, marketing, and purchasing new inventory. A low turnover implies weak sales and possibly excess inventory, while a high ratio implies either strong sales or insufficient inventory. b) Average Collection Period (ACP) Having a higher average collection period is an indicator of a few possible problems for your company. From a logistic standpoint, it may mean that your business needs better communication with customers regarding their debts and your expectations of payment. More strict bill collection steps may need to be taken. Additionally, this high number may indicate that your customers may no longer intend to pay or may be unable to pay, serious problems for any business. c) Fixed Asset Turnover A low fixed asset turnover means that annual sales are low relative to fixed assets (property, plant and equipment). It could mean that a company is having trouble selling its product, or that it has excess assets. But it can also be low for reasons of business strategy. It cannot be evaluated in isolation. d) Total Asset Turnover The asset turnover ratio measures the efficiency of how a company uses assets to produce sales. A higher ratio is favorable, as it indicates a more efficient use of assets. Conversely, a lower ratio indicates the company is not using assets as efficiently. This can be due to excess production capacity, poor collection methods, or poor inventory management. 13 Leverage Ratios a) Debt Ratio Some possible causes of high debt ratio. The higher the debt ratio, the more leveraged a company is, implying greater financial risk. At the same time, leverage is an important tool that companies use to grow, and many businesses find sustainable uses for debt. High debt ratio for an industry with volatile cash flows, in which most businesses take on little debt. The company with a high debt ratio relative to its peers would probably find it expensive to borrow and could find itself in a crunch if circumstances change. b) Debt Equity Ratio Some possible causes of high equity ratio. high debt equity ratio indicates that a company may not be able to generate enough cash to satisfy its debt obligations. However, low debt equity ratios may also indicate that a company is not taking advantage of the increased profits that financial leverage may bring. c) Times Interest Earned Some possible causes of low times interest earned. Low times interest earned ratio means fewer earnings are available to meet interest payments. Failing to meet these obligations could force a company into bankruptcy. It is used by both lenders and borrowers in determining a company’s debt capacity. Profitability Ratios a) Gross Profit Margin Possible causes of low gross profit margin. Low gross profit margin may be due to insufficient sales volume or higher costs of goods sold. Costs of goods sold may be high due to expensive sources of goods. It could also be due to high labour costs, high production wastage and low selling price. 14 b) Operating Profit Margin Possible causes of lower operating profit margin. Lower operating profit margin could arise from lower gross profit margins. In this case, the company should try to reduce the costs of goods sold as well as the operating expenses. However, if the gross profit margin is high but the operating profit margin is low, then the problem lies in high but the expenses. Therefore, the company should reduce the operating expenses rather than the costs of goods sold. c) Net Profit Margin Some possible causes of low net profit margin. Low profit margin indicates a low margin of safety and higher risk that a decline in sales will erase profits and result in a net loss, or a negative margin. The low margin can result from inefficient management, high costs of expenses and weak pricing strategies d) Return on Asset Some possible causes of low return on asset. A low return on asset is not a good sign for the growth of the company. A low return indicates that the company is not able to make maximum use of its assets for getting more profits. Too much of wastages could also be inferred as a reason for lower return on asset. Reducing wastages is a major challenge in most of the manufacturing companies. Wastages not only means the product or raw material wastage; the wider meaning of wastage includes idle labor hours. Proper production planning and the process of testing the products at every stage can significantly reduce the wastages. e) Return on Equity Some possible causes of low return on equity. Low return on equity is because the company do not do so well in revenue and profit, also the company face a tough time growing the business. In other words, it also tells you that the business is not worth investing in since the management simply cannot make very good use of investors’ money. 15 4.2 HO HUP CONSTRUCTION COMPANY Liquidity Ratios a) Current Ratios Some company do not like the idea of being in debt for long. With a short term loans the money is often just leant for a few weeks and must all be paid back in full at that point. This means that the debt will normally not last longer than a month. b) Quick Ratios When a company’s liquidity is low, it could be due to several reasons. As the ratios basically compare current assets with current liabilities, the problems may arise from any of these two components. Some of the possible reasons are the company is holding too much inventory, a poor debt collection system, poor cash management or the company using short-term sources of financing to purchase long-term assets. c) Net Working Capital Accounts payable payment period. A company negotiates with its suppliers for longer payment periods. This is a source of cash, though suppliers may increase prices in response. Reducing the accounts payable payment terms has the reverse effect. Efficiency Ratios a) Inventory Turnover When a company’s inventory turnover ratio is lower than other companies or lower than the previous year’s result, it could be various factors. One of the factors is the number of days that your money is locked in goods. So, stock cover is measured in number of days and goal is to have it low as possible in order to increase turnover. Ultimate turnover is stock cover, but it is very difficult not to lose sales in that set up. b) Average Collection Period (ACP) The reasons for longer collection periods include a lax credit policy, poor screening when accepting new customers on a credit basis, no ageing of customer’s accounts, no reminders and follow up for late payment, as well as not enough or no cash discounts given to attract early payment. 16 c) Fixed Asset Turnover One reason for having a low total asset turnover ratio is bad acquisitions. Acquisitions are attractive if they help a company maintain or increase its returns. However, if a company makes purchases and they end up generating weak asset returns, the company will tend to have a low total asset turnover ratio. d) Total Asset Turnover A higher asset turnover ratio implies that the company is more efficient at using its assets. A low asset turnover ratio, on the other hand, reflects the bad management of assets by the company. It may also indicate production or management problems. Leverage Ratios a) Debt Ratio The company cannot afford the monthly payments for keeping company’s debt at a manageable level. The monthly payments are getting higher such as the payday loans, investments loans, mortgage principal, plus interest, property taxes and insurance (PITI) and any homeowner association fees. b) Debt Equity Ratio A high debt equity ratio is often associated with high risk it means that a company has been aggressive in financing its growth with debt. For example, if investors want to evaluate a company's short-term leverage and its ability to meet debt obligations that must be paid over a year or less, other ratios will be used. c) Times Interest Earned The company may be borrowing more than is necessary. This could be due to the firm’s high dividend payout ratio, hence leaving less retained profits for expansion purposes. Therefore, the company must rely more on external financing, such as borrowings. 17 Profitability Ratios a) Gross Profit Margin One of the simplest factors that can lead to declining margin is higher costs of goods sold. These factors may lead to them negotiating or simply charging the company higher rates on goods. If higher Cost of goods sold (COGS) negatively affects your gross profit margin, the company may have to negotiate harder or look for alternative providers. b) Operating Profit Margin Lower operating margins could arise from lower gross profit margins. In this case, a company should try to reduce the costs of goods sold as well as the operating expenses. However, if the gross profit margin is high but the operating margin is low, then the problem lies in high operating expenses. Therefore, the company should reduce the operating expenses rather than the costs of goods sold. c) Net Profit Margin Any decrease in revenue will result in a decrease in profits. Once a company's sales decrease below the total amount spent for expenses and cost of goods sold in each period, a net loss will occur. Poor pricing strategies, ineffective marketing programs, competition, inability to keep up with market changes and inefficient marketing personnel are common causes of decreasing revenues. d) Return on Asset The company has been borrowing aggressively, it can increase return on asset because equity is equal to assets minus debt. The more debt a company borrows, the lower equity can fall. A common scenario that can cause this issue occurs when a company borrows large amounts of debt to buy back its own stock. e) Return on Equity The company has been borrowing aggressively, it can increase return on equity because equity is equal to assets minus debt. The more debt a company borrows, the lower equity can fall. A common scenario that can cause this issue occurs when a company borrows large amounts of debt to buy back its own stock. 18 5.0 RECOMMENDATIONS 5.1 FAJARBARU BUILDER GROUP BHD Liquidity Ratios a) Current Ratios For improving current ratio, the management needs to focus on various strategies including its current liabilities and assets which are not a onetime activity. It must be monitored throughout the year. b) Quick Ratios One of the quickest ways to improve the quick ratio would be to pay off the current bills and at the same time increase sales so that the cash on hand or account receivable increases. As the quick ratio is like the current ratio but does not include stock in current assets, it can be improved by similar actions that increase the current ratio. c) Net Working Capital Some of the ways that working capital can be increased include earning additional profits, issuing common stock or preferred stock for cash, borrowing money on a longterm basis, replacing short-term debt with long-term debt, selling long-term assets for cash. In addition to increasing working capital, a company can improve its working capital by making certain that its current assets are converted to cash in a timely manner. 19 Efficiency Ratios a) Inventory Turnover The need for improving the ratio arises when a stock turnover ratio is lower than industry standards. A lower ratio indicates that the company does more stocking than is required. Generally, if the product sale is faster, inventory operation is more efficient. This is because the inventory churning would be faster and thereby the inventory turnover ratio would be better. This means the business needs less blockage of funds or investment in inventory for on-going operations of a business. So, it is best to have a proper plan for improving inventory turnover ratio either by concentrating on better sales or by lowering the blockage of funds on a stock. b) Average Collection Period (ACP) Your credit policy and credit terms play an important role in the amount of time it takes to collect a customer's account. For example, if your credit terms provide your customers with 30 days to pay their bills, then you should expect that your average collection period will be somewhere around 30 days-maybe longer. Your credit policy and credit terms can also be used to accelerate and improve your cash inflows. Your efforts to collect on your customers' accounts also have a direct impact on accelerating and improving your cash flow. c) Fixed Asset Turnover The assets turnover ratio can be improved by improve debtors collection, improve revenue, liquidate assets and improve efficiency, formulate robust inventory management (example: the company should analyze how its stock move from company to its customer and know whether there are slow moving or fast-moving products of the company) d) Total Asset Turnover A company should try to increase its production, so that the assets are used more efficiency. If this is not possible due to certain factors (for example, the demand for the product could not be increased any more due to market saturation), disposal of idle non-current assets may be necessary. 20 Leverage Ratios a) Debt Ratio To improve debt ratio, avoid taking on more debt. Consider reducing the amount you charge on your credit cards and try to postpone applying for additional loans. Then, increase the amount of pay monthly toward company’s debt. Extra payments can help lower company’s overall debt more quickly. The company can issue new or additional shares to increase its cash flow. This cash can be used to repay the existing liabilities and in turn, reduce the debt burden. The reduction in debt will lower the debt to total asset ratio. b) Debt Equity Ratio The most logical step a company can take to improve its debt equity ratio is that of increasing sales revenues and hopefully profits. This can be achieved by raising prices, increasing sales, or reducing costs. The extra cash generated can then be used to pay off existing debt. c) Times Interest Earned Times interest earned ratio is a measure of a company’s solvency, i.e. its longterm financial strength. It can be improved by a company's debt level, obtaining loans at lower interest rate, increasing sales and reducing operating expenses. Profitability Ratios a) Gross Profit Margin The company need to review the pricing policy, reduce costs of sales by changing the supplier, reducer labour costs and production wastage. b) Operating Profit Margin The company need to reduce cost of sales and operating expenses, depending on the company’s situation. The company may also need to review the selling price. 21 c) Net Profit Margin Improving the net margin through increasing revenue is generally the most popular option. Businesses can increase sales income by raising the price of products or by selling more of them. Then, some of the greatest expenses a company incurs come from the day-to-day running of the business and the production of goods for sale. Operating expenses can be reduced by relocating headquarters to a cheaper part of town, leasing smaller factory space, or reducing the workforce. d) Return on Asset Improving the return on asset through increasing net income, decrease the total assets, improve efficiency of current assets and fixed assets. Improve efficiency ratio on using fixed assets could help the company increase its productivity or in other words, reduce operating cost related to fixed assets. e) Return on Equity Improving the return on asset by using more financial leverage. Company can finance themselves with debt and equity capital. By increasing the amount of debt capital relative to its equity capital, a company can increase its return on equity. Then, increase profit margin. As profits are in the numerator of the return on equity ratio, increasing profits relative to equity increases a company's return on equity. Increasing profits does not necessarily have to come from selling more product. It can also come from increasing prices of each product sold, lowering the cost of goods sold, reducing its overhead expenses, or a combination of each. 22 5.2 HO HUP CONSTRUCTION COMPANY Liquidity Ratios a) Current Ratios That can reduce the current ratio by increasing the current liabilities. So, the companies can increase the proportion of short-term loans as compared to long-term obligations. The companies can also reduce the duration of their long-term loans so that more portion of the loan becomes due in a time period, which in a way will increase the current portion of the liabilities. However, the current liabilities should be increased without any corresponding increase in the company’s current assets. b) Quick Ratios Obviously, it is vital that a company have enough cash on hand to meet accounts payable, interest expenses and other bills when they become due. The higher the ratio, the more financially secure a company is in the short term. A common rule of thumb is that companies with a quick ratio of greater than 1.0 are sufficiently able to meet their short-term liabilities. In general, low or decreasing quick ratios generally suggest that a company is over-leveraged, struggling to maintain or grow sales, paying bills too quickly or collecting receivables too slowly. On the other hand, a high or increasing quick ratio generally indicates that a company is experiencing solid top-line growth, quickly converting receivables into cash, and easily able to cover its financial obligations. Such companies often have faster inventory turnover and cash conversion cycles. c) Net Working Capital Determine whether fixed and variable costs can be reduced. If you examine carefully, you will be able to identify expenses that are wasteful. By eliminating such expenses, you will have more liquidity for working capital. Also, can Ensure that all debt obligations are met on time. Use electronic payment systems to ensure timely payments and avoid situations that delay payments and attract penalty. 23 Efficiency Ratios a) Inventory Turnover Way to increase is managing stock is special discipline that inventory planners do it daily. The company need to start forecasting sales, calculate min-max stocks and watch not to go above or under. Within 3 months working with Inventory Planning Service the company can typically expect to see for example, reduction in inventory levels of between 20-50%. Then, significantly improved customer service levels and increased sales, driving improved profitability. Next, improved supplier relations due to improved forecast accuracy. Lastly, self-financing supply chain improvements due to reduced supply chain costs. b) Average Collection Period (ACP) The company may need to adopt a tighter collection policy, for example, reducing the existing 45-day credit to a 30-day credit period. The company may also prepare the ageing of its debtors’ account, screen new customers before allowing them credit sales and offer cash discounts to encourage early payment. c) Fixed Asset Turnover The easiest way to improve asset turnover ratio is to focus on increasing revenue. The assets might be properly utilized, but the sales could be slow resulting in a low asset turnover ratio. The company needs to increase its sales by more promotions and by quick movements of the finished goods. d) Total Asset Turnover The easiest way to improve asset turnover ratio is to focus on increasing revenue. The assets might be properly utilized, but the sales could be slow resulting in a low asset turnover ratio. The company needs to increase its sales by more promotions and by quick movements of the finished goods. 24 Leverage Ratios a) Debt Ratio Firstly, increase the amount you pay monthly toward your debt. Extra payments can help lower your overall debt more quickly. Second, avoid taking on more debt. Consider reducing the amount you charge on your credit cards and try to postpone applying for additional loans and postpone large purchases, so you are using less credit. More time to save means you can make a larger down payment. You will have to fund less of the purchase with credit, which can help keep your debt-to-income ratio low. b) Debt Equity Ratio Changes in long-term debt and assets tend to have the greatest impact on the Debt Equity ratio because they tend to be larger accounts compared to short-term debt and short-term assets. If investors want to evaluate a company’s short-term leverage and its ability to meet debt obligations that must be paid over a year or less, other ratios will be use c) Times Interest Earned A firm should have an optimum mixture of source of financing. This will result in the lowest cost of capital and hence maximize firm value. Profitability Ratios a) Gross Profit Margin Along with higher supplier pricing, ancillary costs contribute to higher COGS. If the company business moves to more environmentally friendly packaging, for instance, the company can either pass the costs on to customers or take a hit on gross profit margin. Distribution or transportation costs can also increase your COGS. Again, figuring out ways to minimize gains in these product-related areas or passing on the costs to customers are possible protective measures. 25 b) Operating Profit Margin Reduce cost of sales and operating expenses, depending on the firm’s situation. The firm may also need to review the selling price. c) Net Profit Margin Improving the net margin through increasing revenue is generally the most popular option. Businesses can increase sales income by raising the price of products or by selling more of them. d) Return on Asset Whenever you cut expenses, you increase the revenues you get to keep. This creates a higher return for you. Watch for excessive payroll expenses, rising materials supplies and shipping costs that increase. You can reduce the number of employees you need by improving productivity. Reduce the cost of materials by renegotiating with suppliers or finding new suppliers. Lower shipping costs through renegotiation or by charging a shipping fee to customers. e) Return on Equity The company can finance themselves with debt and equity capital. By increasing the amount of debt capital relative to its equity capital, a company can increase its return on equity. For example, the company will use a (fictional) lemonade stand as an example for how the use of debt can increase a company's return on equity. The company will be created financial statements for this lemonade stand. The first shows a lemonade stand that is financed exclusively with equity; the second shows what happens when the company is financed by equal amounts of debt and equity. 26 6.0 CONCLUSION 27