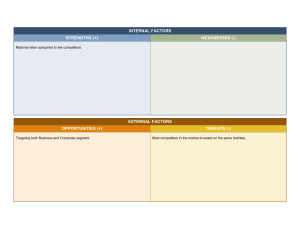
Operations strategy Module-1: What is Operations Operations management can contribute to the success of any organization by providing what the business needs to survive and prosper (higher margins, innovative new products, unique competencies, etc.) and by satisfying its customers. It does this by achieving five broad objectives. It can reduce the costs of producing products and services by being efficient in the way it transforms inputs into outputs. It can increase revenue by promoting outstanding customer satisfaction through its ability to provide exceptional quality, responsiveness, reliability and flexibility. It can reduce operations-related risk and promote resilience (the ability to recover after operations failure). It can reduce the amount of investment (capital employed) that is necessary to produce the required type and quantity of products and services. It can do this by increasing the effective capacity of the operation and by being innovative in how it uses its physical resources. It can provide the basis for future innovation by building a solid base of operations based capabilities, skills and knowledge within the business. What is Strategy Linguistically the word derives from the Greek word strategos meaning ‘leading an army’. And, although there is no direct historical link between Greek military practice and modern ideas of strategy, the military image is powerful. Both military and business strategy can be described in similar ways, and include some of the following. setting broad objectives that direct an enterprise towards its overall goal; planning the path (in general rather than specific terms) that will achieve these goals; stressing long-term rather than short-term objectives; dealing with the total picture rather than stressing individual activities; being detached from, and above, the confusion and distractions of day-to-day activities; Later views of strategy have introduced some of the practical realities of business based on observations of how organizations really do go about making (or not making) strategic decisions. These include the following considerations. Business objectives may not ever become ‘clear’. In fact, most organizations will have multiple objectives that may themselves conflict. For example, an outsourcing decision may improve profitability but could involve a firm in long-term reputational risk. Markets are intrinsically unstable in the long term so there must be some limit to the usefulness of regarding strategy as simply planning what to do in the future. It may be more important to keep close to what is actually happening in the market and adapt to whatever circumstances develop. Many decisions are far less formal than the simple planning model assumes. In fact many strategic decisions ‘emerge’ over time rather than derive from any single formal senior management decision. Organizations do not always do in practice what they say they do, or even what they want to do. The only way to deduce the effect strategy of an organization is to observe the pattern of decisions that it makes over time. Operations strategy: Operations strategy is a process by which key creations decisions are made that are consistent with the overall strategic objective of the firm. Or According to Slack and Lewis, it is the total pattern of decisions which shape the long term capabilities of any type of operations and their contribution to the overall strategy, through the reconciliation of market requirements with operations resources. They also write, Technology and business models are rapidly changing, so businesses must keep pace and look to the future. Operations strategies drive a company’s operations, the part of the business that produces and distributes goods and services. Operations strategy underlies overall business strategy, and both are critical for a company to compete in an ever-changing market. With an effective ops strategy, operations management professionals can optimize the use of resources, people, processes, and technology. What Are the Operations Strategy of a Company? A company’s operations strategies are the activities that produce and deliver a product or service. Operations management is the profession that encompasses planning, implementing, and supervising that production. Some people think of operations as the daily tasks and tactics that transform materials or actions into a product or service, but operations strategy goes a level higher to determine operations approaches and goals. For example: A car company, , operations could include the following: obtaining and transporting raw materials (metal, rubber, and plastic, etc.), dealing with suppliers, conducting and measuring the steps that transform materials into parts, managing the people, machines, and processes, assembling the vehicles efficiently, maintaining quality and troubleshooting problems, delivering car orders on time, and managing and continually optimizing the whole value chain. In addition, operations could play a role in product design, plant capabilities and design, and production or sales forecasting. The Role and Purpose of Operations Strategy: Operations strategy is only one part of overall business or corporate strategy, but it’s crucial for competitiveness and success. Without a strong operations strategy, companies fail to keep up with changing markets and lose out to more strategic competitors. Many companies, big and small, have struggled with operations strategy, often lacking in comparison with technologically savvy competitors. For example, Amazon, while constantly advancing technology such as drones for delivery, has pushed aside myriad brick-and-mortar retailers. To be effective and competitive, all parts of a company must work together. All departments should contribute to the company mission and have strategies underlying the overall corporate/business strategy. In addition to having an operations strategy, they should also have functional area strategies in finance, IT, sales, marketing, human resources, and possibly other departments, depending on the type of business. “An operations strategy should guide the structural decisions and the evolution of operational capabilities needed to achieve the desired competitive position of the company as a whole,” says Tim Laseter in his article "An Essential Step for Corporate Strategy.” These days, however, it’s not enough to simply follow best practices. Companies must innovate, not just play catch-up to practices already mastered by competitors. Authors Steven C. Wheelwright and Robert H. Hayes categorized types of organizations based on a company’s attitude toward operations: Stage 1, Internally Neutral: The operations function is reactive and viewed as a necessary evil. Stage 2, Externally Neutral: The operations function adopts best practices and tries to match the competition. Stage 3, Internally Supportive: The operations function tries to provide support for the overall business strategy. Stage 4, Externally Supportive: The operations function provides competitive advantage for the company, and sets the industry standard. Importance of Operations Strategy Different sources use different terms to describe strategy areas. Here’s one way to categorize core strategies: Corporate: Overall company strategy, driving the company mission and interconnected departments Customer-Driven: Operational strategies to meet the needs of a targeted customer segment Core Competencies: Strategies to develop the company’s key strengths and resources Competitive Priorities: Strategies that differentiate the company in the market to better provide a desired product or service Product or Service Development: Strategies in product design, value, and innovation A company’s key success factors (KSFs) pertain to competitiveness, such as a company’s attributes, resources, capabilities, and competencies. By identifying these, a company can focus on the issues that matter most and measure them with key performance indicators (KPIs). Another way to frame strategic areas is by these “distinctive” competencies: Price Quality, such as performance, features, aesthetics, and durability Service Flexibility Tradeoffs, or competing on one or two distinctive competencies at the necessary expense of others Author Terry Hill used the terms order qualifier and order winner. An order qualifier means a company or product has a characteristic that allows it to be a viable competitor. An order winner is a characteristic that causes customers to choose it over competitors. Tips for Operations Strategies and Tactics Specific strategies depend on your specific business. Here are strategy tips that apply to many companies, whether they are producing goods or services. Take a Global View: See how others worldwide are providing better goods and services. Learn from them, and see how you might compete and innovate in a core competency. Also, improve your supply chain by looking globally, and employ global talent if remote work is an option. Have a Strong Mission Statement: Focus your efforts with a mission statement that truly defines your goals and guides your business approach. Tie your overall business strategy and operations strategy into it. Gain Competitive Advantage with Differentiation: Develop a point of differentiation and a unique value proposition, and consistently innovate and build strategies around them. Don’t just use best practices. Exceed them, and leapfrog the competition. Gain Insights from a SWOT Analysis: Analyse your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats as a catalyst to strategy. Track Progress: Develop strong analytics and KPI dashboards to measure and optimize your operational efforts. Operations Strategy Examples With the rapidly changing marketplace in recent years, some companies have excelled in part due to their strong operations strategies. Here a few examples: Amazon: Once known for books, Amazon is now known as the go-to platform for online shoppers of any product. Its distribution network is widely touted and even includes experiments with drone delivery. Apple Computers: Apple is long recognized in operations circles for its operational excellence and supply chain management. Wal-Mart: This retailing giant managed to undercut many competitors on the price and variety of a wide range of products. FedEx: FedEx made speed of delivery its calling card, achieving it with excellent operations. IKEA: The world’s largest furniture retailer undercut many home goods competitors on price and variety with its warehouse concept. Functions of operation Strategy There are seven main functions of operations are: Product management: Product management is an organizational function within a company dealing with new product development, business justification, planning, verification, forecasting, pricing, product launch, and marketing of a product or products at all stages of the product lifecycle. It is an important organizational role — especially in technology companies — that sets the strategy, roadmap, and feature definition for a product or product line. Supply chain: Inventory: A supply chain is a network between a company and its suppliers to produce and distribute a specific product to the final buyer. The supply chain also represents the steps it takes to get the product or service from its original state to the customer. Supply chain is a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in supplying a product or service to a consumer. Inventory or stock is the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale. Inventory management is a discipline primarily about specifying the shape and placement of stocked goods. Inventory is generally categorized as raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Raw materials are unprocessed materials used to produce a good. Retailers typically refer to this inventory as "merchandise.” Common examples of merchandise include electronics, clothes, and cars held by retailers. Forecasting: Forecasting is the process of making predictions of the future based on past and present data and most commonly by analysis of trends. A commonplace example might be estimation of some variable of interest at some specified future date. Prediction is a similar, but more general term. Once the manager and the forecaster have formulated their problem, the forecaster will be in a position to choose a method. There are three basic types—qualitative techniques, time series analysis and projection, and causal models. Scheduling: Scheduling is the process of arranging, controlling and optimizing work and workloads in a production process or manufacturing process. Scheduling is used to allocate plant and machinery resources, plan human resources, plan production processes and purchase materials. Quality: Quality is the degree to which an object or entity (e.g., process, product, or service) satisfies a specified set of attributes or requirements. Quality is the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements. In business, engineering and manufacturing, quality has a pragmatic interpretation as the non-inferiority or superiority of something; it's also defined as being suitable for its intended while satisfying customer expectations. Facilities planning and management: Facilities planning and management focuses on the operation of commercial and industrial structures, such as office buildings or large shopping complexes. With a degree in facilities planning and management, you could become a facilities manager or a convention planner.