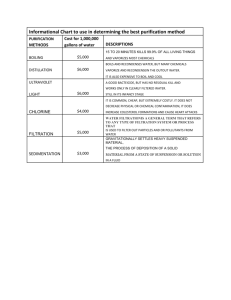
GENERAL LABORATORY RULES & SAFETY PRECAUTIONS PROPER ATTIRE 1. Dress properly during a laboratory activity. 2. Safety goggles and laboratory gowns must be worn whenever you work in the lab. Gloves should be worn whenever you use chemicals that cause skin irritations or need to handle hot equipment. 3. Closed toe shoes and long pants must be worn in the lab. Sandals and shorts are not allowed 4. Long hair must be tied back when working with open flames. CONDUCT INSIDE THE LABORATORY 1. Be familiar with your laboratory assignment before you come to lab premises. 2. Students are not allowed to enter inside the instrumentation room and chemical room without the permission of the instructor. 3. Eating, drinking, and smoking are strictly prohibited in the laboratory. 4. No unauthorized experiments are to be performed. 5. Never taste anything. 6. Never directly smell the source of any vapor or gas. Instead, through your cupped hand, waft a small sample to your nose. 7. Backpacks should be left on the lab shelves. Lab chemicals can destroy personal belongings. 8. Observe good housekeeping practices. Work areas should be kept clean at all times. 9. Know the locations and operating procedures of all safety equipment including fumehood, first aid kit, eyewash station, safety shower and fire extinguisher. 10. Be alert and always proceed with caution in the laboratory. 11. Dispose all chemical wastes properly. 13. Keep your hands away from your face, eyes, mouth and body while using chemicals. Wash your hands with soap and water after performing all experiments. Clean (with detergent powder), rinse, and dry all work surfaces and equipment at the end of the experiment. 14. At the end of the laboratory session, ensure that a) the main gas outlet valve is shut off; b) the water is turned off c) desk top, floor area, and sink are clean; and d) all equipment are clean and arranged properly PROPER HANDLING OF CHEMICALS AND EQUIPMENT 1. Consider all chemicals to be hazardous unless you are instructed otherwise. 2. Know what chemicals you are using. Carefully read the label twice before taking anything from a bottle. 3. Many common reagents are highly flammable. Do not use them anywhere near open flames. 4. Always pour acids into water. 5. If chemicals come into contact with your skin or eyes, flush immediately with abundant amounts of water and consult with your instructor. 6. Contact the stockroom technician for clean-up of mercury spills. COMMON LABORATORY PROCEDURES 1. CLEANING APPARATUS All apparatus must be washed with water and detergent, with the aid of a brush or sponge. 2. RECORDING DATA All data must be recorded first on a small notebook. Data should be organized and entered on the appropriate spaces in the manual. 3. MEASURING VOLUMES The graduated cylinder measures approximately volumes of liquids. “HOW TO READ VOLUMES IN A GRADUATED CYLINDER?” 4. PREPARING A FILTER PAPER FOR FILTRATION Filtration is done to separate a solid from a liquid. “HOW TO PREPARE THE FILTER PAPER FOR FILTRATION?” 5. DETECTING THE ODORS OF GASES “HOW TO DETECT THE ODOR OF GASES?” 6. TRANSFERRING SOLID CHEMICALS Transferring into another container can be done in any of the following ways: a. b. c. From the stock bottle, use a clean spatula. From stock bottle into a test tube, pour the granulated solid into a paper box and into the test tube. From wide-mouthed containers, large quantities of solids can be transferred by shaking the original container to loosen its contents before opening the cap. Tilt the bottle and rotate back and forth, without shaking, as you pour out its contents. 7. TRANSFERRING LIQUID CHEMICALS Place a stirring rod against the inner wall of a beaker. Allow the liquid to flow down the rod into the beaker. 8. DETERMINING THE MASS Electronic Top-Loading Balance. This can weigh up to three decimal places or up to the nearest thousandth of a gram.