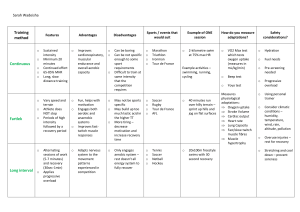
P.E AND HEALTH 11 PEH11FH-Ia-1 INTRODUCTION At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to: 1. Understand the benefits of aerobic, muscle strengthening activities. 2. Explain how aerobic, muscle strengthening, and bone strengthening activities work. 3. Appreciate the important of FITT in doing physical activities ACTIVITY 1 Let me think Make a table with two columns on a sheet of paper. List down the most frequent activities you do in the past and ones you do at present. When I was a kid I used to When I was a kid I used to 1. Playing tumbang preso 2. Jog 20 minutes PROCESSING QUESTION 1. What were the physical activities in your childhood that you still do today? Cite an example. 2. Do you know the benefits of the physical activities that you do? Can you site some of these benefits? AEROBIC ACTIVITIES Aerobic activities are also called “ cardio” exercise. Normally, these activities increase our heart and breathing rate. This cause us to sweat profusely and breathe harder. Our heart pumps blood more vigorously, causing oxygen to circulate throughout our body. This allows us sustain aerobic exercise for a few minutes. For example: Jogging, Running, Swimming and dancing Benefits : Help lower risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis. Guidelines for Aerobic Exercise 1. FREQUENCY- Always considers the number of aerobic exercise sessions per week. When doing cardio exercise, especially to lose weight, frequency is an important factor to make it more effective. Start cardio exercises for at least 3 days a week for the first few weeks, with not more than 2 days' rest between sessions. Afterwards, we can gradually increase the frequency of exercise to 5 days a week 2. INTENSITY -To be effective, aerobic exercises should be done in moderate intensity, that is, our heart rate should be 60 to 80% of our maximum heart rate 3. TIME - More time spent doing aerobic exercises means more calories burned and an increase in endurance. We can at least do 20 minutes per session at first, then gradually increase it to 60 minutes 4. TYPE - Running, jogging, sprinting, swimming, and playing contact sports such as basketball are some activities that we can do to improve our heart rate. It is also important to try diffirent exercises and activities to avoid boredom MUSCLE STRENGTHENING ACTIVITIES Muscle strengthening activities are exercises in which groups of muscles work or hold against a force or some weight. Muscle strengthening activities help build good muscle strength. When muscles do more work, It becomes stronger. Therefore, haing strong and healthy muscles enable us to perform everyday physical task. • Ex. push-ups, situps,squats, and lifting. 1|Page HOPE 11 BONE STRENGTHENING ACTIVITIES Bone growth is stimulated by physical stress brought about by physical activity. As skeletal muscles contract, they pull their attachment on bones causing physical stress. This consequently stimulates bone tissues, making it stronger and thicker. Such bone strengthening activities can increase density throughout our skeletal system. This is called bone hypertrophy. • Ex. running, skipping rope, and playing basketball can make our bones fit AEROBIC ACTIVITIES MUSCLE STRENGTHENING BONE STRENGTHENING ACTIVITIES ACTIVITIES During aerobic activity, Muscle contraction The muscles in Bone oxygen is delivered to occurs during a muscle growth is stimulated by the muscles in our body strengthening activity. the physical stress. As allowing us to sustain The repetitive skeletal muscle the physical activity for contractions during contract, they pull their few minutes exercise cause damage attachment on bones to muscle fibers. causing physical stress. However, these muscle This consequently fibers are ready to be stimulates bone tissue, repaired once they get making it stronger and damaged. There will be thicker. Such bone new muscle fibers strengthening activities produced to replace can increase bone and repair those fibers density throughout our that were damaged. skeletal system Activity 1 Answer the following questions bellow. 1. Differentiate aerobic, muscle strengthening, and bone strengthening activities. 2. How do these activities contribute to your overall health? Cite at least 5 benefits. 3. Explain the importance of Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type (FITT) in doing exercise * Send to my email kristinpablo5@gmail.com (1st week, Friday) PE AND HEALTH 11 PEH11FH-Ib-c-2 AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC PATHWAYS What do I need to know? Key Knowledge Introduction to the characteristics of aerobic and anaerobic pathways (with or without oxygen) and their contribution to movement and dominant fiber type associated with each pathway Key Skills Identify the dominant energy pathway utilized in a variety of aerobic or anaerobic activities determined by the intensity and duration of the activity. Collect, analyses and 2|Page HOPE 11 report on primary data related to responses to exercise and anaerobic and aerobic pathways FOOD FUELS AND THE THREE ENERGY SYSTEMS 1. Carbohydrates (CHO) – Preferred source of fuel during exercise (Glycogen) 2. Fat – Concentrated fuel used during rest and Energy prolonged sub-maximal exercise. 3. Protein – Used for growth and repair (Negligible use during exercise) ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE Food fuels and the three energy systems Rest (Aerobic) Fat and glucose are the preferred fuels During Exercise 1. Short duration / high intensity – Anaerobic systems used using carbohydrate 2. Long duration / low intensity – Aerobic system using carbohydrates. However, fats are used once glycogen stores are depleted Maximal and Sub-maximal activity CONTRIBTION OF CARBOHYDRATES, FATS AND PROTEIN TO ENERGY PRODUCTION Energy demands- intensity Low intensity: ATP requirements are met aerobically using the aerobic system. High Intensity: Explosive movements require instant supply of ATP which can’t be met aerobically; therefore the ATP-PC and lactic acid systems need to be used anaerobically. Aerobic Anaerobic Intensity increase Carbohydrates contribution Storage (Based on 80kg person) Muscle glycogen – 400 g 3|Page HOPE 11 Liver glycogen – 100 g Normal contribution to diet is 55 to 60%CHO Carbohydrate loading80%CHO intake is used for endurance activities. Carbohydrates rich diet, Increases glycogen stores Gycologen is for rebuilding ATP CHO preferred fuel over fats during exercise due to requiring less oxygen to release enrgy Athletes need to be aware of their dietary intakes of CHO. Excess CHO is converted to fat. Fats contribution Storage of fats At rest Adipose tissue 50% of energy supplied by fats Triglycerides Oxygen demand is easily met to (broken in free tiny fatty) Aerobic metabolism of fat is Slow as it require more oxygen that CHO Add stress to the oxygen system burn fats Benefits of fats Large energy store Transport medium for fat soluble transport system vitamins ATP yield is much higher than fat 460 Obesity, heart disease etc molecules) in comparison of glucose 36) Protein contribution Role of protein (Amino acids) in the body; Growth and repair Speed up reactions in the body (Enzymes) Produces hormones and antibodies Protein and exercise Not used as a fuel, therefore low priority. Only used in extreme circumstances Normal diet contains enough protein (15%).Excess protein can lead to; Less intake of CHO Increase in fat intake from animal products Increase in fluid waste PROLONGED ENDURANCE EVENTS During prolonged endurance events such as marathon running and triathlons Body uses a combination of CHO and fats. Trained athletes are able to ‘spare’ glycogen and use free fatty acids. Fats cannot be used alone as a fuel (poor solubility in the blood). ‘Hitting the wall’ occurs when glycogen stores are depleted. This is called ‘hypoglycaemia’ AEROBIC EXERCISE Aerobic exercise includes lower intensity activities performed for longer periods of time. 4|Page HOPE 11 Activities like walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling require a great deal of oxygen to make the energy needed for prolonged exercise. The energy system that is used in aerobic exercise is called the aerobic system. It can also be called ‘oxygen system’ or the ‘aerobic glycolysis system’ ANAEROBIC EXERCISE The term "anaerobic" means "without air" or "without oxygen." Anaerobic exercise uses muscles at high intensity and a high rate of work for a short period of time. Anaerobic exercise helps us increase our muscle strength and stay ready for quick bursts of speed. Examples of anaerobic exercise include heavy weight lifting, sprinting, or any rapid burst of hard exercise. These anaerobic exercises cannot last long because oxygen is not used for energy and fatiguing metabolic by-products. There are two energy systems which use the anaerobic pathways; ATP-PC and the Lactic Acid systems COMMON MISTAKES The three energy systems do not turn on and off like a traffic light. They are always in operation – the relative contribution of each system varies depending on factors such as intensity, type of activity and duration. Activity 2 1. Use a Venn Diagram for the examples of aerobic and anaerobic exercises *send to my email 2nd week (Friday) PE AND HEALTH 11 LESSON Three PEH11FH-Id-3 HEALTH RISK IN OUR LIFESTYE 1. Eating habits 2. Sleep 3. Stress management 4. Hobbies SLEEPING HABITS WHY LACK OF SLEEP IS BAD FOR YOUR HEALTH Effects of lack of sleep, such as feeling grumpy and not working at your best. But did you know that sleep deprivation can also have profound consequences on your physical health? Estudyante life: it’s either kulang sa tulog o kulang sa aral….LEARN TO MANAGE YOUR TIME If you don’t sleep you will experience the fatigue, short temper and lack of focus that often follow a poor night’s sleep. In occasional night without sleep makes you feel tired and irritable the next day. After continuous sleepless nights, the mental effects become more serious. Your brain will fog, making you difficult to concentrate and make decisions. You’ll start to feel down, and 5|Page HOPE 11 may fall sleep during the day. Your risk of injury and accidents at home, work and on the road also increases. PAGHIHIKAB IS A BAD SLEEPING EFFECT OVERSLEEPING effects WHY OVERSLEEPING IS BAD FOR YOUR HEALTH? Sleep plays important role in our brain, as the brain clears our waste byproducts, balance neurotransmitters and processes memories at rest. But too much may have effect on mood and mental health. Cognition, degenerative disease and depression More time in bed linked with more frequent waking after sleep and reduce sleep efficiency. Fatigue causes longer sleep and sleeping more can make people feel more lethargic Underlying disease is obstructive sleep apnea, depression, coronary disease, and generally failing health HOW MUCH DO WE REALLY NEED? Sleep is a vital indicator of overall health and well-being. We spend up to one-third of our lives asleep, and the overall state of our "sleep health" remains an essential question throughout our lifespan. EATING HABITS Things that we eat can influence your risk of dying from heart disease, sroke, or type 2 diabetes. Eating habit is one of the great influences to improve our health HEALTHY FOR GOOD IS A REVOLUTIONARY MOVEMENT TO INSPIRE YOU TO CREATE LASTING CHANGE IN YOUR HEALTH AND YOUR LIFE, ONE SMALL STEP AT A TIME. THE APPROACH IS SIMPLE: EAT SMART. ADD COLOR. MOVE MORE. BE WELL EATING HABITS We all know that healthy eating plan includes vegetables, fruits, whole grain and fatfree or low-fat dairy products. But a healthy diet also includes lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts. Because it limits saturated and Trans fats, sodium, and added sugar Lot of factors affect your risk of death from heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These are known as cardio metabolic diseases The risk of death from the 3 said diseases was higher for those who consumed too much sodium, processed meat, sugar-sweetened beverages, and unprocessed red meat Risk of death was also higher to those who didn’t eat enough nuts and seeds, seafood omega-3 fats, vegetables, fruits, whole grain, or polyunsaturated fats According to analysis, nearly half (45%) of deaths in 2012 from this 3 diseases was associated with too much or too little of these dietary factors. Dr. David Goff Heart Disease & Public health expert The study establishes the number of cardio metabolic deaths that can be linked to eating habits. Dr. David Goff Heart Disease & Public health expert. TECHNIQUES FOR A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE ARE EAT SMART • MOVE MORE • BE WELL EAT SMART 6|Page HOPE 11 Healthy eating starts with healthy food choices. You don’t need to be a chef to create nutritious, heart-healthy meals your family will love. Learn what to look for at the grocery store, restaurants, your workplace and any eating occasion. Make healthy, delicious choices wherever and whenever you eat. HEALTHY NA YUMMY PA! MOVE MORE A good starting goal is at least 150 minutes a week, but if you don’t want to sweat the numbers, just move more! Find forms of exercise you like and will stick with, and build more opportunities to be active into your routine. Infuse more movement in your life for optimal health. GALAW GALAW DIN PAG MAY TIME! BE WELL How do you want to live? Along with eating right and being active, real health includes getting enough sleep, practicing mindfulness, managing stress, keeping mind and body fit, connecting socially, and more . Create balance, vitality and wellbeing through SELF CARE. AYUS AYUS DIN PAG MAY TIME! ACTIVITY ENUMERATE AT LEAST 3 POSSIBLE DISEASES THAT WE CAN GET IN POOR EATING HABIT. LIST DOWN THE 3 TECHNIQUES OF A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE Makes an Itinerary of activities every day. PEH11FH-Ie-4 and PEH11FH-If-5 STRESS MANAGEMENT WHAT IS STRESS? Mental or emotional tension or strain resulting from adverse or very demanding circumstances FACTS ON STRESS Stress helps the body to prepare to face danger. Symptoms can be both physical and psychological. • Short-term stress can be helpful, but long-term stress is linked to various health conditions. • We can prepare for stress by learning some self-management tips Why is it important to manage stress? If you’re living with high levels of stress, you’re putting your entire well-being at risk. Stress wreaks havoc on your emotional equilibrium, as well as your physical health. It narrows your ability to think clearly, function effectively, and enjoy life Why is it important to manage stress? Effective stress management, on the other hand, helps you break the hold stress has on your life, so you can be happier, healthier, and more productive. The ultimate goal is a balanced life, with time for work, relationships, relaxation, and fun—and the resilience to hold up under pressure and meet challenges head on. But stress management is not one-size- fits-all. That’s why it’s important to experiment and find out what works best for you. The following stress management tips can help you do that COMMONLY SOURCES OF STRESS School demands and frustration. 7|Page HOPE 11 Negative thoughts and feeling about Changes in their bodies Problems with friends and/or peers at school unsafe living environment/neighborhood separation or divorce of parents Chronic illness or severe problems in the family. Death of a loved one. Taking too many activities. Having too high expectation. Family and financial probl TEENS CAN DECREASE STRESS WITH THE FOLLOWING BEHAVIORS AND TECHNIQUES: Exercise and eat regularly. Decrease negative self talk. Avoid excess caffeine intake Learn to feel good about doing which can increase feelings of a competent or good enough anxiety and agitation. job rather than demanding Avoid illegal drugs, alcohol and perfection. cigarette. Take a break from stressful Learn relaxation exercises situation. Develop assertiveness training Build a network of friend who skills. help you cope in a positive way Rehearse and practice situation which causes stress. EFFECTIVE STRESS MANAGEMENT TOOL Minsan kakaisip mo sa FUTURE, Change your mindset from Hindi mo na naeenjoy yung Problem TO CHALLENGE Demoralizer TO MOTIVATOR present. Pressure TO OPPORTUNITY Overwhelming TO MANAGEABLE TOP 10 EMERGENCY STRESS STOPPERS 1. Count to 10 before you speak or react 2. Take a few slow, deep breaths until you feel your body un-clench a bit 3. Go for a walk, even if it’s just to the restroom and back. It can help break the tension and give you a chance to think things through 4. Try a quick meditation or prayer to get some perspective 5. If it’s not urgent, sleep on it and respond tomorrow. This works especially well for stressful emails and social media trolls 6. Walk away from the situation for a while, and handle it later once things have calmed down 7. Break down big problems into smaller parts. Take one step at a time, instead of trying to tackle everything at once 8. Turn on some chill music or an inspirational podcast to help you deal with road rage 9. Take a break to pet the dog, hug a loved one or do something to help someone else 10. Work out or do something active. Exercise is the great antidote for stress. STRESS-BUSTING ACTIVITIES 1. Doing things you enjoy is a natural way to relieve stress and find your happy place. Even when you are down you may find pleasure in simple things like going for a walk, catching up with friends or reading a good book 2. MAKE ART Draw, color, paint or play a musical instrument 8|Page HOPE 11 3. WORK ON SCRAPBOOK Making scrapbook and photo album to focus on good memories 4. READ A BOOK Reading short story or magazine 5. MEET A FRIEND Meet your friend for coffee or meal 6. PLAY YOUR FAVORITE SPORTS Play your favorite sports like, chess, badminton, etc 7. DO A YOUR RELAXING HOBBY Like sewing, knitting, or making jewelry 8. PLAY -Play with kids or pets – outside if possible 9. Listen to music or watch an inspiring performance 10. Take a relaxing bath and feel the stress wash away. Activity 4 1. List down all the reason of your stress and how you conquer it. Note: Review and be ready to your preliminary examination. God bless. Prepared by: MA. KRISTINA B. PABLO, LPT Subject Teacher 9|Page Contact # : 0953 165 2827 Email : kristinapablo5@gmail.com FB Account : Kristina Buenaventura Pablo HOPE 11