Lesson 02 - Filled in - Synthesis decomposition and combustion reactions - student
advertisement

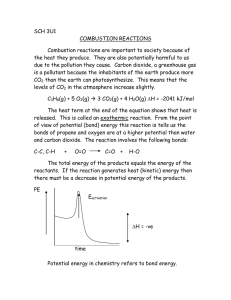
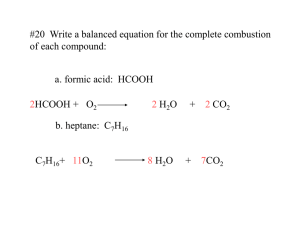
Types of Reactions – Part I 1. Synthesis Reactions • Formation of new product Different Conditions • Element + Element → Compound o Ex. N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) • Element + Compound → More complex compound o Ex. PCl3(l) + Cl2(g) → PCl5(s) • Compound + Compound → More complex compound o I. A Non-metal Oxide Reacting with Water → Acid o Ex. CO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2CO3(aq) o II. A Metal Oxide Reacting with Water → Base o Ex. Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) 2. Decomposition Reactions • Breakdown of a molecule into simpler components Different Conditions • Binary Compound → Element + Element o Ex. 2NO(g) → N2(g) + O2(g) • Metal Nitrate → Metal Nitrite + Oxygen Gas o Ex. 2NaNO3(s) → 2NaNO2(s) + O2(g) • Metal Carbonate → Metal Oxide + Carbon Dioxide o Ex. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) • Metal Hydroxide → Metal Oxide + Water o Ex. Ca(OH)2(s) → CaO(s) + H2O(l) 3. Combustion Reactions • The reaction of a substance with oxygen to produce oxides and energy A) Complete Combustion • Burning of a hydrocarbon (Only H & C) to form only water and carbon dioxide Ex. CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) • Other substances undergo complete combustion to form stable oxides. Ex. Mg (s) + O→ MgO(s) B) Incomplete Combustion • Burning of a hydrocarbon to form carbon dioxide, water along with carbon monoxide and carbon (caused by insufficient oxygen). 4CH4 (g) + 6O2 (g) → C (s) + 2CO (g) + CO2 (g) + 8H2O (g) Practice! For each of the chemical reactions, predict the products and balance the chemical equation: a) K+ Br2 → b) SO3(g) + c) Ni2O3 → d) LiNO3(s)→ e) C3H8 + O2 → (complete) f) C3H8 + O2 → (incomplete) H2O(l) →