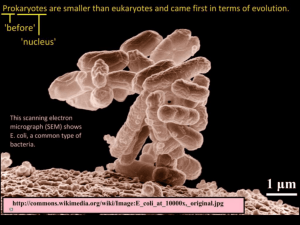
ODESSA NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Microbiology, virology and immunology department MEDICAL FACULTY MODULE 2. SPECIAL MICROBIOLOGY LECTURE №18 PATHOGENIC ENTEROBACTERIA. ESCHERICHIA. SHIGELLA. Odessa-2013 MECHANISM OF INTERACTION BETWEEN CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF ACUTE ENTERIC INFECTIONS WITH INTESTINAL EPITHELIUM Тype of interaction Causative agent 1 type EТEC 2 type 3 type 4 type Mechanism of pathogenic action Multiplication on the surface of intestine without damage of intestinal epithelium Multiplication on the epithelium of intestine EPEC EHEC and colon with destruction of microvilli, damage of apical surface of epithelium EIEC Shigella Penetration and multiplication in epithelial cells of colon mucous membrane, cytotoxic injury and d estruction of epitheliocytes Transcytosis of intestinal epithelium through Salmonella the М-cells with infection of Payer’s patches Yersinia with subsequent multiplication in the macrophages CLINICAL AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF E.COLI E. coli. Gram stain Colonies of lactose positive and lactose negative bacteria Antigenic structure of Еscherichia coli Nutrient media 1.Endo medium: MPA, lactose, fuchsine, decolorized by sodium sulfite 2. Ploskirev medium MPA, bile salts, brilliant green, iodine, sodium thiosulfate, lactose, neutral red 3. McConkey agar 4. Bismuth-sulfite agar 5. Bile broth 6. Selenite broth BASIC GROUPS OF DIARRHEAL E.COLI PATHOGENIC GROUPS SEROGROUPS Entheropathogenic E.coli (EPEC) O26, O55, O86, O111, O114, O119, O125, O126, O127, O128, O142 Entherotoxigenic E.coli (EТEC) O6, O8, O15, O25, O27, O63, O78, O115, O148, O153, O159, O167 Entheroinvasive E.coli (EIEC) O28, O112, O124, O136, O143, O144, O152, O164 Entherohemorrhagic E.coli (EHEC) О26, О55, О111, О113, О117, О145, O157 Entheroadhesive E.coli (EAEC) О3, О15, О44, О77, О86, О111, О127 DISEASES, CAUSED BY DIARRHEAL E. coli Agent ETEC with cholera like toxin. Small intestine is affected Virulence factor Disease Pili, thermolabile (analog of cholera toxin) and thermostable toxins; factors Cholera like diarrhea of adhesion and colonization (CF) of E. in adults and children coli ACTION OF THERMOLABILE TOXIN (LT) OF E. coli THERMOSTABLE TOXIN(ST) Activates guanylate cyclase, Accumalation of cGMP (guanylatemono phosphate), loss of ions and water DISEASES, CAUSED BY DIARRHEAL E. coli Agent EIEC with predominance of invasion factors and subsequent destruction of intestinal epithelium Virulence factor Surface proteins, coded by plasmid, and determine penetration and destruction of intestinal epithelium Protein adhesine of external EPEC with destruction of membrane, coded by plasmid, microvilli, damage of apical protein of external surface of intestinal epithelium and membrane - intimine, coded by chromosomal gene Pilli, Shiga like toxin (SLT, Vero EHEC,for example, Е. coli destroying endothelium 0157:Н7, with predominance of toxin) of small vessels, protein of hemorrhagic factor,causing membrane - intimine, hemolytic-uraemic syndrome. external coded by chromosomal gene Colon and capillaries are and hemolysine, coded by damaged. plasmid 0157 EAEC with persistance, causing dehydratation od children. Plasmid coded aggregation, Adhesion on Hep-2 cell line. prevent adsorption of water Damage of intestine. Disease Dysentery-like disease (stool with blood) Diarrhea in children of 1-st year Hemorrhagic colitis (diarrhea with blood); hemolyticuraemic syndrome Diarrhea in children PENETRATION OF SHIGELLA (and EIEC) INTO INTESTINE Pay attention on «roughing» of М-cell membrane and surround bacterial cell. Penetration of salmonella passes by the same way. SHIGELLA M-CELL PATHOGENESIS of infection by E.coli O157: H7 Enterohemorrhagic E.coli 0157: H7(violet) attach to the intestinal epithelium, destroy microvilli and form pedestal (yellow), which can favorite spreading of shigella on adjacent cells. Pure culture of Shigella flexneri CLASSIFICATION OF SHIGELLA ON ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE Sero types Lactose Mannitol 1 -15 – – B – Shigella flexneri 1-9 – + C – Shigella boydii 1-19 – + D – Shigella sonnei 1 (+) late + GROUP А – Shigella dysenteriae Gram stain Immunofluorescence M cells. Present in Payer’s patches of intestine, provide transport of antigens from intestinal tract for contact with the cells of immune system M-cells of payer plaque. Pay attention on microvilli of surrounding epithelial cells Pathogenesis of Shigellosis. This sequence shows the sequence of infection of the intestinal wall. The bacterium attaches to an M cell of the epithelial wall located over a Peyer’s patch. This is a region adapted to facilitate transfer of antigens across the intestinal mucosa M-cells assures contact between antigens from intestine and cells of immune system VIRULENCE FACTORS OF Shigella Factors Biological effect IраBDEinvasines Ipa (invasion plasmide апtigen) – invasines — proteins of external membrane of bacteria, which attach to apical membrane of M-cells; cause apoptosis of epitheliocytes, lysis of cellular membranes, favorite to intra and intercellular spreading of Shigella Proteinic exotoxin (Shiga toxin) Cause damage of epithelium, injury of kidney with development of hemolytic-uraemic syndrome, injury of CNS and methabolic processes Endotoxin General intoxication, increasing of intestinal peristalsis SCHEME OF BACTERIOLOGICAL EXAMINATION IN ESCHEROCHIOSIS AND SHIGELLOSIS 1 stage Sampling and inoculation of material on selective and differential media Endo medium Coloured colonies FECES Ploskirev media Colourless colonies 2 stage Choose of suspicious colony and Agglutination with material Agglutination with subinoculation on Ressel’s from 10 colonies and mixture material from colonies medium of ОК-serums and mixture of CONCLUSION antiShigella serums 3 stage Examination of isolated culture for identification 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Smear, Gram staining Subinoculation on Hiss media AT on the glass with mixture of antiserums AT with type specific antiserums Sensitivity to antibiotics 4 stage Registration of properties. Identification of isolated culture FINAL CONCLUSION