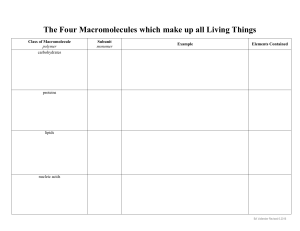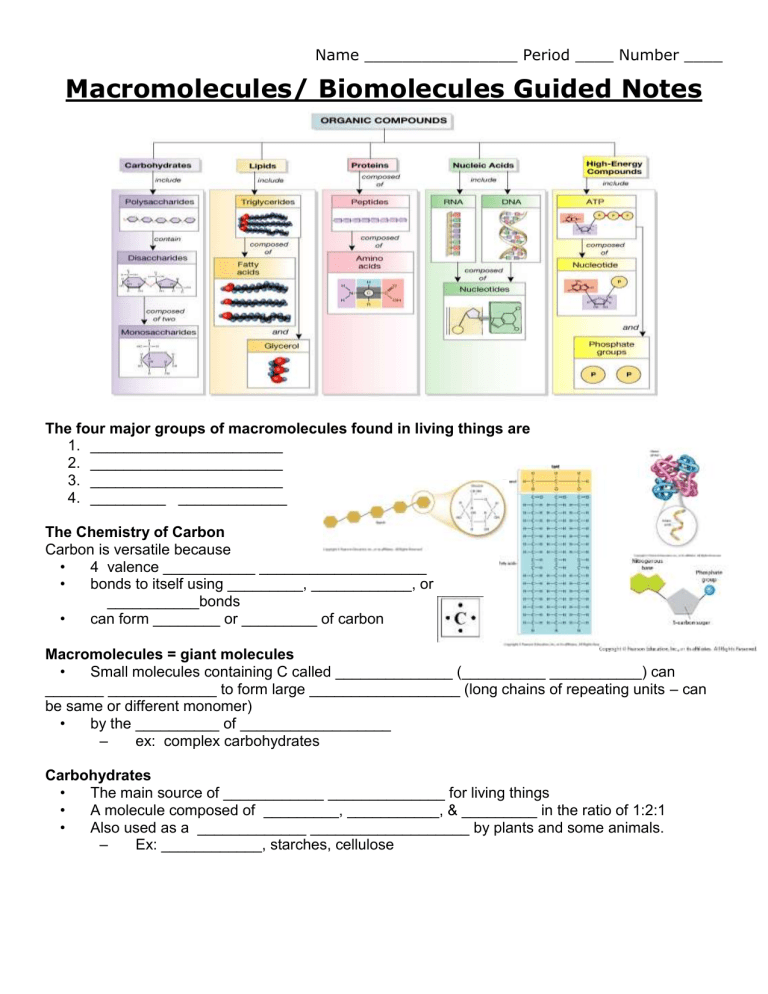
Name ________________ Period ____ Number ____ Macromolecules/ Biomolecules Guided Notes The four major groups of macromolecules found in living things are 1. _______________________ 2. _______________________ 3. _______________________ 4. _________ _____________ The Chemistry of Carbon Carbon is versatile because • 4 valence ___________ ____________________ • bonds to itself using _________, ____________, or ___________bonds • can form ________ or _________ of carbon Macromolecules = giant molecules • Small molecules containing C called ______________ (__________ ___________) can _______ _____________ to form large __________________ (long chains of repeating units – can be same or different monomer) • by the __________ of __________________ – ex: complex carbohydrates Carbohydrates • The main source of ____________ ______________ for living things • A molecule composed of _________, ___________, & _________ in the ratio of 1:2:1 • Also used as a _____________ ___________________ by plants and some animals. – Ex: ____________, starches, cellulose Sugars as Carbohydrates • _________ sugar molecules = _______________________ – Ex: glucose • ______ sugar molecules = _______________________ – Ex: sucrose • ______________ of simple sugars = ____________________ – Ex: ____________, glycogen Lipids • Generally ______ ______________ in H2O (will not dissolve) • used to _________ __________ _________ __________ • part of biological _________________ • waterproof coverings • made of 2 types of monomers – _________ _______ + ________ ______ tails ■ ex: fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Fatty Acids • ________ fatty acids = maximum # of Hydrogen atoms no double bonds ○ Ex: _______ __________ • ________________ fatty acids = at least one double or triple bond between C atoms ○ Ex: _______ __________ Nucleic Acids • __________ & _____________ genetic _______________ • made of ____________ that include 3 parts – 5C __________ - ___________ (RNA) or _______________ (DNA) – a __________________ group – a nitrogenous _____________ – ex: DNA, RNA Proteins • made of a _____________ of _____________ that are made of _________ ________ • fold into __________ ______________ based on use or job • control the ________ of chemical reactions • • _____________ substances into or out of the cell fight disease & create muscle tissue