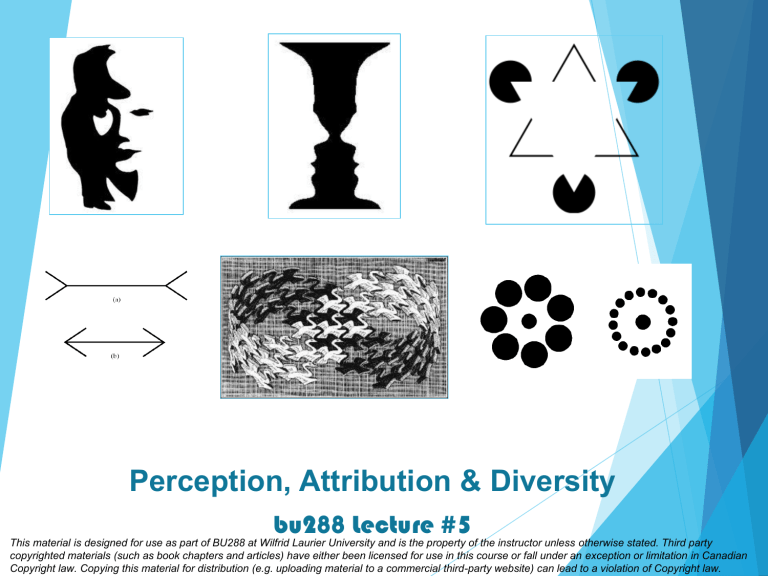
Perception, Attribution & Diversity bu288 Lecture #5 This material is designed for use as part of BU288 at Wilfrid Laurier University and is the property of the instructor unless otherwise stated. Third party copyrighted materials (such as book chapters and articles) have either been licensed for use in this course or fall under an exception or limitation in Canadian Copyright law. Copying this material for distribution (e.g. uploading material to a commercial third-party website) can lead to a violation of Copyright law. A.Boey Perceptions Biases Stereotyping Attribution theory 2 Perception Attribution Diversity What’s new today The process of interpreting the messages of our senses to provide order and meaning to the environment. Our actions are based on our interpretation of reality from our perceptual system, rather than on reality itself. A.Boey 3 Perception Attribution Diversity What Is Perception? A.Boey 4 Perception Attribution Diversity Factors that Influence Perception A.Boey Does perception influence how we see ourselves? How? 5 Perception Attribution Diversity Target: Ourselves The goal of our perceptual system: SHORTCUTS: helpful but can lead to biases We not only make enough fast and good mistakes about our visual world, we make lots of mistakes when we judge other people A.Boey 6 Perception Attribution Diversity Perception: Inside the Brain Why first impressions are so important! A.Boey 7 Perception Attribution Diversity Bruner’s Model Primacy Recency Reliance on Central Traits Implicit Personality Theories Projection These biases can lead to inaccurate perceptions of another person Stereotyping A.Boey 8 Perception Attribution Diversity Biases in Person Perception Possible selection biases: Primacy, recency and contrast effects Possible performance rating biases: Leniency Harshness Central tendency Halo effect Similar-to-me effect A.Boey 9 Perception Attribution Diversity Person Perception in HR There are three specific aspects to stereotyping: We distinguish some category of people We assume that the individuals in this category have certain traits We perceive that everyone in this category possesses these traits Perception Attribution Diversity Stereotyping People can evoke stereotypes with incredibly little information. Stereotypes help us develop impressions of ambiguous targets. Most stereotypes are inaccurate, especially when we use them to develop perceptions of specific individuals. Perception Attribution Diversity Stereotyping Several factors work to reinforce inaccurate stereotypes: 1. Even incorrect stereotypes help us process information about others quickly and efficiently. 2. Inaccurate stereotypes are often reinforced by selective perception. Perception Attribution Diversity Why Do Stereotypes Persist? Attribution is the process by which we assign causes or motives to explain people’s behaviour. About understanding WHY Dispositional (internal) or situational (external) factors. Remember: could be both. Perception Attribution Diversity Attribution: Perceiving Causes and Motives A supervisor wants to know why a mistake was made was it because someone is incompetent, or made an honest mistake? A friend wants to know why another friend stood them up was it because they don’t value you as a friend, or was it a one-time situation? A professor wants to know why a student missed class are they low on conscientiousness, or was it a legitimate illness? An employee wants to know why their boss is being nice to them was it because they are a nice person, or because the organization wants them to act that way? A.Boey 14 Perception Attribution Diversity Attributions: Why Do they Matter? Observe someone’s behaviour Ask yourself: Was the person responsible for that, or was it the result of situational influences? Person responsible: You’ve made a dispositional attribution A.Boey Situation responsible: You’ve made a situational attribution 15 Perception Attribution Diversity Attributions: The Process According to attribution theory, when we are trying to figure out the cause of someone’s behaviour, we act like CSI detectives and consider three pieces of evidence (called cues): 1. Does this person consistently act this way? 2. Is this behaviour similar to other people in this situation? 3. Does this person act this way across situations? A.Boey 16 Perception Attribution Diversity Attributions: The Theory THREE CUES: 1. Consistency: Does this person consistently act in this way? If yes (high consistency), we believe the person was responsible If no (low consistency), we believe the situation was responsible 2. Consensus: Is this behaviour similar to other people in this situation? If no (low consensus), we believe the person was responsible If yes (high consensus), we believe the situation was responsible 3. Distinctiveness: Does this person act this way across situations? If yes (low distinctiveness), we believe the person was responsible A.Boey If no (high distinctiveness), we believe the situation was responsible 17 Perception Attribution Diversity Attributions: The Theory Three employees (from three different companies) are absent from work today. Why? Consider the evidence. Inference About Person: Delinquent ? (Inconclusive) ? (Inconclusive) How consistent is the behaviour in this situation (Is he/she absent a lot?) A.Boey Is the behaviour similar to others in that situation? (Are others absent a lot?) Is this distinctive for this person? (Is he/she absent in other situations?) What is the likely cause of this behaviour? What does that tell me about this person? 18 Perception Attribution Diversity Attributions: An example We often do not perceive and weigh consistency, consensus and distinctiveness cues accurately Attribution Biases: Fundamental attribution error Actor-observer effect Self-serving bias A.Boey 19 Perception Attribution Diversity Attribution Biases “The Danger of a Single Story” TED talk by Chimamanda Adichie (http://www.ted.com/talks/chimamanda_adichie_the_danger _of_a_single_story.html) A.Boey 20 Perception Attribution Diversity Diversity (Watch this TED talk!) perceptual biases and the illusions that play tricks on our mind We are capable of (more) accurately perceiving things if we are really motivated, but most of the time we make errors automatically To overcome biases: Be motivated to put in the effort, question the judgments you make, don’t rely on your perceptions or your memory A.Boey 21 Perception Attribution Diversity We can’t just take a red pill – we have to live with our