Plate Tectonics: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Boundaries
advertisement

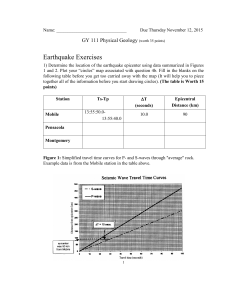
Plate Tectonics IMPLOAR 1. If you were given data indicating the arrival time of P-waves and S- waves recorded from three seismic stations, which of these can you possibly determine? a. damage at the hypocentre b. epicenter of an earthquake c. damage at the epicenter d.intensity of an earthquake 2. From the seismograph, what is being described when measuring the distance to the epicentre? a. the arrival time of surface wave b. the difference in the arrival times of P and S waves c. the ratio of the amplitude of the largest P and S waves d. the speed of the surface waves 3. Which of following is NOT a basis of scientists in dividing Earth’s lithosphere into several plates? a. Seismicity (occurrence of earthquake) b. Climate c. Volcanism d. Mountain formation 4. You were asked to locate the epicentre of a recent earthquake. Which CORRECT sequence of events should you follow? I. Determine the difference in the arrival time of S and P waves II. Use the triangulation method to locate the center III. Obtain data from three different seismological stations IV. Determine the distance of the epicentre from the station a. I, III, II, IV b. III, I, IV, II c. III, IV, I, II d. IV, II, I, III Recall: Sci-Voc Compare and Contrast: CLOANTTNIEN TRUSC and OCICNEA RUCTS THRESPLIEHO EAPLT and STECCITNO EPLTA P SAWVE and S VASEW CPEIETREN and CUFSO MSAEIRSGOM and HOMGSRIEAPS Plate Tectonics LITHOSPHERE PLATE and TECTONICS PLATE Lithosphere Crust Continental and Oceanic Upper Mantle (Asthenosphere) CONTINENTAL CRUST and OCEANIC CRUST EPICENTER and FOCUS P WAVES and S WAVES SEISMOGRAM and SEISMOGRAPH What are the basis of scientists in dividing the lithosphere in this manner? IMPLOAR 1. How will you compare the distribution of mountain ranges with the distribution of earthquake epicenters and volcanoes? A. They are not randomly distributed B. Almost all lie on the same location C. They are randomly distributed D. They are scattered everywhere 2.Volcanoes occur in similar locations to earthquakes, and are common along plate boundaries. What do you call to the location where you can find sixty percent of volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Ocean? a. The hot zone b. The volcano zone c. The ring of fire d. The hot spot 3. A magnitude 6.1 earthquake rocked parts of Luzon in April 22, leaving at least 9 people dead in the province of Pampanga. In a bulletin, Phivolcs said the epicenter of the earthquake was located in Castillejos, Zambales. Why do you think there is greater destruction in the province of Pampanga compared to Castillejos, Zambales which is the epicenter of the earthquake? a. Earthquake destruction does not only depend on location of the epicenter but on geological and structural condition of the place. b. Earthquake destruction depends on the location of the place. c. Deeper earthquakes are less damaging in the epicenter. d. Earthquake that hits in a populated area is more likely to do damage than one that hits an unpopulated area 4. Refer to the illustration below. Identify which will be the most accurate location of epicenter of the earthquake using the triangulation method. D C A B Act. 1: Find the center. Objective: Locate the epicenter of an earthquake using the triangulation method Materials: • hypothetical records of earthquake waves • Philippine map • drawing compass and ruler Procedure: 1. Study the data showing the difference in the arrival time of P-wave and S-wave on three seismic recording stations 33.1 40.5 26.5 2. Compute the distance of the epicenter from each of the stations using this formula: 3. Choose one of the recording stations and measure the computed distance on the map scale (the scale of the map in Figure 3 is 1.5 cm: 200 km). Distance on the map (cm) = Distance of epicenter from the station (km) X 1.5 cm 200 km Set your compass for that computed distance. 4. Center your compass on the station you have chosen. Draw a circle. 5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 for the rest of the stations. You should get three circles that intersect or nearly intersect at a point. This intersection is the epicenter. Q1. Where is the epicenter of this hypothetical earthquake? Q2. What difficulty will you encounter if you only have data from two recording stations? The distance-time graph above shows that S-P interval is about 10 mins. Q3. What is the distance of the epicenter from the seismic station? Q4. What do you think is the importance of determining the epicenter of an earthquake What are the basis of scientists in dividing the lithosphere in this manner? Locating Epicenter: Triangulation Locating Epicenter: Triangulation Philippine Monitoring Stations Seismologists P waves travel faster than S wave You can determine the epicenter of an earthquake using difference of arrival time of P-waves and Swaves recorded from three seismic stations Triangulation method is used to determine the exact location of the epicenter by: 1. Obtaining data from three different seismological stations 2. Determining the difference in the arrival time of S and P waves 3. Determining the distance of the epicentre from the station 4. Using the triangulation method to locate the center Remember: Determining the location of earthquake epicenters plays a vital role in laying the foundations of plate tectonics. But.... How do you think early geologists used the plotted positions of earthquake epicenters throughout the world in conceptualizing crustal movements? Activity 2 Let’s Mark the Boundaries Objectives: • Describe the distribution of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts. • Determine the scientific basis for dividing the Lithospheric plates. Materials: •List of earthquake distribution in the world • List of active volcanoes of the world • List of Mountain ranges of the world • plastic sheet used for book cover, • plastic sheet used for book cover, same size as a book • marking pens Procedure: 1. Study earthquake distribution around the world. Make a dot for each country then connect the dots using a marking pen on the plastic sheet. List of earthquake distribution in the world (21) Argentina Portugal Canada China Egypt Alaska Iceland India Indonesia Japan Mexico New Zealand Hawaii Philippines Russia South Africa South Korea Spain Taiwan United Kingdom USA Q1. How are earthquakes distributed on the map? (Random, almost lie on the same plane, Scattered) Q2. Where are they located? ( Near the ocean, Midcontinent) Q3. Where are there no earthquakes? (Give atleast 1 country) Q4. Why is it important for us to identify areas which are prone to earthquakes? List of active volcanoes (21) Namibia Canada China Kenya Alaska Iceland India Indonesia Japan Hawaii Mexico New Zealand Philippines Russia South Africa South Korea Spain Taiwan UK USA Chile 2. Make a dot for each country then connect the dots using a marking pen on the plastic sheet. Q5. How are volcanoes distributed? (Random, almost lie on the same plane, Scattered) Q6. Where are they located? ( Near the ocean, Mid-continent, in the ocean) Q7. Based on the map, mention a country that is unlikely to experience a volcanic eruption. (Give atleast 1 country) 3. Make a dot for each country then connect the dots using a marking pen on the plastic sheet. List of mountain ranges (20) Argentina Iceland Canada China Kenya Alaska India Indonesia Japan Hawaii Mexico New Zealand Philippines Russia South Africa South Korea Spain Taiwan UK USA 4. Observe the traces you have gathered. Q8. How would you relate the distribution of mountain ranges with the distribution of earthquake epicenters and volcanoes? (Random, almost lie on the same plane, Scattered) Q9. What feature is evident along the pacific ocean, where there are concentration of active volcanoes? Q10. What do you think is the basis of scientists in dividing Earth’s lithosphere into several plates? The plates are in constant motion. As they interact along their margins, important geological processes take place, such as the formation of mountain belts, earthquakes, and volcanoes. Seatwork No. 1 1. If you were given data indicating the arrival time of P-waves and S- waves recorded from three seismic stations, what can you possibly determine? 2. From the seismograph, what is being described when measuring the distance to the epicentre? 3. What are the basis of scientists in dividing Earth’s lithosphere into several plates? 4. What are the steps in finding the epicenter of an earthquake using a triangulation method? ( 4pts) 5. Compare the distribution of mountain ranges with the distribution of earthquake epicenters and volcanoes? 6. What do you call to the location where you can find sixty percent of volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Ocean? 7. Give one factor that can cause heavy damage in a place during an earthquake. 8. What is the point underground where the earthquake begins and seismic waves are propagated (created). 9. What is the difference between continental and oceanic crust? (2 pts) 10. Describe the basic drill during an earthquake. Why do you think there is greater destruction in the province of Pampanga compared to Castillejos, Zambales which is the epicenter of the earthquake? a. Earthquake destruction does not only depend on location of the epicenter but on geological and structural condition of the place. b. Earthquake destruction depends on the location of the place. c. Deeper earthquakes are less damaging in the epicenter. d. Earthquake that hits in a populated area is more likely to do damage than one that hits an unpopulated area 4. Refer to the illustration below. Identify which will be the most accurate location of epicenter of the earthquake using the triangulation method. D C A B Bring: Application A video will be shown about the affected areas of the west valley fault For 2 mins. Each group will role play a certain scenarios of the ways to ensure disaster preparedness before , during, and after an earthquake • a family inside a house, • a barkada inside a mall, • Teacher and students inside a classroom • Employees inside a government office • Employees inside a manufacturing company • A family having an outing in a beach • Barkada inside a car • Mountaineering club climbing a mountain Performance will be graded according to the following