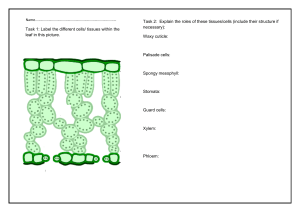
BIOLOGY THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE • Almost all organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or more cells (multicellular). The only exception is very simple organism such as viruses • The cell is the smallest living unit which shows are the characteristics of life. Cells perform vital functions such as : Respiration , Growth , Feeding , Excretion , Locomotion , Reproduction and respond to external stimuli COMPARISON BTWEEN BASIC STRUCTURE OF ANIMAL AND PLANT CELL • Plant and Animal Cell have Three Important Structures in common : Cell Membrane , Nucleus and Cytoplasm STRUCTURE FUNCTION 1. CELL MEMBRANE • A very tiny semi-permeable membrane made up of layers of lipid and protein • Selective control of substance entering and leaving cell . In general it allows certain substance like small molecules of glucose , water , oxygen to enter; waste products to leave but prevents the passage of other substances such as large proteins and starch molecules 2. CYTOPLASM • A jelly like fluid within the cell • The liquid part of cytoplasm has about 90% water with molecules of salt and sugars dissolved in it • Suspend in Cytoplasm are larger fats and protein • Contains two basic types of structure: a. Temporary food storage structures like oil globules , starch granules (in plants) b. Permanent structures which are important for vital activities of cell e.g. mitochondria to release energy for cell activities 3. NUCLEUS • A small dense structure at the center of cytoplasm surrounded by the nuclear membrane • Controls all chemical reactions within the cell and cells division • Contains chromosomes which carry genetic information of the cell • Determines the shape and the function of the cell. • The cytoplasm and nucleus make up the protoplasm of cell Mitochondria : • Under more powerful electron microscope the mitochondria in the cytoplasm becomes more visible • They are small sausage shaped structures with a folded inner membrane • The mitochondria are sites of aerobic respiration which generate energy for essential living process in the cell • The inner membrane contains respiratory enzymes which control the process of respiration release energy from glucose molecules Differences between plant and animal cells FEATURE PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL Cell Wall • Cellulose cell wall present • Cell Wall absent Number and size of vacuoles • One large permanent vacuole • Numerous small temporary vacuoles Chloroplast • Present in large number in the thin cytoplasm living • Relative size • large • small Shape • Regular elongated cylindrical shape • Irregular shape absent • The functions of cellulose cell wall , chloroplast and cell vacuole are summarized in table down below STRUCTURE FUNCTION 1. CELLULOSE CELL WALL • Supports , protects and give shapes to cell • Freely permeable to water , gases and dissolved substances 2. CHLOROPLAST • Contains green pigment , chlorophyll , for absorption of sunlight required for photosynthesis 3. VACUOLE • Filled with cell sap(a watery solution of sugars , salts and pigments) for food storage , osmoregulation and to help maintain the shape of cell • Several organs work together to form an organ system. For e.g. the digestive system in humans is composed of the stomach, duodenum, ileum, liver and pancreas ORGAN SYSTEM MAIN ORGANS MAIN FUCTION Digestive system • Alimentary canal , Liver , pancreas • To digest and absorb food Respiratory system • Nose , trachea , lungs Circulatory system • Heart and blood vessels • To facilitate gaseous exchange. Oxygen breathed into lungs and carbon dioxide expired Nervous system • The brain , the spinal cord and nerves • To conduct nerve impulses and controls voluntary and involuntary actions in body Reproductive system • Testes and ovaries • To produce gametes for sexual reproduction • In flowering plants, the stem, the leaves, and buds make up the shoot system. The main root, the lateral roots and root hair make up the root system ORGAN MAIN FUNCTION LEAF • To produce food by photosynthesis • Also main site for transpiration FLOWER • For sexual reproduction BULB/TUBER/RHIZOME • For asexual reproduction and storage of food substance MODIFICATION OF CELL STRUCTURE FOR SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS • The shape and size of plant and animal cells varies depending on their function within the organism • A cell becomes specialized by doing one particular job. It develops a distinct shape and performs special chemical reactions in order to carry out its function • The specialization of cells to carry out particular functions in an organism is sometime referred to as ‘division of labor’ • A group of similar cell specialized for a particular function forms a tissue an example is muscles cells group together to form muscle tissue • Different type of tissues group together to form an organ for e.g. the stomach is an organ composed of glandular tissues , muscle tissue, nerve tissue etc. • TISSUES FOUND IN ANIMALS TYPE OF TISSUE SPECIALIZED CELLS MAIN FUNCTION Epithelial tissue • Sheets of cells may be ciliated cells • To line alimentary canal , respiratory tracts and forms the skin Blood tissue • Blood cells; white blood cell s , red • For transport of oxygen and food substances blood cells and platelets • For protecting against infections • For blood circulation Nerve tissue • Nerve cell (neurons) • Conduct and coordinate electrical message either to or form central nervous system Muscle tissue • Muscle cell (fibers) • To contract and relax to bring about movement Skeletal tissue • Bone tissue and cartilage • To support and give shape to the body • For locomotion movement is achieved by contraction of muscles which are attached to the jointed bones which act as levers • TISSUES FOUND IN PLANTS TYPE OF TISSUES SPECIALIZED CELLS MAIN FUNCTIONS Epidermal tissues (epidermis) • Sheets of tissues consisting of epidermal cell • Guard cells of a stoma • Protects against bacterial and fungal attack , maintains shape • May be covered with a layer of waxy cuticle to reduce to reduce water loss by evaporation Photosynthetic tissue • Cells with chloroplast , in particular palisade cells • Contains green pigment , chlorophyll , for absorption of sunlight required for photosynthesis Vascular tissue • Xylem and phloem cells • Xylem conducts water and mineral salts from roots to do the rest of the plant • Phloem cells for translocation of food from leaves to all part of the plant Strengthening tissues • Xylem vessels in stem • Dead tissues with thick walls containing lignin and cellulose for mechanical support XYLEM PHLOEM