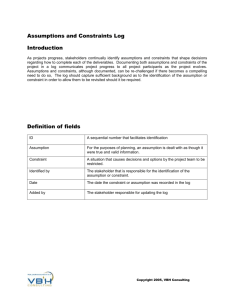
There are Six Basic Assumptions of Accounting: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Economic Business Entity Going Concern Monetary Unit Time Period Accrual Basis Cash Basis All of the business transactions should be separate from the business owner’s personal transactions There should be no combination of personal funds with business funds. An organization will continue its operation for foreseeable future. The company will remain in business indefinitely unless there is sufficient evidence otherwise. This is the concept that a business should only record transactions that can be stated in terms of money only. The entity’s activities are separated into periods of time such as months, quarters or years. Transactions should be recorded in the period in which it is occurred rather when cash is received or paid. Transactions should be recorded when cash is received or paid for that transactions Assumptions Question Combining the activities of Kellogg and General Mills would violate the a. cost principle. b. economic entity assumption. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. 1-9 LO 2 Assumptions Question Combining the activities of Kellogg and General Mills would violate the a. cost principle. b. economic entity assumption. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. 1-10 LO 2 Assumptions Question Purchase a land for taka 50000 but no cash is paid. Based on which assumption land should be purchased a. Accrual Basis Assumption. b. economic entity assumption. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. 1-11 LO 2 Assumptions Question Purchase a land for taka 50000 but no cash is paid. Based on which assumption land should be purchased a. Accrual Basis Assumption. b. economic entity assumption. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. 1-12 LO 2 Following Principles are used in Accounting: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Historical Cost Fair Value Revenue Recognition Matching Assets are recorded at historical cost or its original purchase price. For example, if a company purchases a building for $500,000 it should be recorded as such, and should remain on the books for that amount until disposed of. FAIR VALUE PRINCIPLE states that assets and liabilities should be reported at fair value (the price received to sell an asset or settle a liability). For e.g. You bought a share at taka 10 on 1st January. But 31st January value goes up to taka 12. Here share should be recorded at taka 12. All information relating to the operations and financial position of the entity that make a difference to financial statement users should be disclosed. Revenue is earned and recognized upon product delivery or service completion, without regard to when cash is actually received. Example: A customer purchases inventory from a company on credit. Even though no cash has yet been received, the sale is recorded. The matching principle requires that revenues and any related expenses be recognized together in the same period. Companies must match its revenue with expenses. In other words the matching principle states that expenses should be recorded during the period in which they are incurred, regardless of when the transfer of cash occurs. Example: A company orders goods on credit and has 30 days in which to pay. This purchase is recorded immediately, even though no cash has been paid. By selling these goods company can earn revenue thus expense is matched with revenue. Principles Question You have completed service but not received cash for that service. Service should be recorded under a. cost principle. b. Revenue recognition principle. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. LO 2 Principles Question You have completed service but not received cash for that service. Service should be recorded under a. cost principle. b. Revenue recognition principle. c. monetary unit assumption. d. ethics principle. LO 2 This term refers to the accounting guidelines that creates limitation in preparing accounting Information They consist of: ◦ Cost Effectiveness: ◦ Materiality ◦ Conservatism The cost of providing accounting information should not exceed the benefit of the information it is reporting. States that the requirements of any accounting principle may be ignored when there is no effect on the decisions of the user of financial information. Conservatism helps the accountant choose between 2 equally likely alternatives, where you have to choose that alternative which understates asset & revenue Constraints Question You have option to record your asset at taka 5000 or taka 15000. Which option will you choose under which constraint? a. Taka 5000, conservatism constraint. b. Taka 15000, conservatism constraint c. Taka 10000, monetary unit assumption. d. Taka 2500, cost effectiveness constraint LO 2