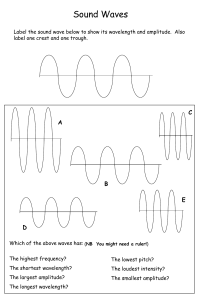
Name ______________________________________________________________________ Page _____________ Screaming Balloons Question: How does the speed the balloon is swirled affect the loudness of the sound? Background: Remember that sound is simply vibrations that travel through a medium and are picked up by our ear and sent as nerve impulses to our brains. Our brain then uses these nerve impulses to determine what the sound is. The volume, or amplitude of the sound, determines how loud the sound is. Louder sounds have higher amplitudes and carry more energy. Quieter sounds have lower amplitudes and carry less energy. Think of a drummer drumming. When he wants the sound to be really loud, he hits the drum as hard as he can, when he wants the sound to be quiet, he hits the drum with less force. The pitch or frequency of the sound is determined by the wavelength of the vibrations. The greater the wavelength of the vibration, the slower the wave moves, the lower the pitch of the sound. The smaller the wavelength, the faster the wave moves, the higher the pitch of the sound. Hypothesis: How does the speed the balloon is swirled affect the loudness of the sound? If ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Then _________________________________________________________________________________________. Materials: latex balloon hex nut Procedure: 1. Grip the balloon at the stem end like you would a bowling ball. Tied end should be in your palm, fingers extending down the side of the balloon. 2. Swirl the balloon in a circular motion until it begins to make a screeching noise. 3. Swirl the balloon fast, medium and slow speeds and circle the appropriate amplitude/volume and pitch/frequency in the data in the data table below. Data: Speed of swirling Amplitude/volume Pitch/Frequency/Wavelength Fast Volume: loud/medium/quiet Pitch: high/med/low Amplitude: high/med/low Frequency: fast/med/slow Wavelength: Long/med/short Medium Volume: loud/medium/quiet Pitch: high/med/low Amplitude: high/med/low Frequency: fast/med/slow Wavelength: Long/med/short Slow Volume: loud/medium/quiet Pitch: high/med/low Amplitude: high/med/low Frequency: fast/med/slow Wavelength: Long/med/short Analysis and Conclusions: 1. How are the vibrations (sound) being made in this experiment? 2. If you replaced the hex nut with a penny, would it make similar sounds or not? Explain. 3. Draw a picture of the amplitude and frequency of the wave created for the fast spinning and slow spinning trials. The resting line has been drawn for you. High amplitude/high frequency drawing Low amplitude/low frequency drawing 4. What is the medium that is creating the sound in this experiment? What would happen if there was no medium? 5. Name one object for each box that have the following conditions: High Frequency: Low Frequency: High Frequency and High Amplitude: Low Amplitutde: