Java Summation Algorithm: Code Examples & Explanation
advertisement

1a.
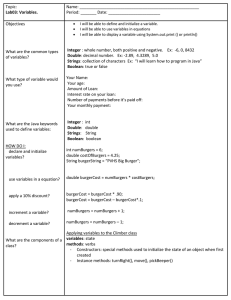
1. Initialise the following variables
1. The numbers that are being accepted
2. int sum = 0;
2. Run the loop so that values are accepted
3. Each iteration of the program should accept a new value from the user.
4. sum = sum + numberaccepted
5. Check whether sum>100 at the end of every iteration.
6. If true, print “Done” and break the loop.
1b.
1c.
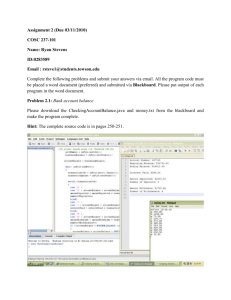
import java.util.*;
public class sumofint
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = o;
do
{
System.out.println(“Enter an integer”);
in = s.nextInt();
sum = sum + in;
if (sum > 100) {break;}
}
while (true);
System.out.println(“Done”);
}
}
1d.
import java.util.*;
public class sumofint
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = o;
while (sum<=100)
{
System.out.println(“Enter an integer value”);
int in = s.nextInt(); // accepts the user input as integer “in”
sum = sum + in;
}
System.out.println(“Done”);
}
}
2.
3.
4.
5.
String[][] students = {{“Chris”, “Natasha”, “Mekhala”, “Aadya”},{“Arjun”, “Pranav”, “Lee”,
“Dakyung”}};