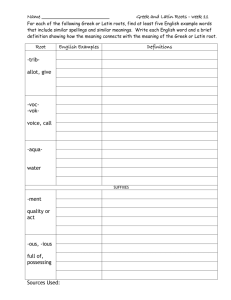
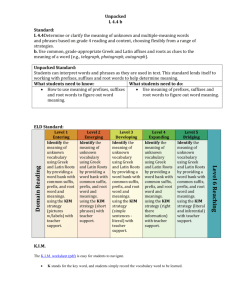
The Language of Science In science, as in other subjects, you should always try to find ways you can learn best and work on improving your study skills. As is the case of other subjects, you will need to learn the language if you are to understand science. Science is a language with a technical vocabulary. Some life science terms may be hard to understand the first time you encounter them. Where do all these strange sounding terms come from? Many of these words are based upon Latin and Greek. For example, the word biology comes from the Greek words bios and logos. Bios is the Greek word for life, and the Greek word logos means the study. Biology, then, is the study of life. Approximately, 80% of all the words in an English dictionary are formed from Greek and Latin parts. Knowledge of these will help you break down unfamiliar words and remember their meanings. Therefore, the language of science can be developed through the use of word analysis. In word analysis, you can see that many scientific terms are built from prefixes, suffixes, and root words that have been derived from Latin and Greek words. To decode the meaning of a new vocabulary term, simply look at the meaning of the PREFIX (beginning of the word) and the SUFFIX (the end of the word). Here is a list of the most popular prefixes and suffixes used in science. The main reason students find it difficult to understand science is because of all the hard to write, spell and read words. Actually, scientific vocabulary is a hodge podge of little words that are linked together to have different meanings. If you learn the meanings of the little words, you'll find scientific vocabulary much easier to understand. Use this LIST (BELOW) to guess the MEANING of each of the TERMS. Place the MEANINGS in the BLANKS next to the TERMS *** TERMS are on the LAST page *** Prefix & Suffix LIST Word a or an auto aero endo entero aero anti amphi aqua arthro auto bi bio carne cephal chloro chromo cide cyto derm di ecto (exo) endo epi gastro genesis herba hetero homo hydro Meaning not, without, lacking self air inner, inside intestine needing oxygen or air against both, doubly water joint self two, twice, double life, living flesh head green color killer, kill, killing cell skin two, double outer, external internal above stomach origin, beginning plants different alike, similar water Word hemo hyper hypo intra itis lateral logy lys meter meso mono morph micro macro multi pod phage phobia philia plasm proto photo poly sclera synthesis sub troph therm vore zoo, zoa Meaning blood above below within, inside disease, inflammation side study of break down measurement middle one, single form small large many foot to eat dislike, fear like form first light many harden to make lesser, below eat, consume heat swallow, devour animal *** TERMS are on the NEXT page *** TERMS 1. Hydrology ________________________________________________ 2. Cytology _________________________________________________ 3. Protozoa ________________________________________________ 4. Epidermis _______________________________________________ 5. Spermatogenesis __________________________________________ 6. Cytoskeleton ______________________________________________ 7. Abiotic __________________________________________________ 8. Dermatitis _______________________________________________ What scientific words can you create or think of from the list? (Come up with at least 4) 9. Hypodermic _____________________________________________ ________________________________ 10. Hemophilia _____________________________________________ ________________________________ 11. Endocytosis ____________________________________________ ________________________________ 12. Insecticide _____________________________________________ ________________________________ 13. Anaerobic _____________________________________________ ________________________________ 14. Bilateral _______________________________________________ ________________________________ 15. Endotherm _____________________________________________ 16. Subspecies ____________________________________________ 17. Arthropod _____________________________________________ 18. Micrometer ____________________________________________ 19. Hypothermia ___________________________________________ 20. Polymorph ____________________________________________ 21. Photosynthesis ________________________________________ 22. Amphibios (amphibian) __________________________________ 23. Heterotroph __________________________________________ 24. Encephalitis __________________________________________ 25. Monochrome _________________________________________ 26. Autolysis _____________________________________________ 27. Herbivore ____________________________________________ 28. Homology ____________________________________________ 29. Macrophage _________________________________________ 30. Carnivore ____________________________________________ 31. Gastroenterologist _____________________________________ 32. Scleroderma __________________________________________ 33. Autotroph __________________________________________ 34. Autolysis __________________________________________ 35. Podiatrist __________________________________________ Apatasaurus, or "deceptive lizard"