Photosynthesis Fundamentals Worksheet
advertisement

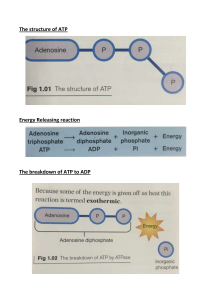
UNIT 4 TOPIC 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1: FUNDAMENTALS Complete the notes sheets below. Where you see a blank (…………………..), decide which word/phrase is most appropriate. What is photosynthesis? Plants are ……………………: this means that they make their own organic compounds using CO2. This is mostly achieved via …………………… whereby they trap energy from the …………………… and …………………… it to …………………… energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates by splitting the H-O bonds in water and combining the …………………… atoms produced with CO2. Save for a relatively small number of …………………… bacteria which synthesize organic food molecules using chemicals (eg. surrounding black smokers), all life on earth depends on the energy trapped during …………………… . Write down the word and symbol equations for photosynthesis: …………………… Word equation: ……………………+…………………………………………+…………………… …………………… …………………… Symbol equation: ……………………+…………………………………………+…………………… …………………… 1|Page DEFINITION: Energy …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ****REMEMBER*** Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form to another. ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) ATP is a phosphorylated nucleotide. It is commonly referred to as the universal ……………………. ……………………… . Add the following labels to the diagram below left and then draw and label a simplified version showing the basic structure to the right: Adenine, Adenosine, Ribose, Phosphate groups. ATP can be …………………… to form ADP and Pi (……………………), releasing 30.6 KJ.mol-1 of energy. This is a reversible reaction. ATP is a ……………………- lived 2|Page molecule which is constantly being hydrolysed (using the enzyme ……………………) and resynthesized (using the enzyme …………………….) . ATP + H20 ADP + Pi (+approx. 34 KJ.mol-1) ATP is derived from…………………… . We can tell this because the sugar is …………………… . Using ATP ATP provides energy for processes such as: a. ……………………………..: Moving ions and molecules against a concentration gradient. b. ……………………………..: Secretion of large molecules. c. ……………………………..: Movement of large molecules into cells. d. ……………………………..: Synthesis of large molecules from smaller ones. e. ……………………………..: Preparing a cell for anaphase. f. ……………………………..: Powering bacterial flagella, eukaryotic cilia, muscle contraction and microtubule motors that transport organelles. 3|Page Forming ATP ATP is formed from …………………… and …………………… . In respiration, some ATP is formed during …………………… in the cytoplasm, but the majority is formed in the …………………… …………………… …………………… (a process that also occurs during photosynthesis). In this process, reduced hydrogen acceptors (NADPH in …………………… or NADH/FADH2 in ……………………) pass electrons along a series of membrane-bound carriers, releasing a small amount of …………………… which is used to pump H+ ions into an intermembrane/interior space. In the final step, H+ ions flow down the resulting …………………… and …………………… gradient, driving the head of an ATP synthase molecule and catalysing the formation of ATP from ADP and Pi (covered in detail in topic 7). This is known as …………………… . 4|Page Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are large organelles containing stacks of membrane discs called …………………… where the green pigment (……………………) is found. The stacks themselves are known as …………………… . The matrix surrounding these ‘stacks’ is called the …………………… . This contains the enzymes needed for the production of …………………… . Label: Stroma, Granum, Outer Membrane, Inner Membrane, Thylakoid 5|Page Chlorophyll There are 5 closely related pigments including …………………… (blue-green), …………………… (yellow-green) and the …………………… (orange carotene and yellow xanthophyll). The most common is ……………………, which is found in all photosynthesising plants, though having different pigments ensures optimum use of …………………… energy. The pigments are found bound to proteins on …………………… membranes. A complex comprising a protein and its associated pigment molecules are known as a …………………… . 6|Page ESSENTIALS 1. Oxidation and reduction ***REMEMBER*** OIL RIG O……………………. I…………………….. L……………………. R…………………….. I……………………… G……………………. Oxidation and reduction are coupled, since if one substrate becomes oxidised, another must be reduced. Such reactions are called REDOX reactions. 2. Photosynthesis is a multi-step process. The multitude of reactions that take place from start to finish can be summarised in two key stages: a. Light-dependent reactions (take place …………………………………………) produce materials which can then be used in the …………………… reactions. These reactions occur on the ……………………, using the sun’s energy to split …………………… molecules (a …………………… reaction), passing the H atoms on to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) (forming NADPH or …………………… NADP). …………………… is also produced in a process called …………………… . b. Light-independent reactions (take place …………………………………………). These reactions use the …………………… and …………………… produced during the light-…………………… reactions. A series of chemical reactions called the …………………… cycle take place in the 7|Page …………………… of a …………………… . CO2 from the …………………… is …………………… to form …………………… . Label: Light-dependent reactions. Products of the light-dependent reactions. Light-independent reactions. Takes place on the thylakoid membranes. Takes place in the stroma. 8|Page