Cell Organelles: Nucleus & Chloroplasts - High School Biology
advertisement

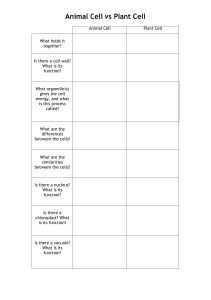
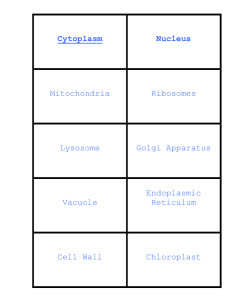
Organelles • Organelles are specialized structures that make up a cell Functions of Organelles Plant cells Animal cells Both cells Nucleus Nucleus Nucleus Mitochondria Mitochondria Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Ribosome Ribosome Ribosome Lysosomes Lysosomes Lysosomes Plasma membrane Plasma membrane Plasma membrane Vacuole Vacuole (small / no) Vacuole Cell wall Centrioles Chloroplast Nucleus Genetic information in the form of DNA is stored in the nucleus, making it the control center of the cell Characteristics • The largest organelle in the cell • Dense and spherical • Consists of three main components: Nuclear envelope – separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm Chromatin – carries genetic material in the form of DNA Nucleolus – a darker and dense region The nucleus acts as the “control center” of the cell, and it is only found in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus contains DNA molecules and a variety of proteins to form chromosomes Function • Controls all cellular activities (eg, cell division) • Contains DNA which determines the characteristics of a cell and its metabolic functions • The information carried by the DNA directs and controls the activities of the cell. Eg, protein synthesis • These proteins determine the structure of the cell and the functions it can perform • The hereditary information stored in the nucleus controls the cell’s growth, reproduction ,intermediary metabolism and protein synthesis. • The nucleus contains a semi-fluid substance called nucleoplasm, which stores chromatin. Chloroplasts Characteristics • Lens-shaped organelles • Have a double membrane • The internal chloroplast membranes contain green pigment called chlorophyll Structure: • The outer and inner membranes: protective coverings that keep chloroplast structures enclosed • Stroma: dense fluid within the chloroplast. Site of conversion of carbon dioxide to sugar • Thylakoid: flattened sac-like membrane structures. Site of conversion of light energy to chemical energy • Grana: dense layer stacks of thylakoid sacs. Site of conversion of light energy to chemical energy • Chlorophyll: a green pigment found in thylakoids. Absorbs light energy Function • Chlorophyll traps the energy from sunlight and converts light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis • The green pigment of chlorophyll gives plants their green colour • Chloroplasts absorb sunlight and use it in conjunction with water and carbon dioxide gas to produce food for the plant. Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cFVsvgiQdx8