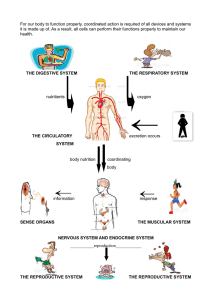
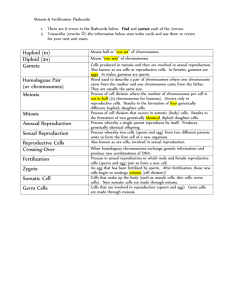
Biology Test 1: Centralized Outcomes 1. What are the structures of the male and female reproductive systems and what are the functions of each? Male Reproductive System The male gametes, i.e., sperms are produced within the male reproductive system. Sperms are small unicellular structures with a head, middle piece, and a tail. The male reproductive system consists of : Testicles (testes): A pair of oval-shaped organs masked in a pouch called scrotum. They are responsible for the production of sperms and the male hormone testosterone. Scrotum: It is a sac-like organ that hangs below the penis and behind it. It is the houses of the testicles, or testes, and maintains a temperature that is required for the production of sperm by it. Vas deferens: The sperms produced in testes are stored in a tube called epididymis. Here the sperms get matured and pass to urethra through the muscular tube called vas deferens. Accessory glands: This includes three glands, namely seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and Cowper’s gland. The secretions from the three glands mix to form a fluid called semen. Semen nourishes the sperm, increases the volume and helps in lubrication. Penis: Penis is a cylindrical tube which serves as both reproductive organ as well as an excretory organ. It delivers sperms into the vagina during sexual intercourse. Female Reproductive System The female reproductive system is active before, during and after fertilization as well. It consists of the following parts: A pair of ovaries: Ovaries produce and store ovum in them. They also produce a female hormone called estrogen. Fallopian tubes (Oviducts): They are the site of fertilization. They connect ovaries with the uterus. Uterus: Uterus is the site of development for the embryo. Vagina: It is the part which connects cervix to the external female body parts. It is the route for the penis during coitus as well as a fetus during delivery. Female reproductive system has two functions – 1. Production of female gamete called ovum/egg. 2. Providing nutrition and protecting the developing embryo. During puberty, eggs in the ovaries start to mature. One of the ovaries releases the matured ovum in every 28 to 30 days and is called ovulation. Reproduction Process in Human Beings The process of fusion of sperm with egg (ovum) to produce zygote is called fertilization. Fertilization is a crucial stage of reproduction in human beings. The fertilized egg is called the zygote.Zygote starts to divide into many cells and develops into an embryo. Embryo moves into the uterus and gets attached to its walls. This process is referred to as implantation, and implanted embryo eventually develops into a fetus. Frequently Asked Questions What is Reproduction? Reproduction is a fundamental biological process of producing young ones or offspring, which are identical to their parents. What is Fertilization? Fertilization is the fusion of male and haploid female gametes (egg and sperm) resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. What is Cell Differentiation? Cell Differentiation is the process through which a young and immature cell develops into a specialized and matured cell. Explain the process of reproduction in human beings? The process of reproduction in humans usually begins with copulation, followed by the Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, and Post-fertilization. During this fundamental process, both male and female reproductive organs play an important role. Explain the term trimester system? In Biology, the trimester system mainly refers to three months. A complete pregnancy period lasts for 38-40 weeks or 9 months from the first day of your last menstrual period to the birth of the baby. This period is divided into three stages, which are collectively called trimesters. 1. First trimester (1st 3-months). 2. Second trimester (2nd 3 months). 3. Third trimester (3rd 3 months). What is Parturition? Parturition is the process of delivering the baby after the completion of pregnancy or a fully grown developed fetus and placenta from the uterus to the vagina to the outside world. This process occurs in three stages, which includes: 1. Stage 1: Preparatory Stage- 2 to 12 hours. 2. Stage 2: Birthing Process –30 to 180 minutes. 3. Stage 3: Placenta Expulsion –1 to 12 hours. How do humans reproduce their young ones? Humans reproduce their young ones sexually by the interaction between the male and female reproductive organs. List out the stages of Sexual Reproduction? Sexual Reproduction is carried out by a set of events and are divided into three stages: Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, and Post-fertilization What is the significance of human reproduction? Reproduction is a fundamental biological process carried out by different living organisms to produce their young ones or offspring. In human, reproduction plays a significant role in the continuity of species from one generation to another generation. Without reproduction, there would no life existing on the planet earth. Difference between sexual and asexual mode of reproduction? Both sexual and asexual are two different modes of reproduction. Sexual mode reproduction takes place in all multi cellular organisms including humans, animals, and higher plants. Asexual mode reproduction occurs only in lower invertebrates and other simpler living species such as amoeba, bacteria, and hydra. How do hormones regulate the male and female reproductive systems? Sex hormones are responsible for driving sexual development (puberty). The main reproductive hormones are oestrogen and testosterone. Oestrogen causes eggs to mature in ovaries once a girl hits puberty. These are then released at regular intervals during the menstrual cycle. Testosterone stimulates sperm production in males. Other hormones involved in the menstrual cycle include: Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), causing maturation of an egg in the ovary. Luteinising hormone (LH) stimulating the release of the egg. Oestrogen and progesterone are involved in maintaining the uterus lining. When these reproductive hormones do not work as they should, fertility problems can occur. Our understanding of these hormones and their functions means we can assist fertility, for example through in vitro fertilisation, also known as IVF. 3.What are the stages of meiosis? 4 What is the importance of meiosis in providing genetic variation? Prophase 1 Explanation: It occurs during the crossing over process in prophase 1 of meiosis. Here, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange random genetic information for variation. The Importance of Meiosis ▪ Meiosis consists of two sets of divisions ▪ Produces four haploid daughter cells that are not identical ▪ Results in genetic variation 5.What is the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics? Mendelian inheritance is a set of rules about genetic inheritance. Gregor Mendel Gregor Mendel, father of modern genetics. The basic rules of genetics were first discovered by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1850s, and published in 1866. For thousands of years, people had noticed how traits are inherited from parents to their children. However, Mendel's work was different because he did experiments on plants, and designed those experiments very carefully. In his experiments, Mendel studied how traits were passed on in pea plants. He started his crosses with plants that bred true, and counted characters that were either/or in nature (either tall or short). He bred large numbers of plants, and expressed his results numerically. He used test crosses to reveal the presence and proportion of recessive characters. Mendelian Genetics Limitations Mendel's laws apply widely, but not to all living things. They apply to any organism which is diploid (has two paired sets of chromosomes) and which engages in sexual reproduction. They would not apply to bacteria, for example, or to asexual reproduction. They do apply to the great majority of plants and animals. Mendel's laws Mendel explained the results of his experiment using two scientific laws: 1. Factors, later called genes, normally occur in pairs in ordinary body cells, yet separate during the formation of sex cells. This happens in meiosis, the production of gametes. Of each pair of chromosomes, a gamete only gets one. The factors (genes) determine the organism's traits, and are inherited from its parents. As the pair of chromosomes separate, each gamete only receives one of each factor. This Mendel called the Law of segregation. Mendel also noted that versions of a gene could be either dominant or recessive. We call those different versions alleles. 2. Alleles of different genes separate independently of one another when gametes are formed. This he called the Law of independent assortment. So Mendel thought that different traits are inherited independently of one another. The second law is only true if the genes are not on the same chromosome. If they are, then they are linked to each other. This was the next great discovery after Mendel: that genes were carried on chromosomes. The closer they were on the chromosomes, the less likely was crossing over between them. Mendel's laws explained the results he got with his pea plants. Later, geneticists discovered that his laws were also true for other living things, even humans. Mendel's findings from his work on the garden pea plants helped to establish the field of genetics. His contributions were not limited to the basic rules that he discovered. Mendel's care towards controlling experiment conditions along with his attention to his numerical results set a standard for future experiments. Consequences When the chromosome pairs are separated in a gamete, they are randomly segregated. A gamete might have any proportion from 100% maternally derived to 100% paternally derived chromosomes. In crossing-over, sections are exchanged between pairs of chromosomes during meiosis. This increases the number of genetically different individuals in a population, which is important in evolution. As a consequence of 1 & 2, except for identical twins, no two siblings have identical genetics. 6. How does the process of meiosis produce genetic recombination? Recombination Homologous chromosomes switch materials in a process known as recombination, or ‘crossing over’, which is mediated by the formation of chiasmata. The two chromatids attached to the chiasmata exchange parts. In this way, some of the genes originally on the father’s chromosomes are now on the mother’s chromosomes, and vice versa. This shuffling process helps to create and maintain variation in a species. after prophase 1 30 minutes 1:00-1:30 Thursday 7/05/2020