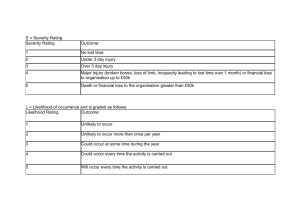
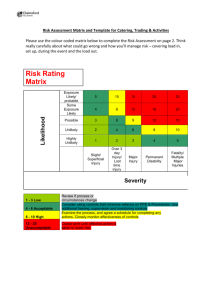
UNIVERSITI KUALA LUMPUR BRITISH MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE INDUSTRY SAFETY AND HEALTH (BGB 32003) PRACTICAL 2 HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT & RISK CONTROL (HIRARC) GROUP L03-T02 DATE OF SUBMISSION 12 MAY 2020 LECTURER: SIR SHAHARUDIN HASHIM GROUP MEMBERS: 1) MUHAMMAD AMIRUL AIZAD BIN KAMAL 2) MUHAMMAD AMIRULIZZAT BIN RAHMAT 3) MUHAMMAD AKRAM BIN ROSLI 4) ANIS NADIA BINTI SUHAIMY 1 [51215118118] [51215118079] [51215118355] [51215118320] TABLE OF CONTENTS Contents Page No TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 TASK 1.0 : INTRODUCTION 3 TASK 2.0 : OBJECTIVES 3 TASK 3.0 : PROCEDURE 4 TASK 4.0 : HAZARD IDENTIFICATION, RISK ASSESSMENT 7 & RISK CONTROL (HIRARC) Hazard 1 7 Hazard 2 10 Hazard 3 13 Hazard 4 16 Hazard 5 19 Hazard 6 22 Hazard 7 25 Hazard 8 28 TASK 5.0 : CONCLUSION 31 TASK 6.0 : RECOMMENDATION 32 TASK 7.0 : REFERENCES 33 TASK 8.0 : APPENDICES 34 2 TASK 1.0: INTRODUCTION Hazard identification, risk assessment and risk control (HIRARC) has ended up being basic to the demonstration of organizing, organization and the activity of a business as a crucial of peril organization. The affiliations that have finished peril assessment at the work have seen different changes in their working practice. The people who have recently finished risk examination in their work, have uncovered constructive changes in their working practice, they see inadequate act and working condition as they make and make significant medicinal move. Approval necessitated that this methodology should be systematic and be recorded with the objective that the results are strong, and the assessment wrapped up. The risk assessment process as far as anyone knows to be constant and not to be seen as a sporadic exercise. As per the office approach of preventive measures as a technique for executing the law on occupational safety and health (OSH), apparently Hirarc has ended up being basic. With Hirarc, one will have the ability to separate peril, explore and assess its related danger and a short time later apply the sensible control measures. This rule should provide guidance on reasoning of driving Hirarc, it expected to be adequately essential to be used by pretty much nothing and medium endeavors and to be versatile to be used by all in various money related parts, either in the amassing division, improvement regions or some other monetary portions. TASK 2.0: OBJECTIVES • To give a decent wellbeing and wellbeing information to the understudies • To instill OSH mindfulness in understudies with the goal that they convey the great OSH practice when they graduate and joint society and the workplace • To have the option to recognize the hazard, dangers and to oversee them utilizing suitable technique 3 TASK 3.0: PROCEDURES 1. Differentiate the risks Initially, it is important to research how people could be harmed particularly while in the work environment. It is scarcely for representatives to see a couple of perils, along these lines here are a few ways to deal with assistance recognize the issues: ● Walk around the workplace and look at what might be depended upon to cause injury. ● Ask the authorities especially on what they think or see. They may have seen things not quite the same as others. ● Check marker; headings or data sheets for synthetic substances and equipment as they can be amazingly helpful in illuminating the dangers and setting them in their genuine perspective. ● Have a look back at experts' mishap and wiped out prosperity records as they could assist with recognizing the more unpretentious threats. ● Remember to consider long stretch risks to prosperity (for example anomalous measures of fuss or prologue to dangerous substances) and likewise peril's security. 2. Unmistakably short who might be harmed in every peril and what could influence them. It will assist us with distinguishing the best strategy when managing the peril. Few out of every odd boss perceives every one of their labourers (e.g.: 'people working in the storeroom' or 'passers-by'), in this way for every circumstance, everybody needs to distinguish how they might be harmed; for example, what sort of harm or wiped out prosperity may occur. For example, 'rack stackers may encounter the episode impacts of reiterated lifting of boxes. Remember: ● Some workers have explicit necessities, e.g.: new and young masters, new or excited specialist and people with failures may be at explicit peril. 4 3. Evaluate the risks and sort out on security measures Risk used to recognize the threat, we as a client need to know and find out about it. The law anticipates that us should do everything reasonably, to shield people from harmed. We can work this out without any other individual, anyway the easiest way is to differentiate what we are doing and incredible practice. Subsequently, as workers we should look on what's going on around us, consider what controls that we have placed in and how the capacity expected to be normalized. For example, setting a mirror on a hazardous outwardly weakened corner to help foresee vehicle setbacks is a negligible exertion wellbeing gauge or can be thinking about as the threat. Failure to stay away from potential hazard can cost essentially more if the incident occurs. Staff ought to be incorporated with the objective of trying to work for all intents and purposes and would not present any new risks. Hazard ought to be resolved utilizing the accompanying: Hazard = LIKEHOOD × SEVERITY 4. Record the discoveries and execute them Recording the consequences of your hazard appraisal and giving them to your staff. On the off chance that you have under five specialists you don't have to record anything, anyway it is useful so you can routinely review. When recording your results, keep it fundamental, for example 'Bumbling over garbage: containers gave, staff taught, step by step housekeeping checks', or 'Smoke from welding: close by exhaust ventilation used and routinely checked'. 5 5. Survey the evaluation and update if essential Take a gander at the danger assessment again. Have there been any movements? Are there any overhauls? Are there any people recognized an issue? Have we taken in anything from incidents or close misses? Guarantee the peril evaluation stays best in class. When considering risk evaluation, review: ● A hazard is whatever may cause occurrence, for instance, synthetic substances, power, working structure ladders, an open cabinet, etc; ● The peril is the chance, high or low, that somebody could be harmed by these and various dangers, together with an indication of how certifiable the harm could be. 6 TASK 4.0: Hazard identification, Risk Assessment & Risk Control (HIRARC) (a) Hazard 1 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Dislocated concreate of the wire fence STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 5 people are exposed to the hazards shown. It happened 3 months ago Occurs due to incomplete movement of soil after heavy rainfall Severity is Minor and possibility is Likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 7 STEP 4: ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =2x3 =6 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 MEDIUM = 6 8 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation, instead of replacing the fence support concreate with better quality concrete. Meanwhile recommendation make a beam which are made of steel or reinforced concrete or steel. The function of beam is to resist loads, connect the structure together and provide a uniform distribution of loads. So the action need to done in this situation is establish a system frame beam around the base of the fence that is planted in the ground to strengthen the concreate from dislocated. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 9 (b) Hazard 2 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Soil erosion at the bottom of the wall. STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 5 people are exposed to the hazards shown. Duration of exposure is about 5 months ago Occurrence of soil erosion at the bottom of the wall due to imperfection of the cultivation system Severity is Minor and possibility is Unlikely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 10 STEP 4 : ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Minor x Unlikely =2x2 =4 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 MEDIUM = 4 11 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The recommendation is based on this situation, creating a more efficient harvesting system and rebuilding the wall according to the specs and security calculations set out as there is a piling system. It can be justify that in home environment, sheet piling is used as permanent walls as they provide stability and durability to the interior walls (especially basement walls). Pilling is also used to prevent floods to structures close to shorelines. To protect foundations from water damage. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 12 (c) Hazard 3 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Unsafe condition at roof STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO 8 people estimated that will be exposed on that condition. 1-month duration of the exposure since past few weeks raining heavily. Severity level is major and possibility is likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 13 STEP 4 : ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =3x3 =9 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 HIGH = 9 14 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation, it would be recommended that the owner to change the roof with high quality roof because it is more safe to neighbour and the owner. Besides, the owner does not have to replace with the new wood when it happens again. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 15 (d) Hazard 4 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Cracked wall at staircase to the attic STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO 8 people are exposed to the hazards shown. It happened 6 months ago Occurs due to the house getting older and wall exposed to some water Severity is Minor and possibility is Unlikely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 16 STEP 4 : ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =2x2 =4 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 Medium = 4 17 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation is that it would be recommend that the owner to change the staircase at new position or remake the wall with high quality materials. This can at the same time reduce and eliminate the exposure of the hazard to the family members. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 18 (e) Hazard 5 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Exposed Roof Zinc at the height of 1.5 Metre STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 11 people are exposed to the hazards shown. It happened 1 months ago Occurs due to misplacement of the roof zinc Severity is Major and possibility is Likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 19 STEP 4: ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =3x3 =9 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 HIGH = 9 20 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation is that the roof zinc can be eliminate from the scene as it is very dangerous. The roof zinc does not provide any benefits therefore it is netter to remove. This can make sure that everyone go to that place will not exposed to the dangerous of roof zinc. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 21 (f) Hazard 6 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Dislocated woof that supporting the roof STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 11 people are exposed to the hazards shown. It happened 4 months ago Occurs due to the nails that supporting the roof rusty and wood damaged Severity is Major and possibility is Likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 22 STEP 4: ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =3x3 =9 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 HIGH = 9 23 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation is that the dislocated wood has to be replace with new nails and new woods. This is because the nails are rusty and wood start to damaged. This can cause the wood dislocated even further and can cause roof to drop to the floor. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 24 (g) Hazard 7 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO The Ceiling Of The Roof Collapsed STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 150 people are exposed to the hazards shown. It happened 5 months ago Occurs due to after heavy rainfall with strong wind Severity is Major, Possibility is Likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 25 STEP 4 : ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Major x Likely =3x3 =9 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 HIGH = 9 26 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The future improvement based on this situation, we need to do change the ceiling and do the maintenance check schedule. Meanwhile recommendation for this situation is to appoint professional and qualified contractor to make sure the construction is doing well. If the construction is conducted by the qualified contractor, this could ensure the high quality of the building constructed. When the ceiling is in a high quality, the safety will be ensured. Life span for the ceiling will be long if the ceiling is in a good quality. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 27 (h) Hazard 8 STEP 1: PHOTO OF SCENARIO Broken Windows STEP 2: DESCRIPTION OF SCENARIO About 50 people are exposed to the hazards shown. duration of exposure is about 2 months ago Occurrence of weather factor and life span of the windows, quality of the windows Severity is Minor, Possibility is Likely STEP 3: CLASSIFICATION OF HAZARD Physical 28 STEP 4 : ACCESSING THE RISK Risk should be determined using the following: Risk = Severity x Likelihood = Minor x Likely =2x3 = 6 Risk Rating Severity Likelihood 4 Fatality Very likely 3 Major Likely 2 Minor Unlikely 1 Negligible Highly unlikely STEP 5: RISK RATING Probabality Severity 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 L L M M L M M H M M H H M H H H L LOW M MEDIUM H HIGH Severity Negligible Minor Injury Major Injury Fatality Highly Unlikely 1 2 3 4 Unlikely 2 4 6 8 Likely 3 6 9 12 Very Likely 4 8 12 16 MEDIUM = 6 29 STEP 6: CONTROLLING THE RISK Eliminate Substitute Modify Isolate Engineering control Administrative control/ Safe system of work Personal Protective Equipment STEP 7: RECOMMENDATION FOR IMPROVEMENT The recommendation is based on this situation, the incident might happen due to weather factor, short life span of the windows and low quality of the windows. To prevent this incident from happening again, maintenance should be done regularly such as applying grease at the hinges of the windows. After controlling the risk, the new risk rating will change to Risk(minimize/reduce) = Severity(control) x Likelihood(control) = Negligible x Highly Unlikely =1x1 =1 30 TASK 5.0: CONCLUSION Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Risk Control, HIRARC is an absolute necessity be obliged to in affirmation of sheltered and solid home. After OSH mindfulness must be understand and practice as a safeguard, so they will be increasingly careful about the hazard. Aside from that, house members should realize how to recognize and manage the peril and risk with a legitimate technique. All in all, house rehearsing the HIRARC will be progressively secure. It can ingrain care in family members from the peril of the dangers. What's more, this additionally could decrease the quantity of mishap and episode at home. In a roundabout way, limiting the chance of cases, fines or disciplines from work sheets. According to, all associations in Malaysia are required to accomplish the HIRARC structure really about the prosperity of the family members . From this evaluation, we can rehearse on the best way to distinguish peril that can be a potential mischief to us and make sense of the most conceivable approach to keep the mishaps from occurring. Other than that, we can have a superior comprehension on the best way to assess the dangers and discover all causes that can prompted mishaps from occurring or to limit the impacts from the mishaps at the house or building site. From the danger, chance evaluation and hazard control the greater part of the high-chance perils that was recorded are effectively avoidable if the correct insurance given that may prompt spare extraordinary measures of lives in the house. 31 TASK 6.0: RECOMMENDATION Making a sheltered domain where your family can develop and flourish is a top need. Fortunately, however various genuine security dangers prowl around the normal home, the greater part of these worries can be tended to pretty without any problem. Ensure you're doing all that you can to keep your family sheltered. Counsel this guide of nine normal wellbeing dangers in the home for fast, straightforward answers for keep you and your friends and family out of mischief's way. Keeping your home free of dangers and equipped with home safety products can prevent mundane accidents such as falls and can protect you from emergencies like fires. Practice some good habits around your home to keep you and your loved ones safe. Home should be where you go to have a sense of security and secure. Tragically, home is the place numerous mishaps happen also. The fundamental driver of death in kids and youthful grown-ups is injury. Coincidental wounds that happen at home record for around 45 percent of these passing. A portion of the more typical sorts of wounds that occur at home incorporate falls, suffocation, harming, consumes, suffocating, gun mishaps and gagging. Regardless of whether a kid is at home alone or with grown-ups present, wounds can in any case occur. It's the ideal opportunity for instructors, guardians and children to cooperate to keep these mishaps from occurring. Perhaps the most ideal approaches to ensure that your house is sheltered is to effectively assess each space for potential perils. Visit examinations, alongside having an arrangement for what to do in the event of a crisis, are your best apparatuses for forestalling injury and demise in your home. Nothing is a higher priority than keeping your family sheltered. Realizing what to pay special mind to and which safety measures to take makes your activity as family defender somewhat simpler, yet nobody can be on the job constantly, so you might need to get some assistance ensuring your friends and family with a checked security framework. Most present frameworks offer home mechanization and remote access so you can ensure all is well as regularly as you need. 32 TASK 7.0: REFERENCES 1. Home Safety Recommendations. (n.d.). Retrieved May 10, 2020, from https://www.myshepherdconnection.org/docs/GENERAL_RECOMMENDATIONS.p df 2. Journal of Hazardous Materials. (2018). Journal of Hazardous Materials. Retrieved from https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-hazardous-materials 3. Natural Hazards. (n.d.). Natural Hazards, 102(1). Retrieved from https://www.springer.com/journal/11069 4. Occupational Safety and Health Act and Regulations, Act 514, published by MDC Publishers Sdn. Bhd, Mac 2017. 33 TASK 8.0: APPENDICES 34 35 36 37