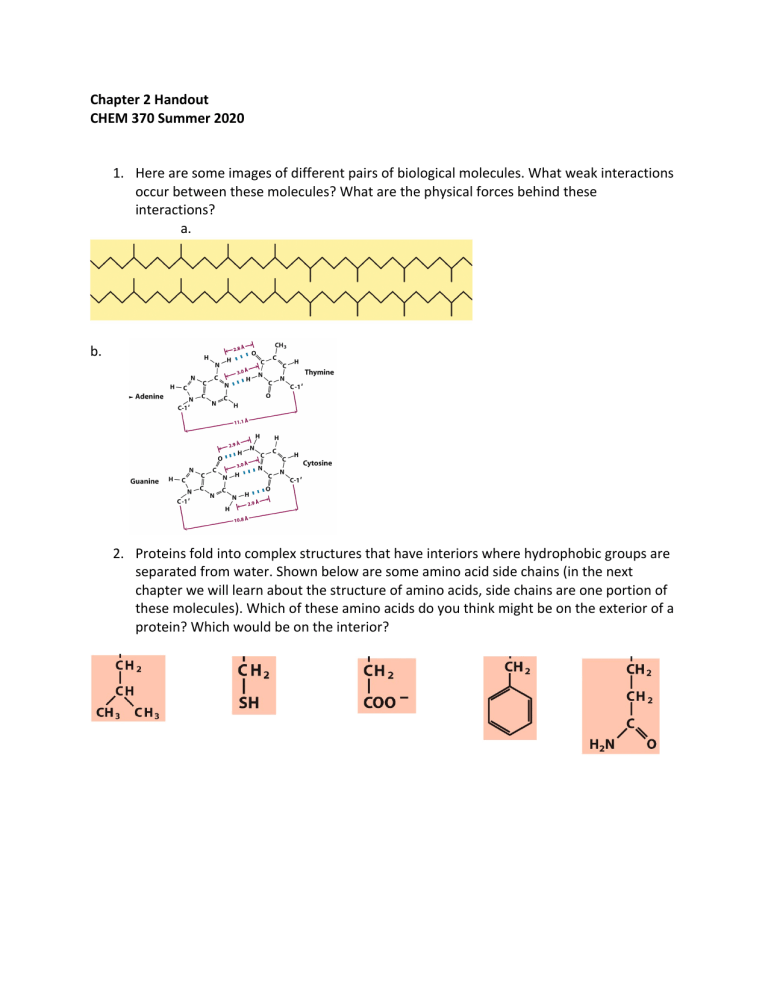
Chapter 2 Handout CHEM 370 Summer 2020 1. Here are some images of different pairs of biological molecules. What weak interactions occur between these molecules? What are the physical forces behind these interactions? a. b. 2. Proteins fold into complex structures that have interiors where hydrophobic groups are separated from water. Shown below are some amino acid side chains (in the next chapter we will learn about the structure of amino acids, side chains are one portion of these molecules). Which of these amino acids do you think might be on the exterior of a protein? Which would be on the interior? 3. You would like to burst cells to extract the insides for an experiment. What type of solution would you put these cells into in order to promote breaking their membranes: an isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic one? If you wanted to purify the mitochondria from these cells to study their function would you use this method? Why or why not? 4. Prolonged low sodium levels can be caused by chronic alcoholism, anorexia nervosa and starvation. Osmotic demyelination syndrome occurs when patients suffering from low sodium levels are given too much sodium too quickly to treat the deficiency. The myelin sheath surrounding encapsulating neurons in the brain stem die, leading to seizures, changes in gait and respiratory function and sometimes para- or quadraparesis and loss of consciousness. Why do you think cells in the myelin sheath die? 5. Recall that 1x10-14=[H+][OH-]. Calculate the concentration of [H+] and the pH when the amount of acid and base are equal. 6. The pH of a solution is 8. a. What is the concentration of H+ in this solution? b. What is the concentration of OH- in this solution? 7. The buffer HEPES (below) is commonly used in biochemistry labs. It has a pKa of 7.5. You make a 100 mM (0.1 M) solution of this buffer and adjust the pH 7.8. + H+ a. In what pH range would HEPES act as a buffer? b. Would you expect there to be more acid or base form of HEPES at this pH (pH 7.8)? c. What are the concentrations of conjugate acid and base at this pH? (Note: The total concentration of the buffer is the sum of the concentrations of the conjugate acid and base.)





