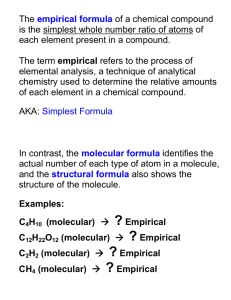
CHAPTER 3 CHEMICAL EQUATIONS AND STOICHIOMETRY MOLECULAR FORMULA A CHEMICAL FORMULA THAT SHOWS THE ACTUAL NUMBER OF ATOMS OF EACH ELEMENT PESENT IN A COUMPOUND EMPIRICAL FORMULA DEFINITION:A formula that shows the simplest ratio of atoms of an element present in a compound. E.g. Molecular formula of glucose:C6H12O6 empirical formula of glucose: CH20 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOLECULAR FORMULA AND EMPIRICAL FORMULA TELLS HOW MANY ATOMS OF EACH ELEMENT ARE IN A COMPOUND AND EMPIRICAL FORMULA TELLS YOU THE SIMPLEST OR MOST REDUCED RATIO OF ELEMENTS IN A COMPOUND. DETERMINING EMPIRICAL FORMULA I. Start with the number of grams of each element,given in the problem II. Convert the mass of each element to moles III. Divide each mole value by the smallest number of moles calculated IV. Round off to the nearest whole number. Determine the empirical formula of a compound contains 2.1% H,65.3% O,and 32.6% of S ( H=1.0 , O=16.0 , S= 32.0 ) HYDROGEN MASS ( GRAMS ) MOLE SIMPLEST WHOLE NUMBER RATIO Thus,the empirical formula of the compound is OXYGEN SULPHUR What is the empirical formula of a compound containing 60.0% sulphur and 40.0% oxygen by mass.(S:32.0 , O:16.0 ) SULPHUR MASS ( GRAMS ) MOLE SIMPLEST WHOLE NUMBER RATIO OXYGEN