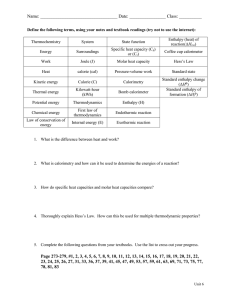
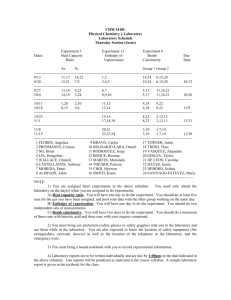
1 – Heat, Calorimetry and Enthalpy Name: 1. How much heat does a 23.0-g ice cube absorb as its temperature increases from -17.4°C to 0.0°C? 2. Copper metal has a specific heat of 0.385 J/g·°C and a melting point of 1083°C. Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 22.8 g of copper from 20.0°C to 875°C. 3. A 15.6-g sample of ethanol absorbs 868 J as it is heated. If the initial temperature of the ethanol was 21.5°C, what is the final temperature of the ethanol? 1 – Heat, Calorimetry and Enthalpy 4. A 77.5-g sample of an unknown solid is heated to 62.5°C and placed into a calorimeter containing 93 g of water at 23.3°C. If the final temperature of the solid sample and the water is 26.2°C, what is the specific heat of the solid? 5. A 50.6-g sample of iron metal is heated and put into 104 g of water at 19.7°C in a calorimeter. If the final temperature of the iron sample and the water is 24.3°C, what was the temperature of the iron sample when it was placed in the water? 6. If 40.0 g of water at 70.0°C is mixed with 40.0 g of ethanol at 10.0°C, what is the final temperature of the mixture? 1 – Heat, Calorimetry and Enthalpy 7. In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 100.0 g of H2O and 100.0 mL of HCl are mixed. The HCl had an initial temperature of 44.6°C and the water was originally at 24.6°C. After the reaction, the temperature of both substances is 31.3°C. a. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? Explain. b. Calculate how much heat the water lost or gained. 8. If 22.0 grams of propane (C3H8) is combusted in a bomb calorimeter containing 3.25 liters of water, calculate the molar heat of combustion of propane if the water temperature rises 29.5°C. 1 – Heat, Calorimetry and Enthalpy 9. From the following data at 25°C, H2(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2 HCl(g) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2 H2O(g) DH = -185 kJ DH = -483.7 kJ Calculate DH at 25°C for the reaction below. 4 HCl(g) + O2(g) ® 2 Cl2(g) + 2 H2O(g) 10. From the following data at 25°C, H2(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2 HCl(g) DH = -185 kJ H2(g) + Br2(g) ® 2 HBr(g) DH = -73 kJ Determine DH for this single-displacement reaction. Cl2(g) + 2 HBr(g) ® 2 HCl(g) + Br2(g) 1 – Heat, Calorimetry and Enthalpy 11. From the following data at 25°C, 2 CO(g) + O2(g) ® 2 CO2(g) DH = -566 kJ 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ® 2 H2O(l) DH = -572 kJ 2 CH3OH(l) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) DH = -1452 kJ Determine DH for the reaction of carbon monoxide and hydrogen to form methanol (CH3OH). CO(g) + 2 H2(g) ® CH3OH(l) 12. Find the standard enthalpy of formation for ethylene, C2H4(g), given the following data. C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) C(s) + O2(g) ® CO2(g) H2(g) + 1 O2(g) 2 ® H2O(l) DH° = -1411 kJ DH° = -393.5 kJ DH° = -285.8 kJ