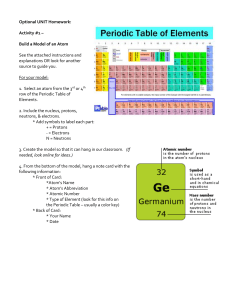
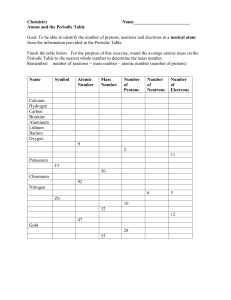
Exercise 1: Produce a time line of events that relates to the changing atomic model. See the tutorial here to make one in word using smart art https://support.office.com/enus/article/create-a-timeline-9c4448a9-99c7-4b0e-8eff-0dcf535f223c Watch this clip as a starter https://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-2-400-year-search-for-the-atom-theresa-doud Must include: Year, who with picture, diagram of model, any evidence they acquired. Print out once complete Exercise 2: Produce a fact sheet on the Rutherford Gold Foil experiment Watch these clips as a starter https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dNp-vP17asI https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XBqHkraf8iE&t=70s Much include: When, who, how, where Diagrams Conclusion drawn Print out once complete Exercise 3: Draw a detailed diagram of Thompsons model and Bohrs model of the atom. Exercise 4: Write a letter to a scientific colleague containing the results like you were Rutherford after completing the Gold Foil experiment Including what he found and why it was different from what he had predicted Exercise 5: Create a table comparing the properties of each subatomic particle Must include: names of the three particles, charge, location in atom, relative size, discovery of. Watch this clip to help. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h6LPAwAmnCQ&index=1&list=PL3hPm0ZdYhywb0pyaNI sXFzIOB3FESr0y 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Exercise 6: Name that element Make a list of the 12 elements that do not have symbols based on their English names. Include the English name, the symbol, the language of the original name and the original name in a table. Find six of the elements named after famous scientists. List the scientist, the name of the element and the symbol. Four of the elements are named after planets. List the name of the planet, the name of the element and the symbol. Four countries and two continents have also been used to name elements. List them including the name of the country or continent and the symbol. Make sure you know the difference between countries and continents. One of the states of the United States of America has an element names after it. Which one? Can you find out why? Superman’s birthplace has the same name as an element. Which element is that? Watch this clip to help https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dRfrvpVdKGM&list=PL3hPm0ZdYhywb0pyaNIsXFzI OB3FESr0y&index=2 Without the use of a computer just a periodic table, complete the table below. Element Symbol Atomic Number Hydrogen 1 Mass Number 2 4 4 B 12 6 6 Nitrogen 7 O 8 9 Ne 10 Na 11 Magnesium 13 Si 10 20 12 24 Aluminium 12 27 28 14 Phosphorus 15 S 16 Cl 18 Potassium 19 16 32 35 Argon 7 16 Fluorine Sulphur 5 11 Carbon Number of neutrons 2 3 Be Boron Number of Electrons 1 He Lithium Number of Protons 18 40 Ca 20 20 20 Exercise 7: Create a 'How to read the periodic table' help sheet: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yADrWdNTWEc Must include: How to identify the individual elements Where to find/calculate the atomic number, atomic mass and number of neutrons What the placement of the element in the table can tell us about it. Exercise 8: Change the order of the items in the last four columns to match the dates of the first column. Date Person Model Description 350 bc Solar system model Atoms consisting of a positive nucleus with electrons in certain orbits of fixed energy called ‘shells’. Thomson 1803 Rutherford ad Indivisible Positively particles— charged atoms spheres with electrons embedded in them. 1897 Chadwick ad Shell model Matter made up of tiny indivisible particles. This model was based on observations of pure substances. Diagram 1909 Democritus Plumad pudding model The atom as mostly empty space with a positively charged nucleus and electrons orbiting the nucleus. 1913 Bohr ad Neutrons in the nucleus All matter made up of tiny building blocks, given the Greek word atomos meaning unable to be divided. 1932 Dalton ad Indivisible The particles— discovery of atomos neutrons explained why an atom was heavier than expected if it contained only protons and electrons. Exercise 9: Draw straight lines matching each term on the left with its definition on the right. atom Negatively charged particle that orbits around the nucleus of an atom. Pure substance made up of atoms of only one type. proton Central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons. neutron Smallest piece of ordinary matter. electron Positively charged sub-atomic particle. nucleus Organised chart of all known elements. element atomic number Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Columns of the periodic table. mass number Metals found in group 1 of the periodic table. atomic mass unit The number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. isotopes Elements found in group 17 of the periodic table. valence electrons Used for measuring the mass of sub-atomic particles. periods Electrons in the outermost shell. groups Rows of the periodic table. alkali metals The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. alkaline earth metals Metals found in group 2 of the periodic table halogens Sub-atomic particle that has no charge. periodic table