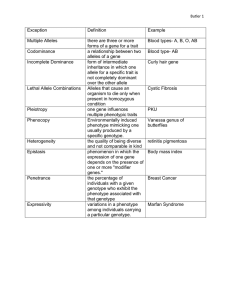
Inheritance The process of physical traits being passed on from one generation to the next The Blending Theory of Inheritance Sperm and egg combine resulting in a blend of parental characteristics Traits Distinguishing characteristics that make up a unique individual Gametes A mature haploid male or female germ cell that can unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote. Charles Darwin English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection Gregor Mendel Augustinian monk and botanist whose experiments in breeding garden peas led to his eventual recognition as founder of the science of genetics Monohybrid cross A mating between two organisms with different variations at one genetic chromosome of interest. Purebred Offspring resulting from a true breeding True breeding A cross that will only produce a certain phenotype Parent generation The first set of parents crossed in which their genotype is the basis for predicting the genotype of their offspring Filial generation A generation in a breeding experiment Hybrid Carries two different alleles of the same gene Dominant An allele or a gene that is expressed in an organism's phenotype, masking the effect of the recessive allele or gene when present. Recessive A gene that can be masked by a dominant gene Latent Being in a condition of biological rest or inactivity Principle of dominance When individuals with contrasting traits are crossed, the offspring will express only the dominant trait Law of segregation Inherited traits are determined by pairs of factors, which segregate, or separate in the gametes (sex cells), with one in each gamete Mendelian ratio The F2 generation resembled one parent from the P generation 75% of the time, and the other parent only 25% of the time Genes The part of the chromosome that regulates the expression of a trait Alleles A gene that occurs in alternate forms Homozygous When both alleles in a gene are the same. Heterozygous When alleles in a gene are different Punnett square A square diagram that is composed of a grid of usually four boxes and is used to calculate and depict all the combinations and frequencies of the different genotypes and phenotypes among the offspring of a cross Genotype Genetic make-up of the organism Phenotype Physical characteristics of the organism