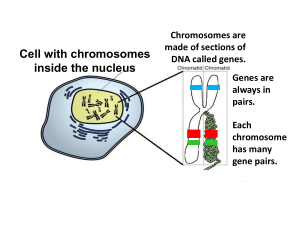
Genetics & Heredity Review Sheet ANSWERS List and describe six steps of the cell cycle in order: 1. Interphase- the cell grows, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares to divide into two cells 2. mitosis:prophase- the chromatin (DNA strands) in the cell’s nucleus condenses to form chromosomes 3. mitosis:metaphase- the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell 4. mitosis:anaphase- the centromeres split and the chromatids separate 5. mitosis:telophase- a new nuclear envelope forms around each region of chromosomes 6. Cytokinesis – the cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two new cells. How many chromosomes do human body cells contain? ____46 _______ How many chromosomes are there in each cell at the end of mitosis? ____46 _______ How many chromosomes are there in each cell at the end of meiosis? _____23 _______ Below are diagrams of two types of cell division (Mitosis and Meiosis). Identify which process is which: meiosis s mitosis What type of cells are produced in this process? (body cells or gametes) What type of cells are produced in this process? (body cells or gametes) Why is mitosis important for living things? (What is its purpose?) Asexual reproduction and general growth and repair of the body. Why is meiosis important for living things? (What is its purpose?) Genetic diversity of organisms through sexual reproduction (crossing over in the chromosomes). What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? Sexual reproduction is the combining of two parents’ genetic material to produce a new organism. Asexual reproduction is when one parent produces offspring that are identical to the parent. What is the benefit to an organism/species to be able to reproduce asexually? The organisms can reproduce rapidly and without the need for another organism’s gametes. What is the benefit to an organism/species to be able to reproduce sexually? There is genetic diversity/variety created through sexual reproduction and it also makes a species less susceptible to diseases. Know how to complete Punnett Squares: _T_ __t__ TT Tt Tt Tt T t _T__ _T__ _t_ Tt Tt _t_ Tt Tt Find the percentages: 9/25 ___36%_____ 17/20 ____85%________ 9/10 _________90%________ 3/5 __________60%_________ If tall (T) is dominant over short (t), complete the following: Write the Genotypes: Homozygous Dominant = __TT___ Homozygous Recessive = __tt___ Heterozygous = __Tt___ If black fur (B) is dominant over white fur (b), complete the following Write the Phenotypes: BB = _____Black_________ Bb = _____Black______________ bb = _____White______________ In pea plants, the allele for green for green pods (G) is dominant over the alleles for yellow pods (g). The table below shows the phenotypes of the offspring produced from a cross of two plants with green pods. Phenotype Green Pods Yellow Pods Number of Offspring 27 9 a. Calculate what percent of the offspring produce yellow pods. 9/36 = 25% b. Calculate what percent of the offspring produce green pods. 27/36 = 75% c. What is the genotype of the offspring with yellow pods? gg d. What are the possible genotypes of the offspring with green pods? GG, Gg e. What are the genotypes of the parents? How do you know? Gg and Gg because they only way two green pods plants can produce a yellow pod plant is if they both carry the allele for yellow pods. In rabbits, the allele for a spotted coat (S) is dominant over the allele for a solid-colored coat. A spotted rabbit was crossed with a solid-colored rabbit. The offspring all had spotted coat. What are the probable genotypes of the parents? Explain how you know. SS for the spotted coat and ss for the solid colored coat because all of the offspring showed the dominant trait which means that the spotted coat rabbit probably could only pass alleles for spotted coat. What would be the probability of getting a bunny with black fur, it the parents are a homozygous black fur (BB) and a homozygous white fur (bb)? ______100% (Bb)__ Study DNA and genetics vocab.