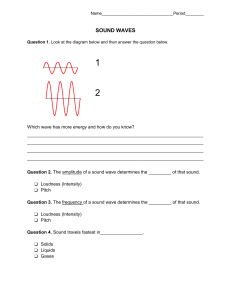
HOW TO IDENTIFY TYPES OF WAVES •In a transverse wave, the particles are displaced perpendicular to the direction the wave travels. •Examples of transverse waves include vibrations on a string and ripples on the surface of water. Figure 1: The parts of the slinky in a transverse wave move vertically up and down while the wave disturbance travels horizontally. HOW TO IDENTIFY TYPES OF WAVES •In a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. •An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky. Figure 2: The parts of the slinky in a longitudinal wave and the wave disturbance travel horizontally. COMMON MISTAKES AND MISCONCEPTIONS •Sometimes people forget wave speed isn't the same as the speed of the particles in the medium. COMMON MISTAKES AND MISCONCEPTIONS •The wave speed is how quickly the disturbance travels through a medium. COMMON MISTAKES AND MISCONCEPTIONS •The particle speed is how quickly a particle moves about its equilibrium position. •A certain sound wave traveling in the air has a wavelength of 322 nm when the velocity of sound is 320 m/s. What is the frequency of this sound wave? F represents frequency, V represents the velocity of the wave, and Λ represents the wavelength of the wave. convert the wavelength into meters, if necessary. If the wavelength is given in nanometers, you need to convert this value into meters by dividing it by the number of nanometers in a single meter. Divide the velocity by the wavelength. Divide the velocity of the wave, V, by the wavelength converted into meters, λ, in order to find the frequency, f. Write your answer. After completing the previous step, you will have completed your calculation for the frequency of the wave. Write your answer in hertz, hz, which is the unit for frequency. VOCABULARY •Intensity – the amount of energy an sound wave carries per second through a unit area. Measured in watts per meter squared. W/m² • Example – when a sound wave carries a large amount of energy, the molecules of the medium move a greater distance as the wave pass by, and the sound has a greater amplitude VOCABULARY •Loudness – sound level, describes what you actually hear. A sound wave of greater intensity sounds louder •Decibels (db) – measures loudness. A sound you can barely hear is 0 db. 100db can damage your ears. INTENSITY DETERMINES LOUDNESS. A sound wave with a higher amplitude and energy is perceived as a louder sound. EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? SECTION OUTLINE INTENSITY DETERMINES LOUDNESS. A sound wave with a lower amplitude and energy is perceived as a softer sound. EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? VOCABULARY FREQUENCY – THE NUMBER OF VIBRATIONS THAT OCCUR PER SECOND IN A SOUND WAVE. MEASURED IN HERTZ. A FREQUENCY OF 50HZ MEANS 50 VIBRATIONS PER SECOND. • WE HEAR SOUNDS WITH FREQUENCIES THAT ARE BETWEEN 20HZ AND 20,000HZ ULTRASOUND – SOUND WAVES WITH FREQUENCIES ABOVE THE NORMAL RANGE OF HEARING INFRASOUND – SOUND WAVES WITH FREQUENCIES BELOW THE HUMAN RANGE OF HEARING EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? VOCABULARY • PITCH – A DESCRIPTION OF HOW HIGH OR HOW LOW A SOUND SEEMS TO A PERSON. • PITCH DEPENDS ON THE FREQUENCY OF A SOUND WAVE • HIGH FREQUENCY MEANS HIGH PITCH • LOW FREQUENCY MEANS LOW PITCH EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? FREQUENCY DETERMINES PITCH. A sound wave with a lower frequency and longer wavelength is perceived to have a lower pitch. A sound wave with a higher frequency and shorter wavelength is perceived to have a higher pitch. EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? PIANO EXAMPLE OF PITCH TENSION - A TIGHTER STRING PRODUCES A HIGHER FREQUENCY. THEREFORE YOU HEAR THE SOUND AT A HIGHER PITCH. LENGTH OF THE STRING - RIGHT SIDE OF THE PIANO HAS HIGHER PITCH, SHORTER STRING. LEFT SIDE OF PIANO HAS LOWER PITCH, LONGER STRING THICKNESS OF A STRING – THICKER MEANS LOWER PITCH EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? VOCABULARY • RESONANCE – WHEN THE FREQUENCY OF THE SOUND WAVE EXACTLY MATCHES THE FREQUENCY OF AN OBJECT EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? DOPPLER EFFECT THE APPARENT CHANGE IN FREQUENCY AS A WAVE SOURCE MOVES IN RELATION TO THE LISTENER EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves? DOPPLER EFFECT • AS A SOUND SOURCE MOVES TOWARD THE LISTENER, THE WAVES REACH THE LISTENER WITH A HIGHER FREQUENCY. THE PITCH APPEARS TO INCREASE BECAUSE OF THE DOPPLER EFFECT CLASS WORK AND HOMEWORK FILL IN • WHAT DID I LEARN • CONFUSED • SAY • READ PAGES O 46 – O 51. • QUESTIONS 1-6, P. O 51 • 2-2 WORKSHEET EQ: How does intensity, loudness, frequency and pitch affect sound waves?