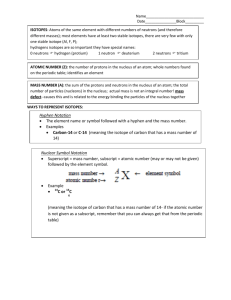
NAME_____________ ________ PERIOD __________ DATE _______________ __ ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND ISOTOPES WORKSHEET 1. Use the periodic table to complete the following table. c. silicon-29 5. How many neutrons does europium-151 have? What is the isotope’s mass number? 6. How many more neutrons does thorium-230 have than protons? How many electrons does thorium-230 have? 2. Give the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in each of the following atoms. a. 108 47 b. 40 20 7. Give the mass number of each isotope. a. Be with 5 neutrons Ag b. Ga with 39 neutrons Ca c. Si with 16 neutrons c. 23 11 Na 3. Name each isotope, and write it in symbolic notation. a. atomic number 26; mass number 56 b. atomic number 29; mass number 64 d. Ti with 26 neutrons 8. Give the atomic number of each isotope. a. magnesium-25 b. bromine-79 c. antimony-121 c. atomic number 17; mass number 37 4. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in each of the following isotopes? a. uranium-235 9. Neon has two isotopes: neon-10 and neon-12. a. Which isotope has the greater mass? b. Which has more neutrons? c. Which has more protons? b. hydrogen-3 d. Which has more electrons? Use the table below to calculate the atomic mass 10. of element X. Then use the periodic table to identify the element. Show all your work. 13. An element has three naturally occurring isotopes. Isotope 1 has a mass of 19.992 amu. Isotope 2 has a mass of 20.994 amu. Isotope 3 has a mass of 21.991 amu. The pie graph shows the relative abundance of each isotope. Magnesium has three isotopes. Magnesium-24 has 11. a percent abundance of 78.99%. Magnesium-26 has a percent abundance of 11.01%. What is the percent abundance of magnesium-25? Assume that there are no other magnesium isotopes. a. Calculate the atomic mass of the element. b. Identify the element, using the periodic table. 12. Calculate the atomic mass of iridium. Iridium has two isotopes. Iridium-191 has a mass of 191.0 amu and a percent abundance of 37.58%. Iridium-193 has a mass of 193.0 amu and a percent abundance of 62.42%. Show all your work. Chemistry: Matter and Change 2 Supplemental Problems 14. An element has three naturally occurring isotopes. Information about each isotope is summarized below. all the isotopes of carbon, including carbon-14. Carbon-14 undergoes radioactive decay continuously. After an organism dies, the carbon-14 in its body continues to decay. However, its body no longer takes in new carbon-14. Thus, by measuring how much carbon-14 a once-living object contains and comparing it with the amount of carbon-14 in a currently living thing, you can determine the age of the object. a. In terms of subatomic structure, how does carbon14 differ from carbon-12 and carbon-13? b. How is carbon-14 like carbon-12 and carbon-13? c. Carbon-14 emits a beta particle as it decays. What atom does carbon-14 decay to? d. Write an equation to represent the decay of carbon-14. a. Find the atomic mass of this element. Show all your work. b. Identify the element, using the periodic table. c. Write each isotope in symbolic notation. 15. The isotope carbon-14 can be used to determine the ages of objects that were once living, such as wood, bones, and fossils. While alive, living things take in Chemistry: Matter and Change 3 Supplemental Problems Answer Key b. atomic number 29; mass number 64 Chapter 4 1. Use the periodic table to complete the following table. copper-64; 64 29 Cu Atomic number number of protons number of electrons c. atomic number 17; mass number 37 chlorine-37; 37 17 Cl 4. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in each of the following isotopes? Atomic number number of protons number of electrons Number of neutrons mass number atomic number a. uranium-235 2. Give the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in each of the following atoms. 92 protons, 92 electrons, 143 neutrons (23592 143) Atomic number number of protons number of electrons b. hydrogen-3 Number of neutrons mass number atomic number a. 108 47 1 proton, 1 electron, 2 neutrons (3 1 2) Ag c. silicon-29 47 protons, 47 electrons, 61 neutrons (10847 61) b. 40 20 14 protons, 14 electrons, 15 neutrons (2914 15) Ca 5. How many neutrons does europium-151 have? What is the isotope’s mass number? 20 protons, 20 electrons, 20 neutrons (4020 20) c. 23 11 Number of neutrons mass number atomic number Na 151 63 88 neutrons 11 protons, 11 electrons, 12 neutrons (2311 12) The mass number is 151. 6. How many more neutrons does thorium-230 have than protons? How many electrons does thorium-230 have? 3. Name each isotope, and write it in symbolic notation. a. atomic number 26; mass number 56 iron-56; 56 26 Fe Chemistry: Matter and Change 4 Supplemental Problems Answer Key (continued) Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number c. antimony-121 230 90 140 neutrons 51 Difference between the number of protons and the number of neutrons 140 90 50 10. Neon has two isotopes: neon-10 and neon-12. a. Which isotope has the greater mass? Therefore, thorium-230 has 50 more neutrons than it does protons. Atomic number number of protons number of electrons neon-12 Therefore, thorium-230 has 90 electrons. b. Which has more neutrons? 7. Show that the mass number and the number of protons are conserved in the following nuclear 230 equation: 234 92 U 90Th He. neon-12 c. Which has more protons? Nuclear equation: 234 92 U Th He 230 90 Mass number: 234 2304 Atomic number: 92 902 They have an equal number of protons. d. Which has more electrons? They have an equal number of electrons. 8. Give the mass number of each isotope. Number of neutrons number of protons mass number 11. Use the table below to calculate the atomic mass of element X. Then use the periodic table to identify the element. Show all your work. a. Be with 5 neutrons 5 neutrons4 protons 9 b. Ga with 39 neutrons 39 neutrons31 protons 70 c. Si with 16 neutrons 16 neutrons14 protons 30 Mass contribution (mass)(percent abundance) X: (15.995 amu)(99.762%) 15.957 amu 16 d. Ti with 26 neutrons X: (16.999 amu)(0.038%) 0.0065 amu 17 X: (17.999 amu)(0.20%) 0.036 amu 18 26 neutrons22 protons 48 Atomic mass of X 15.957 amu 0.0065 amu 0.036 amu 16.000 amu 9. Give the atomic number of each isotope. From the periodic table, a. magnesium-25 The element is oxygen. 12. Magnesium has three isotopes. Magnesium-24 has a percent abundance of 78.99%. Magnesium-26 has a percent abundance of 11.01%. What is the percent abundance of magnesium-25? Assume that there are no other magnesium isotopes. 12 b. bromine-79 35 Chemistry: Matter and Change 5 Supplemental Problems Answer Key (continued) a. Calculate the atomic mass of the element. All the percentages should add up to 100%. Therefore: Mass contribution (mass)(percent abundance) Isotope 1: (19.992 amu)(90.51%) 18.09 amu Isotope 2: (20.994 amu)(0.27%) 0.057 amu Isotope 3: (21.991 amu)(9.22%) 2.03 amu Atomic mass 18.10 amu0.057 amu 2.03 amu 0.18 amu 100% (percent abundance of magnesium-24)(percent abundance of magnesium-25)(percent abundance of magnesium-26) 100% 78.99%(percent abundance of magnesium25)11.01% Percent abundance of magnesium-25 100%(78.99%11.01%) 10.00% b. Identify the element, using the periodic table. 13. Calculate the atomic mass of iridium. Iridium has two isotopes. Iridium-191 has a mass of 191.0 amu and a percent abundance of 37.58%. Iridium-193 has a mass of 193.0 amu and a percent abundance of 62.42%. Show all your work. The element is neon. 15. An element has three naturally occurring isotopes. Information about each isotope is summarized below. Mass contribution (mass)(percent abundance) Ir-191: (191.0 amu)(37.58%) 71.78 amu Ir-193: (193.0 amu)(62.42%) 120.5 amu Atomic mass of Ir 71.78 amu 120.5 amu 192.3 amu 14. An element has three naturally occurring isotopes. Isotope 1 has a mass of 19.992 amu. Isotope 2 has a mass of 20.994 amu. Isotope 3 has a mass of 21.991 amu. a. Find the atomic mass of this element. Show all your work. Mass contribution (mass)(percent abundance) Isotope 1: (23.985 amu)(78.70%) 18.88 amu The pie graph shows the relative abundance of each isotope. Isotope 2: (24.946 amu)(10.13%) 2.531 amu Isotope 3: (25.983 amu)(11.17%) 2.902 amu Atomic mass of element 18.88 amu 2.527 amu2.902 amu 24.31 amu b. Identify the element, using the periodic table. The element is magnesium. c. Write each isotope in symbolic notation. 24 12 Mg , 25 12 Mg , 26 12 Mg 16. The isotope carbon-14 can be used to determine the ages of objects that were once living, such as wood, bones, and fossils. While alive, living things take in all the isotopes of carbon, including carbon-14. Carbon-14 undergoes radioactive decay continuously. Chemistry: Matter and Change 6 Supplemental Problems Answer Key (continued) After an organism dies, the carbon-14 in its body continues to decay. However, its body no longer takes in new carbon-14. Thus, by measuring how much carbon-14 a once-living object contains and comparing it with the amount of carbon-14 in a currently living thing, you can determine the age of the object. c. Carbon-14 emits a beta particle as it decays. What atom does carbon-14 decay to? a. In terms of subatomic structure, how does carbon14 differ from carbon-12 and carbon-13? d. Write an equation to represent the decay of carbon-14. If carbon-14 emits a beta particle, then it must become nitrogen-14 (1 x 6; thus, x 7, which is the atomic number of nitrogen). The equation that shows this change is 14 14 6 C 7 N . Carbon-14 has 8 neutrons, carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, and carbon-13 has 7 neutrons. Carbon-14 has a larger atomic mass than the other two isotopes have. b. How is carbon-14 like carbon-12 and carbon-13? All three isotopes have 6 protons and 6 electrons. They all show the same physical and chemical properties of the element carbon. Chemistry: Matter and Change 7 Supplemental Problems