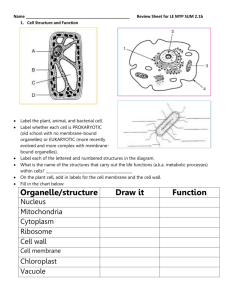
2.1a What is the primary function & specific activities of each lobe of the brain? Region Location Front top corner Posterior to frontal lobe Anterior to the occipital lobe. Lateral to the pons and medulla oblongata. Posterior cranial fossa Inferior to the occipital lobe, anterior of temporal lobe Anterior edge of cerebellum & inferior edge of temporal lobe 2.1b Label the lobes of the brain: Primary Function Specific Activities and Processes 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals _____________ System Chemical Signals _____________ System Word Bank (words can be used more than once): Axon / Axons Neuron’s dendrites Synapse / Synapses Axon terminals Neuron/ Neurons Synaptic cleft Action potential Neurotransmitters Dendrites The nervous system is made up of ____________. ____________ communicate just like people do, but they send messages using _______________________ (electricity passing through their _________). Each __________ picks up signals at its _____________, passes the signals down the __________, into the ______________________, and into the ________________. The _______________ then drops _____________________________ into the ___________________ between the first _____________________the next ____________________. That signals ___________ #2 to pass the message on. 2.2.b What is the basic structure and function of a neuron? Function Structure Sends electrical signals through body Dendrites (“trees”)— Axon— Myelin Sheath— Nodes (“knots”) of Ranvier— Axon Terminals (“ends”) — Synapses— Synaptic Cleft— Neurotransmitters (“to carry across a nerve”) Give specific examples — 2.2.c How do the different types of neurons work together to send and receive signals? Send info from PNS to CNS Found in CNS In PNS, receive info from CNS 2.2.d How are electrical impulses created in the human body? Na+/K+ pump keeps outside of membrane ___ and inside ___ by pumping positive ______ out of the membrane, priming the membrane to carry charges During an __________________, there’s a sudden reversal of _________, carrying a message down the axis Put the following statements in the correct order of events that happens during a reflex arc. Put the correct number, 1-14, in the blanks provided. Label the following picture: _____ Generation of the action potential. _____ Depolarization of cell membrane. _____ Dendrite receives a stimulus. _____ Repolarization occurs. _____ Action potential arrives at the axon terminal. _____ The neuron makes and stores neurotransmitters in the vesicles. _____ Vesicles in the axon terminal fuse with the plasma membrane. _____ Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft. _____ Ion channels close and action potential moves down the axon. _____ Ion channels open allowing Na+ ions to move through the membrane. _____ Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the receiving neuron’s membrane. _____ Neurotransmitters are released and move across the synaptic cleft. _____ Action potential moves down the axon. _____ Calcium channels open and calcium ions move into the neuron. 2.2.e How do neurons convey information using both electrical and chemical signals? Electrical _____________________ down axis of Chemical ____________________ conduct each neuron (________________ each neuron) signals ______________neurons 2.2.f What factors impact our ability to react to a stimulus? 2.2.g How and why does reaction time differ in reflex and voluntary actions? Reflex— Voluntary— 2.2.h How do errors in communication impact homeostasis in the human body? Epilepsy Parkinson’s Huntington’s Alzheimer’s Multiple Sclerosis Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's) 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? Neurologist – Pharmacists – Researchers – Nurses – Brain surgeons – Psychiatrists – Physical therapist –