jeopardy-2.ppt
advertisement
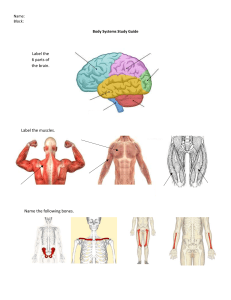
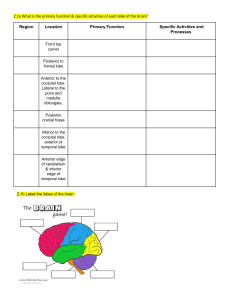
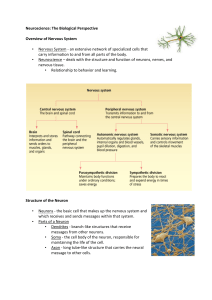
All about the Neuron The Mighty Neurological Neuroscience Come to Brain Disorders Methods Your Senses 1 pt 1 pt 1 pt 1 pt 1 pt 2 pt 2 pt 2 pt 2 pt 2 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 4 pt 4 pt 4 pt 4 pt 4 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt Another name for a “nerve cell.” What is a neuron? The part of the neuron that brings information to the cell body. What is a dendrite? The part of the neuron that takes information away from the cell body. What is the axon? The junction between two neurons. What is a synapse? The explosion of electrical activity sent down an axon when a neuron sends information. What is an action potential? The weight of the adult human brain. What is about 3 pounds or 1.4 kilograms? The two main divisions of the nervous system. What are the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system? Area of the brain responsible for thought, language and planning. What is the cerebral cortex? Connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain. What is the corpus callosum? Name of the man who survived after an iron rod went through the frontal lobe of his brain in 1848. Who is Phineas Gage? Memory loss, dementia, depression, social withdrawal; plaques and tangles. What are symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease? Disease characterized as an electrical “brainstorm.” What is epilepsy? Excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations. What are symptoms of narcolepsy? Transmitted by ticks; joint pains, chills, fever and headache. What is Lyme disease? Weakness, paralysis, death of neurons in the motor cortex and spinal cord; named for a famous baseball player. What is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? (Lou Gehrig’s Disease) General term for someone who studies the nervous system. What is a neuroscientist? Uses detection of radio frequency signals produced by displaced radio waves in a magnetic field. What is MRI? (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Electrical activity of the brain recorded with scalp or brain electrodes. What is an EEG? (Electroencephalography) Scanning method that detects radioactive material that is injected or inhaled to produce an image of the brain. What is PET? (Positron Emission Tomography) Brain scan that uses a series of X-ray beams passed through the head. What is a CT scan? (Computed Tomography Scan) Another name for the sense of sight. What is vision? Lobe of the brain important for hearing. What is the temporal lobe? Sour, sweet, salty, bitter and umami. What are the five basic tastes? Free nerve endings, Pacinian corpuscles, Ruffini endings. What are sensory receptors in the skin? Location of photoreceptors in the eye. What is the retina?