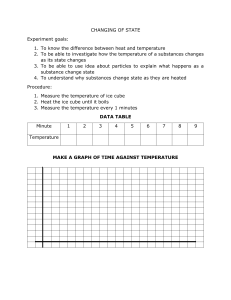
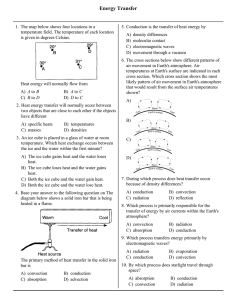
TEST NAME: Heat Transfer TEST ID: 3527706 GRADE: 05 - Fifth Grade SUBJECT: Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Heat Transfer Page 1 of 8 Student: Class: Date: 1. Sandra washed her hair. She dried it with warm air from a blow dryer before going to school. Which statement BEST explains why the blow dryer was able to dry Sandra’s hair quickly? A. The blow dryer used electricity. B. C. The blow dryer transferred heat. The blow dryer created sound waves. D. The blow dryer used mechanical energy. Heat Transfer Page 2 of 8 2. The area in front of a fire feels warm on a cold evening. What are the processes that cause the person in front of the fire to feel warm? A. B. C. D. conduction and convection radiation and conduction radiation and convection radiation, convection, and conduction Heat Transfer Page 3 of 8 3. Yuko designed an experiment to test the effect of heating and cooling on air. She blew up two balloons to similar sizes and measured their circumferences. She placed one balloon in a freezer for one hour and left the second balloon on the table. After one hour she measured their circumferences again. She then left both balloons on the table for one more hour. The graph below shows the change in the sizes of the balloons during the experiment. Which statement BEST explains the differences seen between the two balloons during the experiment? A. B. C. D. 4. Air contracts when cooled but is not affected by warming. Cooling causes air to contract and heating causes air to expand. Balloons put more pressure on cold air than room temperature air. Freezing causes balloons to contract and thawing causes them expand. Manuel was having trouble opening a new glass jar of pickles. His father told Manuel to hold the metal lid of the jar under running hot water for a few seconds, then try again. Then the lid opened easily. What is the MOST likely reason Manuel’s father suggested using hot water to loosen the lid? A. B. C. D. Glass contracts when it is heated. Metals expand when they are heated. Metals are easier to grip when they are warm. Hot water reduces friction between metal and glass. Heat Transfer Page 4 of 8 5. This illustration shows how heat can move through the atmosphere as air circulates. What causes the circulation of air? A. B. C. D. Air in the atmosphere is heated by the Sun and sinks to the ground. The ground is heated by the Sun and then heats the air, causing the air to rise. Air loses heat to the ground and then rises upward to obtain more energy. The Sun heats the clouds which forces the cooler air to move away and sink. Heat Transfer Page 5 of 8 6. Although the heat source is at the bottom of the beaker, all of the water is the same temperature. What keeps the water at the top of the beaker the same temperature as that of the bottom? A. B. C. D. 7. Heat from the burner radiates through the liquid and causes even heating. Evaporation heats the water at the top and the flame heats the water at the bottom. The walls of the beaker reflect heat toward the center, so the water heats evenly. Heated water molecules and steam rise in the beaker, carrying heat by convection. A dark-colored wall becomes warm when the sun shines on it. After sunset, a person standing a meter away can feel warmth from the wall. How does heat transfer from the wall to the person? A. B. C. D. radiation conduction convection insulation Heat Transfer Page 6 of 8 8. Anya placed an ice cube on the sidewalk on a warm day. The ice cube soon melted to form a puddle. What process caused the ice cube to melt? A. B. C. D. 9. Clarissa wants to determine the best material to make a new type of cookware. What type of material should she choose? A. B. C. D. 10. B. C. D. Submerge each rod in ice water to find out which loses the most heat. Place the three rods in a freezer to find out which becomes the coldest. Place one end of each rod in very hot water to find out which becomes hot the fastest. Place the rods on a table in a warm room and find out which feels warmest after a period of time. What conditions are necessary for heat conduction to occur between two objects? A. B. C. D. 12. A material that conduct heats evenly. A material that can be easily bent into shape. A material that does not transmit electricity. A material that will remain cool to the touch. Kayla has a wooden rod, a steel rod, and a glass rod. How could she compare the materials to find out which transfers thermal energy BEST? A. 11. Heat transferred through the ice cube by convection. Heat transferred from the air to the ice cube by radiation. Heat transferred from the air and the pavement by conduction. Heat transferred through the ice cube into the pavement by conduction. The objects must be surrounded by air or water. Two objects at different temperatures are touching one another. Two objects at different temperatures are located close to one another. One object must emit energy as light and heat and another object absorbs the energy. An engineer can choose from four different materials to make a heat-resistant handle for a stirring spoon. Which material is LEAST likely to get hot when the spoon is placed in boiling water? A. B. C. D. Ceramic Wood Glass Iron Heat Transfer Page 7 of 8 13. A small ice cube at a temperature of 0°C is dropped into a glass of water at 28°C and melts. What is the temperature of the water in the glass just after the ice cube melts? A. B. C. D. 14. What causes your skin to feel warm when it is in the sun on a summer day? A. B. C. D. 15. 0°C between 0°C and 28°C 28°C greater than 28°C Particles in the atmosphere reflect energy from the Sun downward. Hot particles from the Sun still carry some heat when they reach your skin. The solar wind carries heated air from the Sun’s atmosphere to Earth’s surface. The Sun radiates energy that passes through space and the atmosphere to your skin. What is the original source of most of the energy that people use? A. B. C. D. Energy that reaches Earth’s surface by radiation from the Sun. Energy that reaches Earth’s surface by convection from the Sun. Energy that reaches Earth’s surface by radiation from Earth’s core. Energy that reaches Earth’s surface by conduction from Earth’s core. Heat Transfer Page 8 of 8