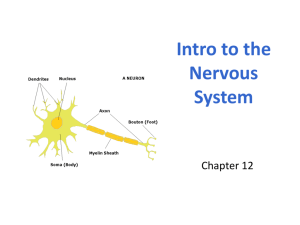
Nicole Garcia Borjas PSY1012 Neuroscience and Behavior – 8/22/19 Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system - Conduct electricity in body Made of 3 parts - Soma (Cell body) - Dendrite -Axon (covered in Myelin), main tube and branches on the sides SOMA - houses the nucleus - nucleus houses genetic material Chromosomes -looks like an X - made of long strings of genes - Genes: subsections of the chromosomes that produce proteins - 46 in body (23 from each parent) - located in every neuron within your nervous system Genes & Cellular Signaling - genes create hormones - hormones are released from the cell into the surrounding blood supply - hypothalamus and pituitary gland are two common areas that generate hormones - Hormones control behaviors: - feeding (hunger, fullness) - emotions - sexual responsiveness (pre/post puberty) - wakefulness (sleep-wake cycle) Dendrite - Bring charged particles (ions) into a neuron - Lead to the soma where they are accumulated about 1 millisecond Soma - if there is sufficient signal strength (+10mV) during this 1 millisecond period, then this cell will produce its own signal at the axon hillock Axon - Each new action potential develops in the axon hillock - Each one has the same strength (+40 mV) - Action potentials from different cells can have different speeds - Cells fire by the All- or-None law - if it doesn’t fire, it remains at -70 -only place where electricity exists Interconnecting Neurons Vesicles filled with neurotransmitters in the presynaptic neuron are pushed against the cell wall Vesicles merge with the cell wall Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic gap - They land on their binding sites at the postsynaptic membrane - Mechanical properties of binding cause them to be released and move toward the presynaptic membrane - The neurotransmitter undergo reuptake. Basic rules of Psychopharmacology - Shapes of NT’s &receptors - Each NT has its own chemical shape and therefore a unique receptor with which It binds - Behavior altering drugs- drugs that have shapes similar to the naturally occurring NT’s - Drugs from these classes may also modify psychological characteristics for treatment purposes as well -Depression - Anxiety - Hallucinations - Thought disorders - Neurotransmitter Pathways - Each neuron typically carries only one class of neurotransmitter - Neurons generally only communicate w similar neurons - This produces NT pathways in the brain - NT pathways are anatomically isolated from the surrounding cellular pathways NT, pathways &brain processing - Each area of the brain is involved in one general classification of activity - Sensory processing or motor processing - NT pathways will be a part of one of these areas - NT type, specific brain area, and sensory/motor processing are strongly correlated Interconnecting Neurons Sensory neurons- neurons that bring information into the brain from sensory receptors - Sensory pathway Motor neurons- send information from the brain to the muscles - Motor pathway Interneurons- link sensory neurons to motor neurons - Brain circuits Input-Output Nervous System - All sense reception signals pass through specific unchanging pathways in the nervous system - All motor output signals pass through specific unchanging pathways in the nervous system - The interneuron pathways in the brain change regularly This gives us a sensory input >>>motor output system w/intervening adaptable connections Neuroplasticity refers to these adaptable connections everything it does to repair or rewire itself. The brain rewires itself every day, usually when asleep (REM sleep) Neuroanatomy 2 main branches of the nervous system Central nervous system – brain/spinal cord Peripheral nervous system – everything else Neurons can be lined up and regrown (ex. Gotham) All encased in bone, and surrounded by cerebral spinal fluid, always used and working 100% of the time >> (everything is available to be used) Brain Stem Medulla – heart rate & breathing Cerebellum – coordination & balance Reticular Formation – alertness Thalamus – central location of all sensory input, involved in sensory integration Limbic System – controls emotions - Expression & detection of emotional behavior - Always working, all behavior has emotional component Reward Center – located in limbic system - Any behavior consequence w/ reward will increase in frequency - drug addt - learned relations through social attention (ex someone says thank you and it makes you feel good) - Damage or drugs that reduce its activity cause a reduction in pleasant emotions - long term use of MDMA (Ecstasy) causes reductions in dopamine and serotonin concentrations in reward center >>>> permanent low-grade depression Cortex - 4 lobes - Parietal – touch and vestibular input - Occipital – visual input - Temporal –auditory & gustatory/ olfactory input - Frontal – planning and model output - Each lobe has a primary and association cortex -Primary cortexes are used for initial sensory input or final motor output