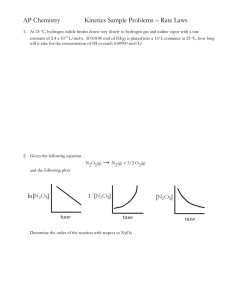
Riverdale Collegiate Institute June Examination 2016 Chemistry, Grade 12, University Preparation (SCH4U1) STUDENT’S NAME:_________________________________ HOME FORM: ______ Circle the name of your teacher Mr. Dermer Ms. Likins Friday, June 17th, 2016 9:00 – 11:00 am 2 hours 13 (including this one) 85 Date: Time: Duration of Exam: Total Number of Pages: Total Number of Marks: SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS: PART A: Using only PENCIL, record the best answer in the SCANTRON sheet provided. Additional time will not be given to complete the Scantron card. PART B: Complete each question in the space provided. Non-programmable calculators may be used, but may not be shared. Tabular values are located at the BACK of the exam paper and may be detached for convenience. Should you require additional space to answer a question from PART B, use the back side of the page containing that particular question. Be sure to make a clear indication that the back side of the page is to be marked. Examination Breakdown: EXAM PART TOTAL MARKS PART A Multiple Choice (40 questions) 40 MARKS 50 MINUTES PART B Full Solutions (9 questions) 45 MARKS 65 MINUTES REVIEW EXAM SUGGESTED TIME 5 MINUTES 85 MARKS TOTAL 120 MINUTES Mark breakdown by unit Part A: Multiple Choice Part B: Short Answers Total Unit 1 7 Unit 2 12 Unit 3 6 Unit 4 10 Unit 5 5 Total 40 9 10 5 14 8 14 18 29 5 21 45 85 Unit 1: Electrochemistry Unit 2: Unit 3: Unit 4: Unit 5: Atomic Structure and Bonding Organic Chemistry Thermodynamics and Kinetics Chemical Equilibrium Periodic Table 1 1 H 1.01 18 2 He 2 4 Be 13 5 B 14 6 C 15 7 N 16 8 O 17 9 F 4.00 3 Li 6.94 9.01 10.81 12.01 14.01 16.00 18.99 20.18 11 Na 12 Mg 13 Al 14 Si 15 P 16 S 17 Cl 18 Ar 22.99 24.31 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 26.98 28.09 30.97 32.06 35.45 39.95 19 K 20 Ca 21 Sc 22 Ti 23 V 24 Cr 25 Mn 26 Fe 27 Co 28 Ni 29 Cu 30 Zn 31 Ga 32 Ge 33 As 34 Se 35 Br 36 Kr 39.10 40.08 44.96 47.90 50.94 51.99 54.94 55.85 58.93 58.71 63.55 65.37 69.72 72.59 74.92 78.96 79.90 83.80 37 Rb 38 Sr 39 Y 40 Zr 41 Nb 42 Mo 43 Tc 44 Ru 45 Rh 46 Pd 47 Ag 48 Cd 49 In 50 Sn 51 Sb 52 Te 53 I 54 Xe 85.47 87.62 88.91 91.22 92.91 95.94 99 101.07 102.91 106.4 107.87 112.40 114.82 118.69 121.75 127.60 126.90 131.30 55 Cs 56 Ba 57 La 72 Hf 73 Ta 74 W 75 Re 76 Os 77 Ir 78 Pt 79 Au 80 Hg 81 Tl 82 Pb 83 Bi 84 Po 85 At 86 Rn 132.91 137.34 138.91 178.49 180.95 183.85 186.2 190.2 192.2 195.09 196.97 200.59 204.37 207.19 208.98 210 210 222 87 Fr 88 Ra 89 Ac 104 Unq 105 Unp 106 Unh 107 Uns 223 226 227 261.11 262.11 263.12 262.12 58 Ce 59 Pr 60 Nd 61 Pm 62 Sm 63 Eu 64 Gd 65 Tb 66 Dy 67 Ho 68 Er 69 Tm 70 Yb 71 Lu 140.12 140.91 144.24 147 150.35 151.96 157.25 158.92 162.50 164.93 167.26 168.93 173.04 174.97 90 Th 91 Pa 92 U 93 Np 94 Pu 95 Am 96 Cm 97 Bk 98 Cf 99 Es 100 Fm 101 Md 102 No 103 Lw 232.04 231 238.03 237 242 243 247 249 251 254 253 256 254 257 10 Ne SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute SCH4U1 – Review Standard Reduction Potentials Riverdale Collegiate Institute SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Exam Review: Breakdown of topics by unit Unit 1: Redox Oxidation number Oxidation Reduction Galvanic cells Balancing Redox Equations Oxidizing / Reducing agent Labs Electrolytic cells Unit 2: Structure and Properties Nuclear Atomic model Quantum model Electron configuration Orbitals Explaining multiple valences Periodicity Bonding models VSEPR Molecular shape and polarity Intra/intermolecular forces Labs Unit 3: Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbons Alcohols Carboxylic acids Aldehydes / Ketones Ethers Properties Reactions Organic halides Aromatics Esters Amines Amides Labs Unit 4: Energy Changes and Rates of Reaction Heat / Thermal Energy Measuring the rate of reaction Factors that affect the rate of a reaction Q=mcT Calorimetry Collision Theory Heats of Formation Reaction mechanism Hess’s Law Activation energy Enthalpy diagrams Potential energy diagrams Entropy Gibbs Free Energy Labs Unit 5: Equilibrium and Acid/Base Chemistry Closed systems Approximation method Equilibrium expression Le Chatelier’s Principle SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Review questions from Chemistry 12,McGraw-Hill Unit 1(pg. 112): 1,2,5,10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 22, 26, 27 Unit 2 (pg. 214): 1-56 Unit 3(pg. 112): 1-45 (Skip 10,12,13,16,17,22,23,27,35,36,37,38,39,41,44) Unit 4 (pg 316): 1- 38 (Skip 34) Unit 5 (pg 458): 1- 43 (Skip 10,11,28,33,35,38,39,41) Additional Questions 1. Compare and contrast the following forces by filling in the table below Type of force Intramolecular Intermolecular London / Van der Waals Particles involved Model Individual strength (kJ/mol) 0.05-40 Dipole-Dipole 5-25 Hydrogen Bond 10-40 Ion-dipole 40-600 Metallic 75-1000 Electrostatic 150-1100 Covalent 400-4000 2. Using knowledge from the organic chemistry, and structure and properties unit predict the relative boiling points of the following molecules. Justify your answer. Butanoic acid Ethoxyethane 2-butanone 2-butanol Ethyl ethanoate butanamine N-ethyl butanamide 2-butene Butane 2-methylpropane Example SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute SCH4U June Exam Review Package (Chapter 1 – Chapter 10 (inclusive)) Unit 1 - Organic Chemistry - Chapter 1 & 2: 1. Name and draw the isomers of C5H12 2. a) Which of the following formulas correspond with an alkane? i) C2H4 ii) C6H14 iii) CH3 iv) C4H10 b) Which of the following formulas correspond with a cycloalkane? i) C2H4 ii) C3H6 iii) C4H8 iv) C5H10 v) C10H22 v) C8H18 3. Circle and identify the functional groups in the molecule below. If it is an alcohol or amine, then indicate if it is primary, secondary, or tertiary: H2N N O O NH O O O O OH H2N HO OH O HO 4. Rank the following molecules according to their boiling point (from lowest to highest): butan-1-ol, butanoic acid, butane, cis-but-2-ene, butan-1-amine, butanone, methyl propanoate, 1methoxypropane 5. For the following reactions, draw the product(s) using any structural diagram, provide their IUPAC names, and identify the type of reaction a) b) c) d) e) f) g) ethanol + propan-2-ol methanol + butanoic acid ethanamine + ethanoic acid butan-2-ol + [O] 2-methylpent-2-ene + H2O hept-3-ene + HCl propan-1-amine + chloroethane 6. Name the following molecules using IUPAC: a) b) c) F OH OH Br O d) e) f) O HO O OH O OH 7. Draw the following compounds: a) 4-amino-2-chlorohex-1-en-5-yn-3-ol c) cycloocta-1,7-dien-1-ol e) propyl 2-hydroxypropanoate b) 2-amino-3-methylcyclohexanone d) 5-tert-butyl-8-hydroxy-7-oxodecanal f) butoxymethanol SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Unit 2: Structure and Properties - Chapter 3 & 4: 1) Complete the table below: Molecule Lewis Structure VSEPR Notation Name of Molecular Shape Polar Molecule? (Yes or No) SCl2 NSF3 H3O+ SF6 FCl22. State the n, l, and ml values for these orbitals: n M ml (all values) 4s 3d 5f 3. In each case, name the element with the following valence electron configuration a) 1s2 b) 6s24f145d1 c) 3s23p4 d) 4s13d10 4. Explain what n, l, ml, and ms represent 5. Define ionization energy (I.E.) and electron affinity (E.A.). Explain the periodic trends for each. Suggested Text Questions: Chapter 3 Review: pg. 159-160 #4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 13, 14, 16, 19 Chapter 4 Review: pg. 209-210 #2, 3, 5-7, 9, 15, 16, 19, 29, 30 Unit Review: pg. 214 – 216 #1, 2, 3, 5-9, 15-17, 20, 30-32, 36-40, 42, 51 Unit 3: Energy Changes and Rates of Reaction Chapter 5: 1) Two reactions are given by the following equations: X(g) + W (g) → Z(g) + Y(g) + 30.0 kJ Z(g) + Y(g) + 25 kJ → P(g) Find the ∆Hº value for the reaction P(g) → X(g) + W (g). 2) Use the data table of standard enthalpies of formation to help determine the enthalpy of reaction for each of the following reactions. (a) N2O4(g) + 3CO(g) → N2O(g) + 3CO2(g) (b) 4FeS2(s) + 11O2(g) → 8SO2(g) + 2Fe2O3(s) 3) a) Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of glucose, C6H12O6(s), to form carbon dioxide gas and water. b) When a 2.000 g sample of glucose is burned in a calorimeter, the temperature of 200.00 g of water rises by 37.3ºC. What is the molar enthalpy of combustion of glucose? 4) Using the data table on standard enthalpies of formation, determine the heat absorbed when a 5.00 g sample of Fe2O3(s) undergoes the following reaction. 6Fe2O3(s) → 4Fe3O4(s) + O2(g) Recommended Textbook Review Questions: Page 235 #5-8 Page 238-9 #9 – 12 Page 247 #13-16 Page 254 #21-24 (for #24a also answer using bond enthalpies: answer: -751 kJ/mol Page 333 #3,4 Chapter 6: 1) Given the following reaction: D+E F+G Assume that this reaction has a two step mechanisms. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction that correctly incorporates each of the following labels: Potential Energy Reaction Progress SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute ΔH = -75 kJ Ea(rev) = 100 kJ Transition State Intermediate A + B D+E F+G a) Is this reaction exo- or endothermic? b) Determine Ea(fwd) for this reaction. Add this value to your diagram c) Show how your diagram would change if a catalyst was present. 2) An investigation is carried out in which evidence is collected for the following hypothetical chemical reaction: W + 2X + 2Y Z (W, X, and Y could be either elements or compounds, but Z is a compound) a) What is the rate law equation for the reaction? b) What is the rate-determining step? c) What is a possible mechanism, including the slow step? d) Determine the instantaneous rate when [W] = 0.05 mol/L; [X] = 0.1 mol/L; [Y] = 0.002 mol/L Text questions: Pg 284 # 5 – 8 Pg 288 # 1 – 7 Pg 301 # 17 – 20 Pg 309 #6, 7, 9 SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Unit 4: Equilibrium Chapter 7: 1) Scientists and technologists are particularly interested in the use of hydrogen as a fuel: 2 H2(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g) K = 1 x 1080 at SATP What interpretation can be made about the relative proportions of reactants and products in this system at equilibrium? 2) Predict the shift in the following equilibrium system resulting from each of the following changes. 4 HCl(g) + O2(g) 2 H2O(g) + 2 Cl2(g) + 113 kJ (a) an increase in the temperature of the system (b) an increase in the volume of the container (c) an increase in the concentration of oxygen (d) the addition of a catalyst (e) addition of Ne(g) at constant volume 3) For each example, predict whether, and in which direction, the equilibrium is shifted by the change imposed. Explain any shift in terms of changes in forward and reverse reaction rates. 4) In a container at high temperature, ethyne (acetylene) and hydrogen react to produce ethene (ethylene). The equilibrium constant is 0.072.At a specific time, the substance concentrations are [C2H2(g)] = 0.40 mol/L, [H2(g)] = 0.020 mol/L, and [C2H4(g)] = 3.2 x10–4 mol/L. Predict the direction of the reaction shift. 5) For the reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) 2 HBr(g) K = 12.0 at t°C calculate the concentrations of all three substances at equilibrium, if the following amounts of reactants are mixed in a 2.00-L reaction container. (a) 8.00 mol of hydrogen and 8.00 mol of bromine (b) 12.0 mol of hydrogen and 12.0 mol of bromine (c) 12.0 mol of hydrogen and 8.00 mol of bromine 6) CO(g) + H2O(g) CO2(g) + H2(g) K = 4.00 at 900°C In a container, carbon monoxide and water vapour are in the process of reacting to produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The concentrations are: [CO(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, [H2O(g)] = 2.00 mol/L, [CO2(g)] = 4.00 mol/L, and [H2(g)] = 2.00 mol/L. Determine the direction in which the reaction proceeds to establish equilibrium. 7) Predict the algebraic sign of the entropy change for each of the following reactions: 8) Calculate the value of ΔG0 for the following reactions and interpret the results: Text Questions Pg 333 #2-4 Pg 347 #11-14 Pg 349 - 350 #16 – 20 Pg 352 #21-25 SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Chapter 10 1) Determine the oxidation number of a. S in SO2 b. Cl in HClO4 c. S in SO42d. Cr in Cr2O72e. I in MgI2 f. H in CaH2 2) For each of the following chemical reactions, assign oxidation number of each atom/ion and indicate whether the equation represents a redox reaction. If it does, identify the oxidation and reduction 3) Write a pair a balanced half-reaction equations for each of the following reactions. Label each half reaction as either oxidation or reduction. 4) For each of the following, complete the half-reaction equation and classify it as an oxidation or a reduction: 5) Balance the following equations representing reactions that occur in an acidic solution: 6) Balance the following equations representing reactions that occur in a basic solution: SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute SCH4U Final Exam Review Solutions Chapter 1/2 1. pentane 2. 2-methylbutane a) ii, iv, & v b) ii, iii, & iv 2,2-dimethylpropane primary amine tertiary amine H2N N ketone 3. ester O O secondary amine NH O aldehyde ether O O O tertiary alcohol OH amide H2N HO OH tertiary alcohol O carboxylic acid HO primary alcohol 4. butane, cis-but-2-ene, 1-methoxypropane, butanone, methyl propanoate, butan-1-amine, butan-1-ol, butanoic acid 5. a) b) c) d) O O O O NH O 2-ethoxypropane + water (condensation) methyl butanoate + water (condensation/exterification) e) N-ethylethanamide + water (condensation) f) butan-2-one (oxidation) g) Cl NH Cl OH 2-methylpentan-2-ol (hydration) 3-chloroheptane + 4-chloroheptane (hydrohalogenation) 6. a) 4-isopropylheptane c) 4-bromo-5-fluorohexane-1,3-diol e) 5-hydroxy-4-oxooct-7-en-2-ynal 7. a) Cl N-ethylpropan-1-amine + hydrogen chloride (substitution) b) trans-4-ethylhept-2-ene d) 2-methylbutyl 2-hydroxypropanoate f) 2-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol NH2 b) H2N OH c) d) O O HO O OH e) OH f) HO O O O Chapter 3/4 State the n, l, and ml values for these orbitals: 4s 3d 5f n 4 3 5 l 0 2 3 ml (all values) 0 -2, -1, -, 0, 1, 2 -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute 2. In each case, name the element with the following valence electron configuration a) 1s2 He b) 6s24f145d1 Lu c) 3s23p4 S d) 4s13d10 Cu 3. n = the main electron energy levels or shells l = the electron sublevels or subshells ml = the orientation of a sublevel ms = the electron spin 4. I.E. = the energy needed to completely remove one electron from a ground state. I.E. increases as one moves across a period, and decreases as one moves down a group. E.A. = the change in energy that occurs when an electron is added to an atom. E.A. increases as one moves across a period and decreases as one moves down a group Chapter 5 1) 5 kJ 2)a) –778.5 kJ b) –3310kJ 3) a) C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g) b) H0f -2.81 x 103 kJ/mol 4) 2.46 kJ 5) -92.4 kJ/mol Chapter 6 1 a. exo b. 25 kJ 2) a. r = 1.2 x 104 L2 smol-2[X][Y]2 b. X + 2Y product(s) c. X + 2Y B (slow) answers may vary B + X + W Z (fast) d) 48 molL-1s-1 3) 6.25 % Chapter 7 1. [products]>>[reactants] 2 a) left b) left c) right d) no effect 3 a) right b) left c) no effect d) left 4. Q = 0.04 (shift right) 5. a. [H2]eq = [Br2]eq = 1.5 mol/L [HBr]eq = 5.0 mol/L b. [H2]eq = [Br2]eq = 2.2 mol/L [HBr]eq = 7.6 mol/L c. [H2]eq = 3.0 mol/L [Br2]eq = 1.0 mol/L [HBr]eq = 6.0 mol/L 6. Q = 1 (shifts right) 7. a) positive b) negative c) negative 8. a. G = -208.05 kJ/mol b. G = 739.2 kJ Chapter 10 1) a. 4 b) +7 c) +^ d) +6 e) -1 f) -1 2) 3) 4) e) no effect e) right f) no change SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute 5) 6) SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Appendix SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute SCH4U1 – Review Riverdale Collegiate Institute Periodic Table 1 1 H 1.01 18 2 He 2 4 Be 13 5 B 14 6 C 15 7 N 16 8 O 17 9 F 4.00 3 Li 6.94 9.01 10.81 12.01 14.01 16.00 18.99 20.18 11 Na 12 Mg 13 Al 14 Si 15 P 16 S 17 Cl 18 Ar 22.99 24.31 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 26.98 28.09 30.97 32.06 35.45 39.95 19 K 20 Ca 21 Sc 22 Ti 23 V 24 Cr 25 Mn 26 Fe 27 Co 28 Ni 29 Cu 30 Zn 31 Ga 32 Ge 33 As 34 Se 35 Br 36 Kr 39.10 40.08 44.96 47.90 50.94 51.99 54.94 55.85 58.93 58.71 63.55 65.37 69.72 72.59 74.92 78.96 79.90 83.80 37 Rb 38 Sr 39 Y 40 Zr 41 Nb 42 Mo 43 Tc 44 Ru 45 Rh 46 Pd 47 Ag 48 Cd 49 In 50 Sn 51 Sb 52 Te 53 I 54 Xe 85.47 87.62 88.91 91.22 92.91 95.94 99 101.07 102.91 106.4 107.87 112.40 114.82 118.69 121.75 127.60 126.90 131.30 55 Cs 56 Ba 57 La 72 Hf 73 Ta 74 W 75 Re 76 Os 77 Ir 78 Pt 79 Au 80 Hg 81 Tl 82 Pb 83 Bi 84 Po 85 At 86 Rn 132.91 137.34 138.91 178.49 180.95 183.85 186.2 190.2 192.2 195.09 196.97 200.59 204.37 207.19 208.98 210 210 222 87 Fr 88 Ra 89 Ac 104 Unq 105 Unp 106 Unh 107 Uns 223 226 227 261.11 262.11 263.12 262.12 58 Ce 59 Pr 60 Nd 61 Pm 62 Sm 63 Eu 64 Gd 65 Tb 66 Dy 67 Ho 68 Er 69 Tm 70 Yb 71 Lu 140.12 140.91 144.24 147 150.35 151.96 157.25 158.92 162.50 164.93 167.26 168.93 173.04 174.97 90 Th 91 Pa 92 U 93 Np 94 Pu 95 Am 96 Cm 97 Bk 98 Cf 99 Es 100 Fm 101 Md 102 No 103 Lw 232.04 231 238.03 237 242 243 247 249 251 254 253 256 254 257 10 Ne