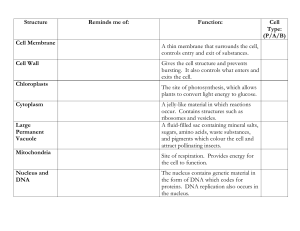
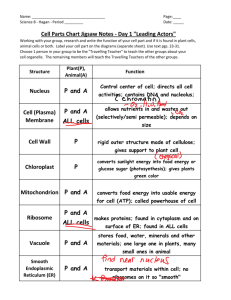
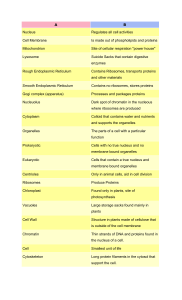
CELLS CELL DISCOVERY •In 1665 Robert Hooke used a micro scope to examine a small piece of cork (remains of dead plant cells) •Cell means ‘small boxes’ •Anton Van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe living cells. CELL THEORY •All living things are composed of one or more cells •Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism •Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. PROKARYOTES •Unicellular •No membrane- covered organelles •No nucleus •Circular DNA •Bacteria EUKARYOTES •Cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus and other organells •DNA in the nucleus •Linear DNA •Animals, Plants, Protists, and Fungi PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL PARTS OF A EUKARYOTIC CELLS •Cell Membrane •Allows nutrients and other materials in and wastes out •Selectively Permeable- only allows certain things in or out •Primarily made up of proteins and lipids •Phospholipids- one of the major types of lipids in the cell membrane (made of a head and two nonpolar tails) (head close to water, tail away from water) •Phospholipid Bi-Layer- double layer of phospholipids PHOSPHOLIPID BI-LAYER PARTS OF CELL CONT. •Cytoplasm- fluid (Cytosol) and organelles that make up the inside of the cell NUCLEUS •Stores heredity information in its DNA ( Chromatin) •Site where RNA is copied from DNA •Surrounded by the nuclear envelope •Contains the Nucleolus (site where ribosomes are synthesized and partially assembled) MITOCHONDRIA •‘Power House’ •Large organelles where chemical reactions transfer energy from organic compounds to ATP (Ex: the food you eat into energy for cells) •More numerous in cells that have high energy requirement (ex: muscles, liver ect) •Contain their own DNA •Cristae-large folds inside the mitochondria where the chemical reactions occur. RIBOSOMES •Made of two parts- proteins and RNA •Most numerous organelle •Not membrane bound •Produces protein •Both free (protein used in the cytosol) and attached to the Rough ER. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) •Intercellular highway (path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another) •Two types of ER •Rough ER- produces protein to be exported from the cell or inserted into the cell membrane (ribosomes attached to the outside) •Smooth ER- synthesizes steroids, regulates calcium levels, and breaks down toxic substances (no ribosomes) GOLGI APPARATUS •Processes, packages, and secretes proteins for export from the cell. •Appears to be a series of flattened sacks LYSOSOMES •Contain enzymes that break down and help recycle large proteins in animal cells •Selectively destroys tissue (ex: tadpoles tail, tissue between your fingers) CYTOSKELETON •Structure that maintains the shape and size of the cell •Two major components: •Microfilaments- threads made of a protein called Actin (small strands) •Microtubules- large strands that provide support for the cell and aide in the division of the cell (spindle fibers) MICROFILAMENTS AND MICROTUBULES CILIA AND FLAGELLA •Hair like organelles that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in the movement of the cell. MORE PARTS OF THE CELL •Vacuole- stores enzymes and waste products •Cell Wall- supports and protects the cell (in plants, not animals) •Chloroplast- (plastid) stores food or pigments transfers energy from light to organic compounds (in plants not animals) •Centrioles: aid in cell division