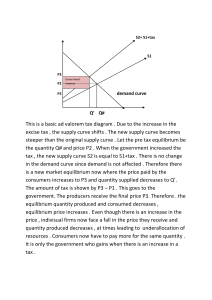
Chapter 4 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium Problems 3. The following two incidents involve simultaneous shifts in the demand and the supply curves. Analyze the final effects on the equilibrium price and quantity after the changes. Explain your answers. a. Severe drought at the peak of summer reduces the production of watermelons. With even more people consume the fruit to quench their thirst, the equilibrium quantity remains unchanged. b. The government allocates land to build more houses in the country. At the same time, it relaxes the criteria of citizenship to entice more foreigners to settle down in the country. The price of houses increases. Answer: a. The hot weather reduces the watermelon crop and thus, for a given price, supply decreases. This will increase the equilibrium price and decrease the equilibrium quantity of the fruit. At the same time, when more people consume watermelons, for a given price, the demand for watermelon increases. This will lead to a higher equilibrium price and higher equilibrium quantity of watermelons. Since the equilibrium quantity of watermelons ultimately remains unchanged, the supply curve shifts by the same magnitude as the demand curve. b. With more land available to build houses, for a given price, the supply of houses increases. This results in a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity in the housing market. As more people take up citizenship in the country, for a given price, the demand for houses increases. This will lead to a higher equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity. Since the price of houses ultimately increases, the demand curve shifts by a larger magnitude than the supply curve. drought in Brazil in 2013-14 that a. Draw and discuss a supply and demand diagram to explain the increase in coffee prices. b. Are coffee and tea substitutes or complements? Explain. c. What do you think the impact of this drought has been on the equilibrium price and quantity of tea? Draw a supply and demand diagram for the tea market to explain your answer. Answer: a. The drought will cause the supply curve to shift to the left from S to S′. As a result the equilibrium price of coffee rises from P1 to P2. 7. An appendectomy is an opera'on to have your appendix removed. To simplify the analysis, assume that everyone has health insurance, so that anybody who needs an appendectomy will have one. (a) Show that the demand curve for appendectomies is ver'cal. (b) There is a technological breakthrough that allows surgeons to perform appendectomies at a much lower cost. Will the equilibrium price of appendectomies rise, fall, or remain constant? Will the equilibrium quan'ty of appendectomies rise, fall, or remain constant? Present a supply-and-demand curve diagram to defend your answers. Answer: a. The quantity of appendectomies demanded will not change if the price of an appendectomy changes. No one who does not need an appendectomy would rush out to have one if the local hospital held an appendectomy sale. Assuming everyone has health insurance, anyone who needed an appendectomy would have one no matter how high the price rose. Therefore the demand curve for appendectomies is vertical. b. The technological breakthrough shifts the supply curve to the right from S to S′. As a result, the equilibrium price falls from P1 to P2 but the equilibrium quantity is unchanged 9. A rightward shift in demand will cause an increase in price. The increase in price will cause a rightward shift of the supply curve, which will lead to an offsetting decrease in price. Therefore, it is impossible to tell what effect an increase in demand will have on price. Do you agree with your friend? If not, what is the flaw in your friend’s reasoning? Answer: The given argument is flawed because it claims that an “increase in price will cause a shift of the supply curve...” The increase in price will cause a movement along the supply curve and not a shift of the curve. baht. a. How is this likely to affect other buyers in the domestic market for rice? b. Present a supply and demand diagram to show how much rice the Thai government will have to buy under this program. Answer: a. If a single buyer in the market (the government) is willing to buy any amount of rice at a price that is higher than the market price, then suppliers would be unwilling to sell to consumers at a price below the government’s price. Therefore everyone in Thailand would have to pay the government’s price of 140 baht. . © 2015 Pearson Educa'on, Inc.