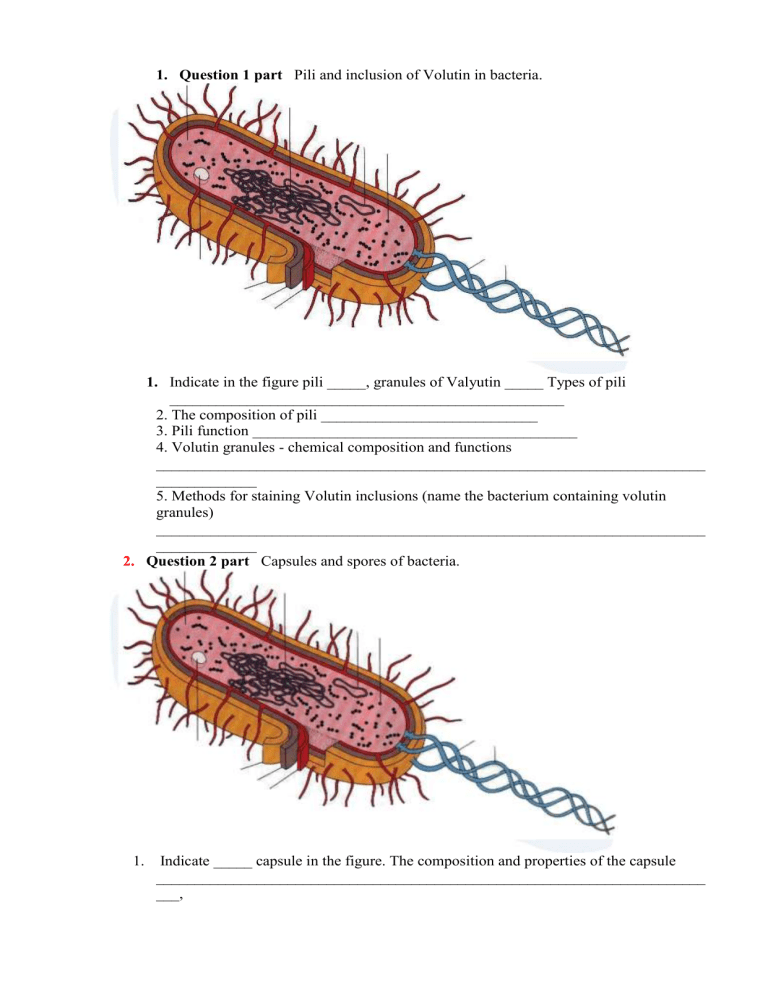
1. Question 1 part Pili and inclusion of Volutin in bacteria. 1. Indicate in the figure pili _____, granules of Valyutin _____ Types of pili ___________________________________________________ 2. The composition of pili ____________________________ 3. Pili function __________________________________________ 4. Volutin granules - chemical composition and functions _______________________________________________________________________ _____________ 5. Methods for staining Volutin inclusions (name the bacterium containing volutin granules) _______________________________________________________________________ _____________ 2. Question 2 part Capsules and spores of bacteria. 1. Indicate _____ capsule in the figure. The composition and properties of the capsule _______________________________________________________________________ ___, _______________________________________________________________________ ____ 2. Function of the capsule ___________________________________________________________ 3. Capsule staining methods (Examples of capsule-forming microorganisms) _______________________________________________________________________ _____ 4. Method of staining spores in bacteria _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ 5. Examples of spore-forming bacteria _________________________________________ 3. Question 2 part Flagella of bacteria. 1. Indicate flagella in the figure ____ Flagella composition _________________________________________________________________ 2. Structure of flagella _____________________________________________________________ 3. Function of flagella ______________________________________________________________ 4. Methods for the detection of flagella ___________________________________________________ 5. An example of a monotrich _________________________________________ peritrich __________________________ 4. Question 1 part You are shown the structure of the cell wall of the bacterial cell. You must indicate - this is the cell wall of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria? _______________________________________________________________________ 1. Give a detailed description of the presented cell wall - both in structure, in composition and function.. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ___ 2. Cell wall function _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______ 3. The staining method used to differentiate the cell wall _______________________________________________________________________ _______ 4. What is protoplast _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________ 5. What is a spheroplast _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 5. Question 1 part 1. Explain the nature of the growth of microorganisms. Indicate which in the figure. 2. facultative anaerobes because _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 3. Obligatory anaerobes, because _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 4. Microaerophiles, because _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 5. Aero tolerant because _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 6. Obligatory aerobes because _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ______________ 1 2 3 4 5 6. Question 1 part Distribute the antibiotics described below according to their mechanism of action : Penicillin G, Amoxicillin, Flucloxacillin, Cefoxitin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Imipenem, Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Enoxacin, Ofloxacin, Gentamicin, Amikacin, Tetracycline, Sulphonamides, Rifamycinum 1. Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ 2. Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ 3. Blocks bacterial cell metabolism by inhibiting enzymes _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ 4. Inhibits bacterial DNA replication and synthesis _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ 5. Inhibits the synthesis of bacterial mRNA ________________________________________________________ 7. Question 1 part The infectious process is (give definition)______________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 1. How to determine the incubation period ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Transmission ways for various infection __________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. Source of infection __________________________________________________ 4. Define what an epidemic is______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 5. Infectious Disease Prevention ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 8. Question 1 part Features of morphology and cultural properties of bacteria. 1. Spherical bacteria ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. Rod-shaped bacteria ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. Inoculation method according to Drigalsky _________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Gould’s inoculation method ______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 5. forms of colonies S – type_______________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 9. Question 1 part Methods for detecting the structural components of a bacterial cell.. 1. Purpose Gram methods ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Purpose of Burri-Gins methods ___________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. The purpose of the methods Romanovsky - Giemsa ___________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Purpose of the Ozheska method __________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 5. The purpose of the Ziel - Nielsen method __________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 10. Question 1 part Sterilization, disinfection, aseptic and antiseptic. Antibiotics. 1. Definitions of sterilization ____________________________________________ 2. Definitions of disinfection _____________________________________________ 3. Definitions of aseptic ________________________________________________ 4. Definitions of antiseptics _____________________________________________ 5. What are the methods used to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics ____________________________________________________________________ 1. 2question (particular microbiology) S aureus belongs to staphylococci Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by S aureus 2. 2question (particular microbiology) Streptococcus pyogenes - streptococci Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Streptococcus pyogenes 3. 2question (particular microbiology) Mycobactérium tuberculósis Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Mycobactérium tuberculósis Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Brucella melitensis 4. 2question (particular microbiology) Brucella melitensis Morphology and tinctorial properties Cultural properties 1. culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Virulence factors 5. 2question (particular microbiology) Corynebacterium diphtheriae Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae 6. 2question (particular microbiology) Salmonella enterica serotype typhi Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Salmonella enterica serotype typhi 7. 2question (particular microbiology) Yersinia pestis Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Yersinia pestis 8. 2question (particular microbiology) Clostridium tetani Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Clostridium tetani 9. 2question (particular microbiology) Treponema pallidum Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Treponema pallidum 10. 2question (particular microbiology) Flu Infectious Agent Morphology and Cultural Virulence factors tinctorial properties 1. properties culture media 2. cultivation conditions t-? pH? Principles and features of the laboratory diagnostics Diseases caused by Flu Infectious Agent 1. 3.question (situational task) Distribute antibiotics according to their mechanism of action: Penicillin G, Amoxicillin, Flucloxacillin, Cefoxitin, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, Imipenem, Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Gentamicin, Amikacin, Tetracycline, Sulphamamides, Sulphamamin Inhibits the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis _____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ It blocks the metabolism of bacterial cells by inhibiting enzymes _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ Inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis _____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Inhibits RNA synthesis_____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 2. 3.question (situational task) Hepatitis D virus (HDV); Delta infection is caused by a defective virus, which can propagate only in cells already infected with some complete virus. 1. Indicate the virus that is involved in the replication of hepatitis D. Explain why this virus cannot reproduce on its own ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Routes of transmission of HDV _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. Material for research _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 4. Methods of laboratory (microbiological) diagnosis of HDV _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________ 5. Is HbS antigen a marker for HDV? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 3. 3.question (situational task) Respiratory syncytial virus is the main cause of bronchiolitis and community-acquired pneumonia in newborns. 1. Describe the virus genome _______________________________________________ 2. Virus taxonomy ________________________________________________ 3. Routes of transmission of the virus ________________________________________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods __________________ 5. Specific prevention _____________________________________________ 4. 3.question (situational task) A boy of 7 years old, fell ill acutely, with complaints of fever up to 38 C and headache. The next day, a swelling appeared in the left parotid region, on the 4th day from the onset of the disease, a swelling was noticed in the parotid region on the right. The temperature and pain during chewing, dry mouth was maintained up to 3 days. A preliminary diagnosis was made: Mumps. 1. Describe the genome of the virus ______________ 2. Virus taxonomy ____________ 3. Routes of transmission of the virus ________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods _____________________________________ 5. Specific prevention __________________________________________ 5. 3.question (situational task) For a patient with paroxysmal spasmodic cough to confirm the diagnosis of “Whooping cough”, it is necessary to take material for the bacteriological examination by the method of “cough plates”. Select a culture medium for inoculating material. 1. Describe the morphology of the bacterium _____________________ 2. Features of the cultivation of bacteria ____________________________________ 3. Routes of transmission ______________________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods _________________________________ 5. Specific prevention __________________________________________ 6. 3.question (situational task) A district pediatrician was called to a boy of the 9th grade. The boy was sicked the 3rd days ago. During the examination, the doctor noted a high fever in the boy (38.20С), a dry, rough cough, pain and lacrimation of the eyes, mucous membranes of the conjunctiva and nasopharynx are hyperemic and irritated, nasal breathing is blocked. Filatov-Koplik spots are on the mucosa of the buccal surface and upper palate. Preliminary diagnosis: "Measles, catarrhal period of development"? 1. Describe the virus genome ______________________________________________ 2. Virus taxonomy _________________________________________ 3. Routes of transmission of the virus _______________________________________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods ____________________________________ 5. Specific prophylaxis _________________________________________ 7. 3.question (situational task) Several students have been admitted to the infectious diseases hospital. The students were from the same class. At admission, all schoolchildren noted a condition as, severe meningeal syndrome and a temperature of more than 40 ° C. Microscopy of the cerebrospinal fluid revealed a large number of neutrophils containing bean-shaped diplococci. 1. Describe the morphology of the bacterium __________________________________ 2. Features of the cultivation of bacteria ____________________________________ 3. Routes of transmission ______________________________________________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods ________________________________________ 5. Specific prevention ___________________________________________ 8. 3.question (situational task) Several workers dined in the factory cafeteria. Pork cutlets seemed to them insufficiently cooked. After 8-10 hours, they showed signs of acute gastroenteritis: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, frequent loose stools and fever up to 38 ° C. Two workers in serious condition were hospitalized. The doctor made a preliminary diagnosis: Salmonellesis. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Опишитесь морфологии бактерии___________________ Особенности культивирование бактерии ____________________________________ Пути передачи __________________________________________________________ Методы лабораторной диагностики ______________________________ Специфическая профилактика _____________________________________ 9. 3.question (situational task) A 45-year-old patient was admitted to the infectious diseases hospital on the 5th day of illness with complaints of decreased visual acuity, diplopia, and fog before the eyes. Dry mouth, muscle weakness, and poor swallowing were observed. On the eve of the disease was at a party where he ate canned home-made mushrooms. Based on clinical symptoms, a diagnosis of Botulism was made. 1. Describe the morphology of the bacterium _______________________________________ 2. Features of the cultivation of bacteria ____________________________________ 3. Routes of transmission _____________________________________________________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods _____________________________________ 5. Specific prevention _________________________________________ 10. 3.question (situational task) In one of the villages, a boy from a large family, 6 years old, who fell ill 5 days ago, was brought to the doctors. The disease was manifested by a sudden increase in temperature, severe headaches. Repeated vomiting, pain in the arms and legs was observed. In the following days, the condition of the child worsened. During the examination, the child observed meningeal symptoms, muscle tone on the right leg was decreased, tendon reflexes were sharply weakened, the foot dangled. Preliminary diagnosis: "Paralytic form of poliomyelitis"? 1. Describe the genome of the virus ______________ 2. Taxonomy of the virus _________ 3. Routes of transmission of the virus __________ 4. Laboratory diagnostic methods ____________________ 5. Specific prevention __________________________________________